CS3402 Introduction
Introduction
File Systems
- permanent records stored in various files
- application programs are written to extract & add records
Disadvantages of traditional FS
- data redundancy & inconsistency
- difficult to access
- concurrent access anomalies
- Security problem
Database Management System (DBMS) Characteristics
DBMS provides efficient, reliable, convenient and safe multi-user storage of and access to a massive amount of persistent data.
- Massive: TB Scale
- Persistent: Like file systems
- Safe: No loss of data
- Multi-user: Concurrency
- Convenient: Easy to extract information
- Efficient: High Performance
- Reliable: Up all the time
Key Concepts
- Data Model: Relational (set of records, XML, graph)
- Schema versus data: Types versus variables
- Data definition language (DDL): Set up schema or structure for a particular database
- Data manipulation language (DML): Querying and modifying the database
Relational Model
The Relational Model
- Used by all major commercial DB Systems
- Very simple
- Ad-hoc Query with high-level languages
- Many existing efficient implementations
Basic Structure
- Database = set of named relations (or tables)
- Each relation has a set of named attributes (or columns)
- Each tuple (or row) has a value for each attribute
- Each attribute has a type (domain)
Schema: The schema consists of the structure of the relation and the attributes of the relation
Instance: Actual contents at given point in time
NULL: Unknown/Undefined
Key: Unique value attribute
模式(Schema)
定义:也称逻辑模式,是数据库中全体数据的逻辑结构和特征的描述,是所有用户的公共数据视图。
理解:
① 一个数据库只有一个模式;
② 是数据库数据在逻辑级上的视图;
③ 数据库模式以某一种数据模型为基础;
④ 定义模式时不仅要定义数据的逻辑结构(如数据记录由哪些数据项构成,数据项的名字、类型、取值范围等),而且要定义与数据有关的安全性、完整性要求,定义这些数据之间的联系



Querying Relational Databases
Creating and using a (relational) database
- Design schema: Define table structures and the type of each attribute (create using DDL)
- Load initial data (Files, Excel sheets): Load data from outside source
- Query and modify the data: (Repeat)
- Insert rows,
- Modify tables and attribute types
- Run queries
Relational Algebra*
Select operator (σ): To pick certain rows out of a relation
σ cond Rel
Project operator (π): To pick certain columns out of a relation
π A1,..., An Rel
To pick both rows and columns: Project and select
σ cond (Expression)
π A1,..., An (Expression)
Join (⋈)
A theta join allows for arbitrary comparison relationships (such as ≥).
An equijoin is a theta join using the equality operator.
A natural join is an equijoin on attributes that have the same name in each relation.
Additionally, a natural join removes the duplicate columns involved in the equality comparison so only 1 of each compared column remains; in rough relational algebraic terms: ⋈ = πR,S-as ○ ⋈aR=aS
Union operator (U): To combine information
Difference operator (-):
关系代数概览
传统的关系代数的操作包含四个大类
1 平常的集合操作—并、交、差
2 selection(选择):选择满足某些条件的行; projection(投影):选择某些属性 的列
3 合并两个关系元组的操作,包括笛卡尔乘积(Cartesian product)以及联合(join)操作
4 重命名(renaming)操作
以上是关系代数的操作,下面对其进行一一讲解:
关系的集合操作
三个基本的集合操作如下
-
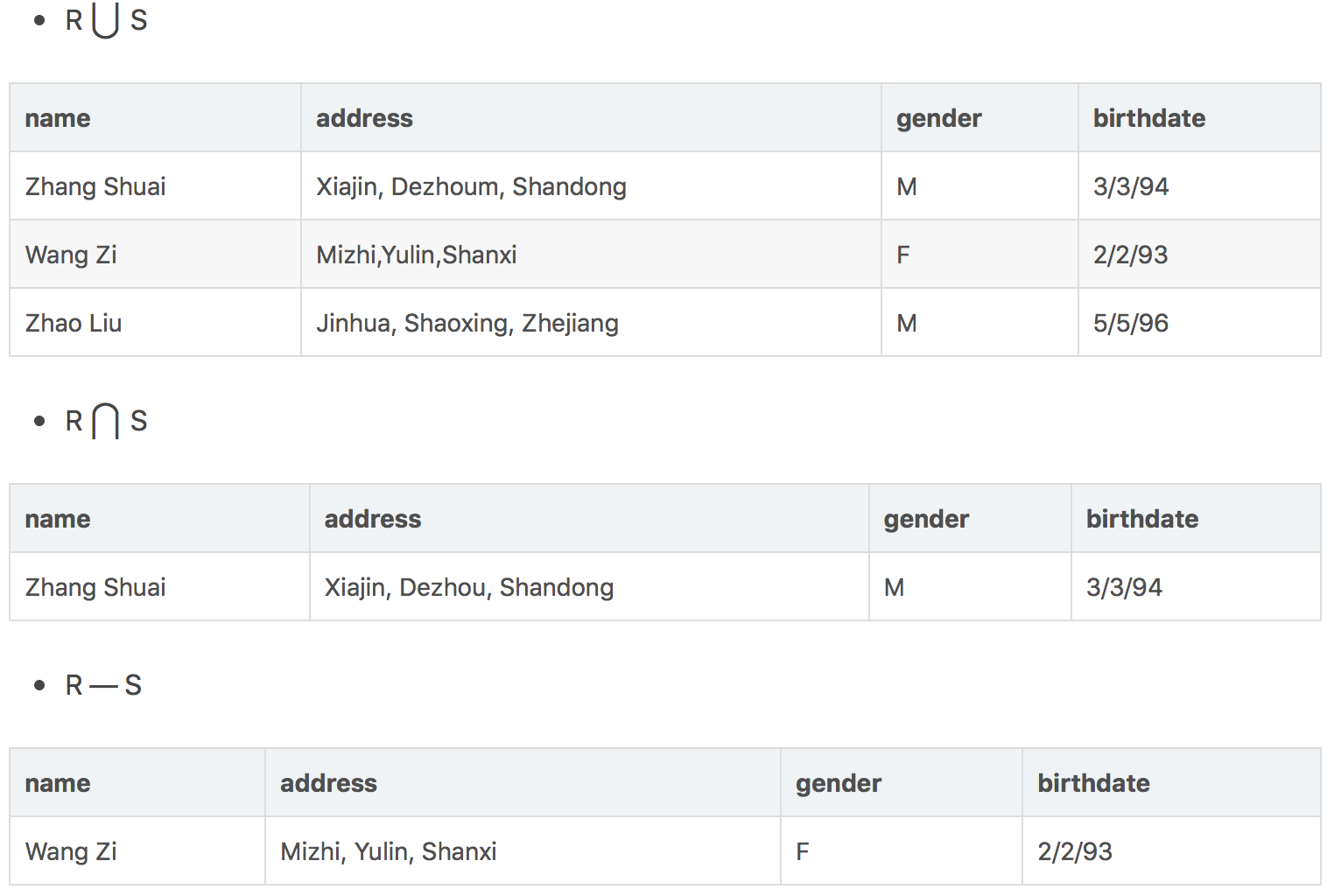
R ⋂ S
R和S的并,是R有的或S有的或者两者都有的,如果一个元素在R和S中都有的话,那么只出现一次 -
R ⋃ S
R和S的交,是R和S所共有的元素 -
R — S
是R和S的差集,其结果是出现在R中而不出现在S中的元素,R-S和S-R是不同的,S-R是出现在S中而不出现在R中的元素
在应用以上三个操作的时候,需要对关系R和S做出一定的限制
-
R和S必须具有相同属性集合的模式
-
在应用以上三个操作的时候,关系S和R的列必须是有序的,两个关系的属性的顺序应该是一致的
例子:
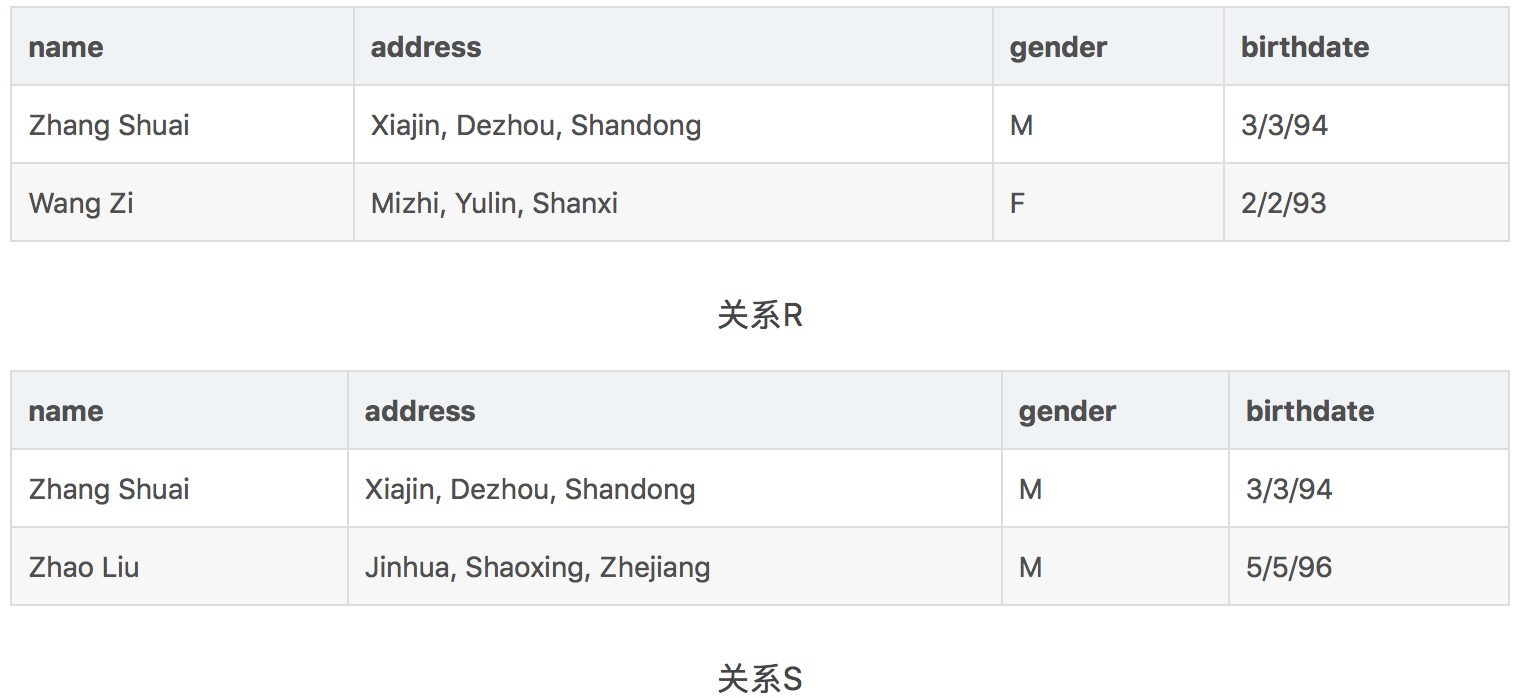
应用三个集合操作的结果:
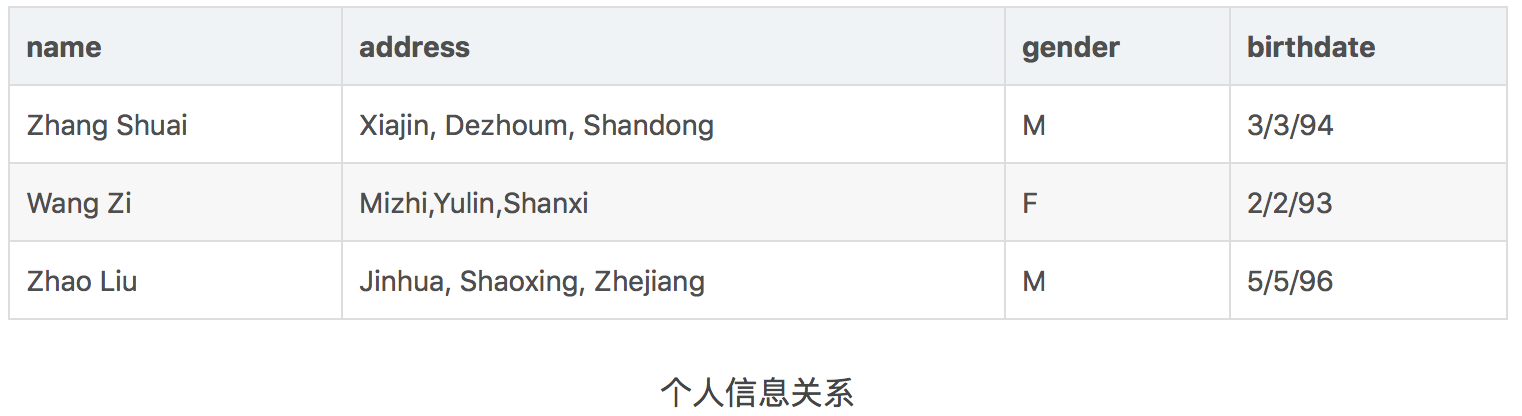
投影(projection)
投影操作用于从关系R中找出拥有某些属性的列,表达式πA1,A2,...,An(R) 的值为属性A1,A2,...,An的列,将这些列选择出来后,按原顺序排列.
使用表达式: πname,birthdate
可以得到关系:
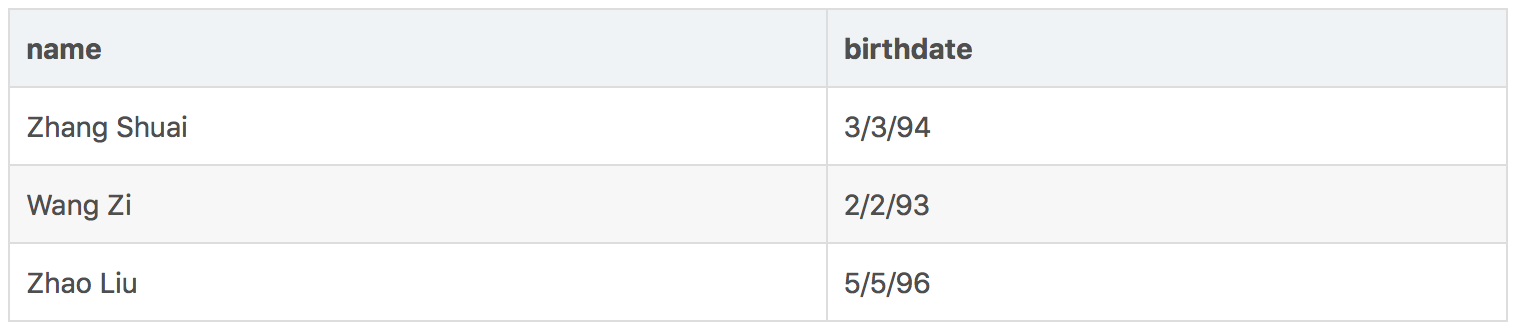
需要注意的是:当仅选出一列时,如果该列中存在相同的值,那么只会保留一个值.
选择(Selection)
选择操作用于选出满足条件的某些行,并且将整个操作记为 σC(R)。C被称作条件表达式。考虑如下关系:
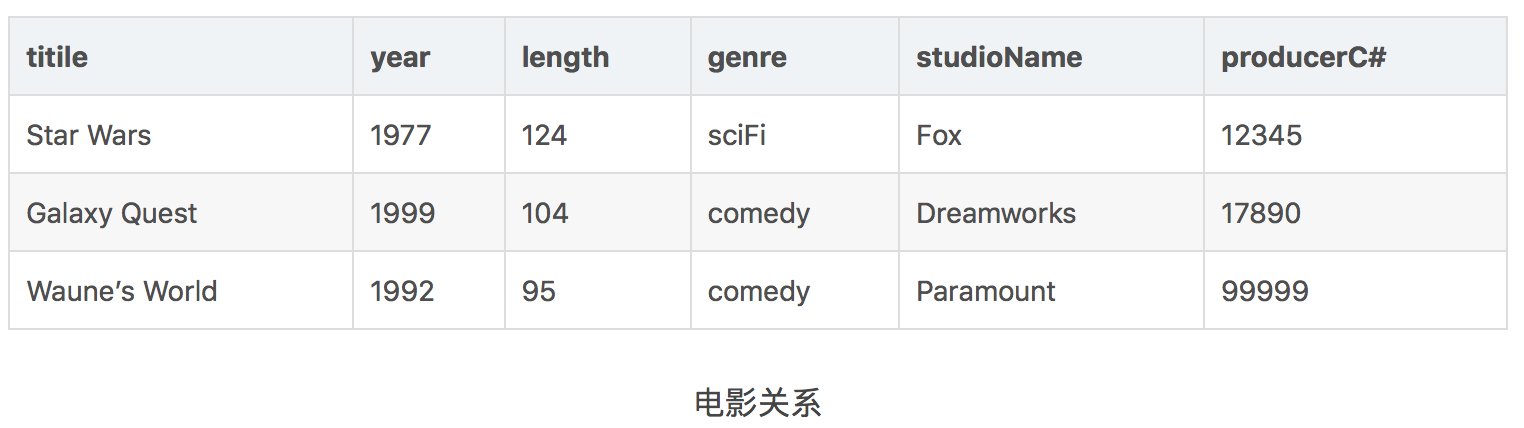
使用操作: σlength≥100(Movies)
可以得到关系:
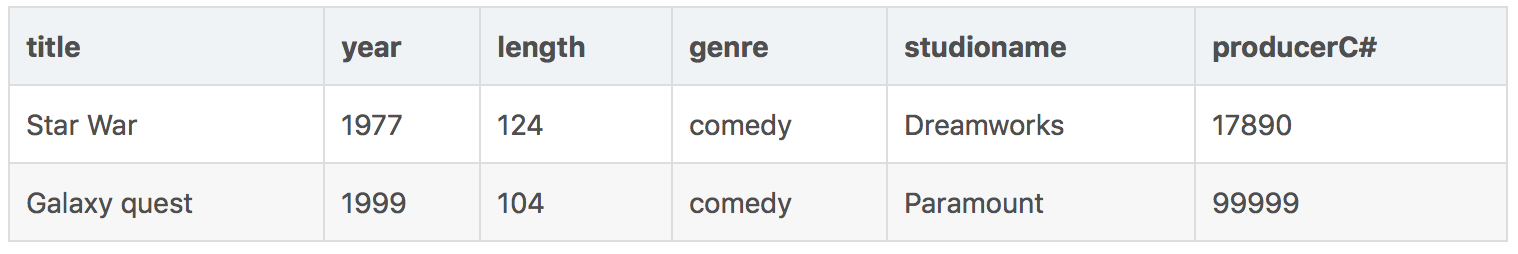
使用操作: σlength≥100 AND studioName=′Fox′(Movies)
可以得到关系:
![]()
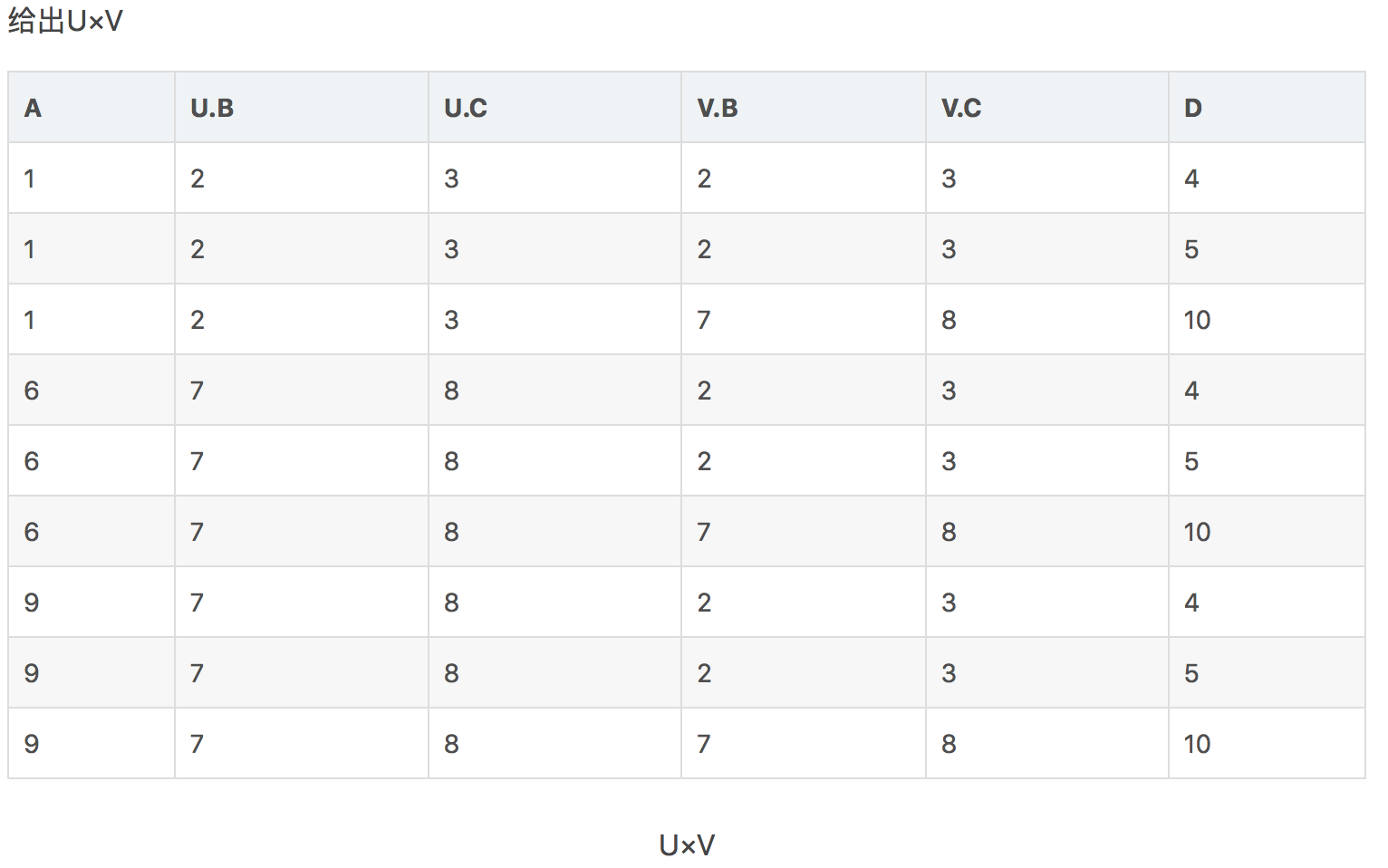
笛卡尔乘积(Cartesian Product)
假设有两个关系R和S,则笛卡尔乘积就是将两个关系进行组合,组合的结果中第一部分可以是R中的任意一行,第二部分可以是S中的任意一行。其表达式为R×S,在进行组合的过程中,如果两个关系有相同的属性,且属性值是相同的,那需要将R或者S作为前缀放在属性之前,下例:
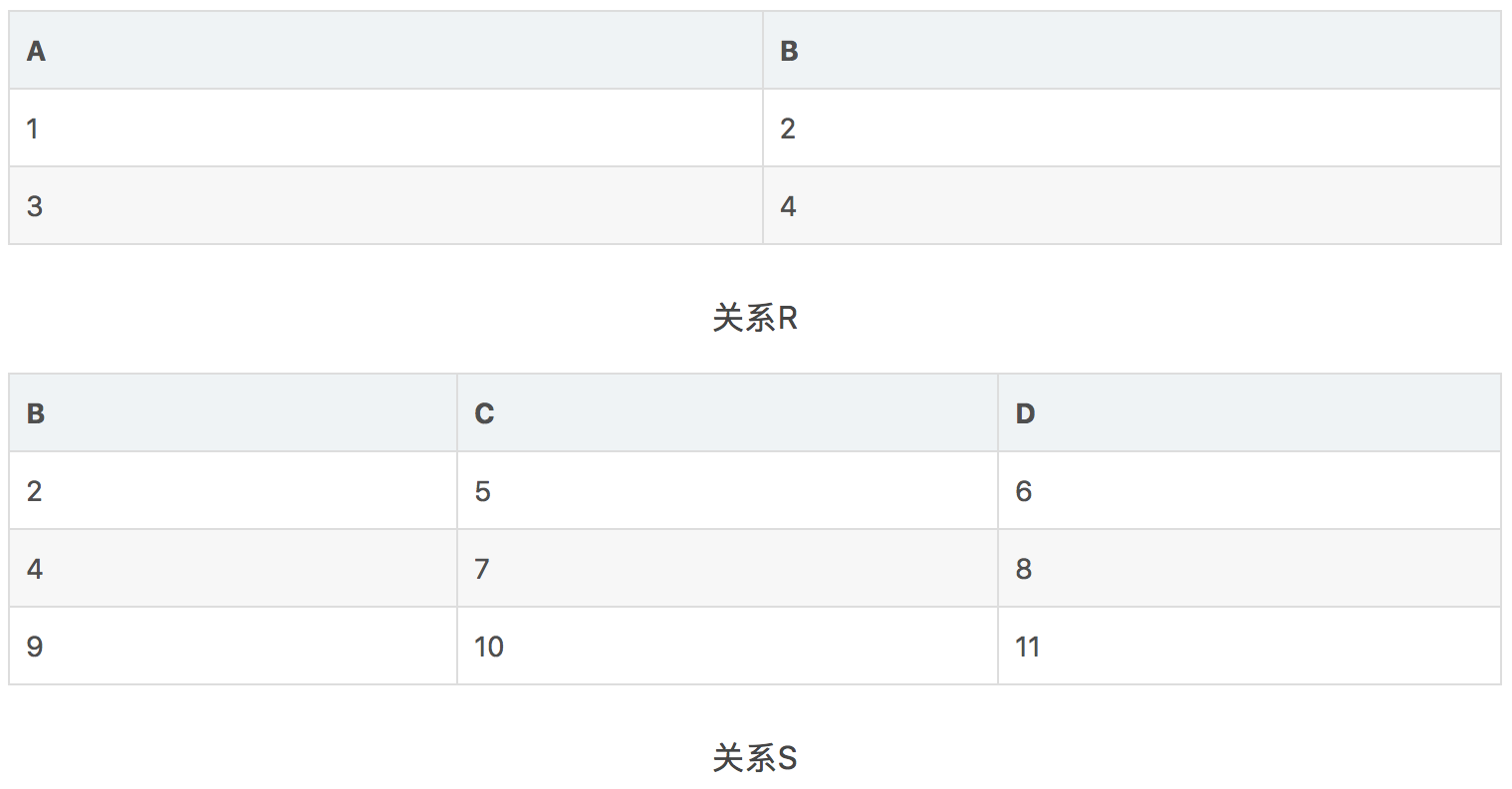
结果: R × S
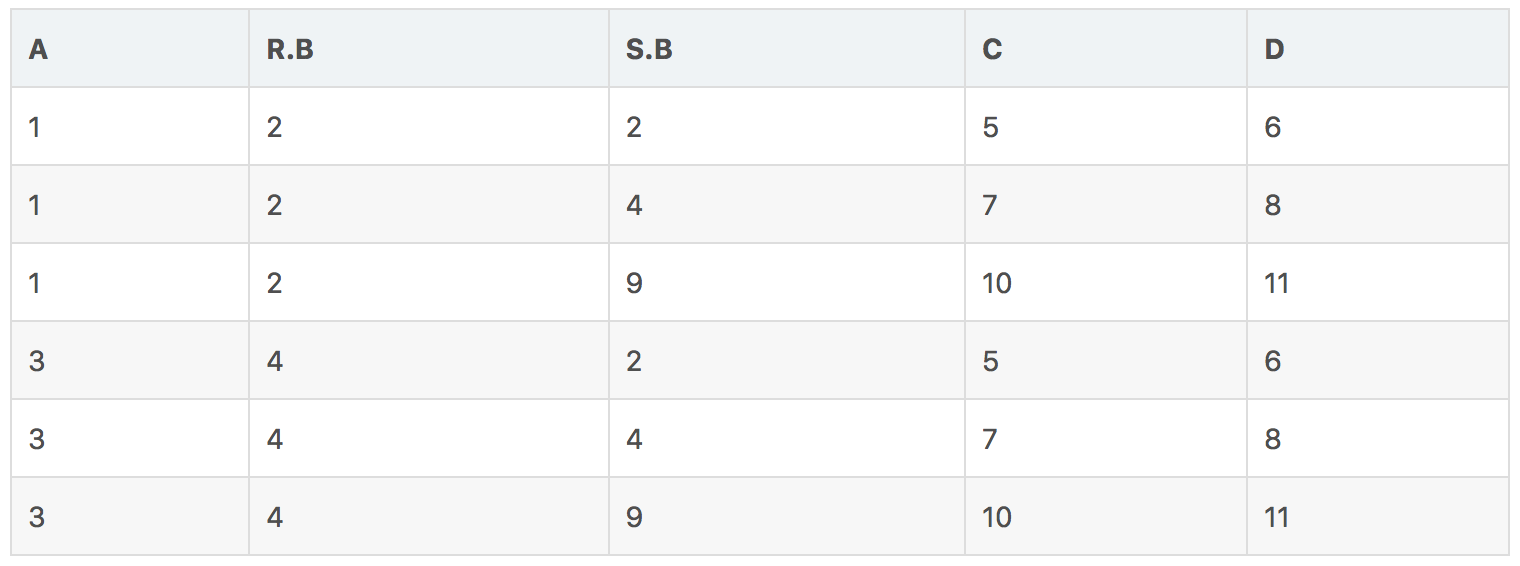
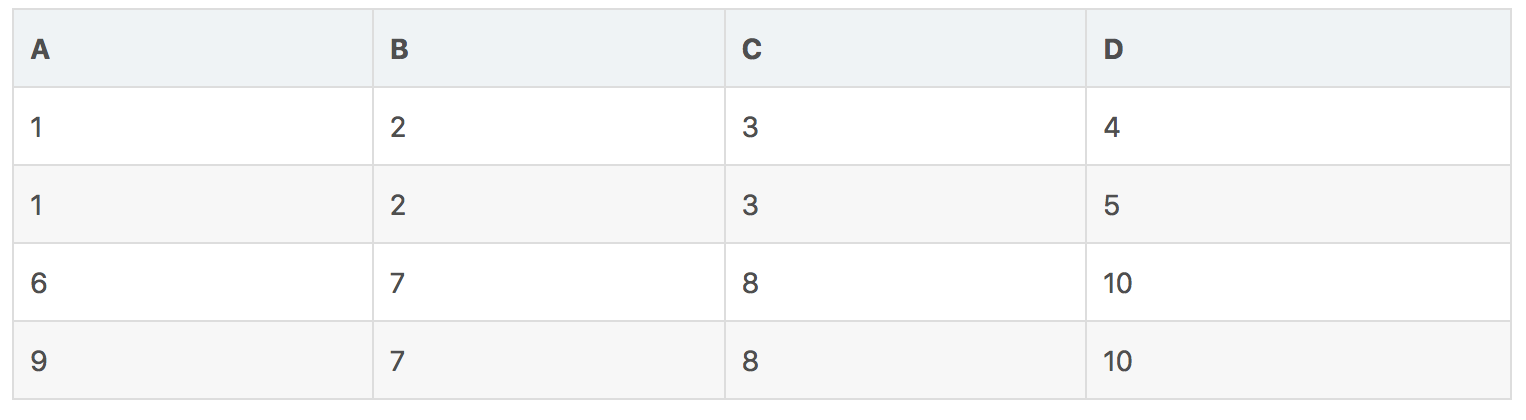
自然连接(natural Joins)
自然连接是一种比较特殊的等价连接,其将关系中具有相同的列名的列进行匹配,对于某行来说,如果两个列名相同,且元素相同,则进行连接,使用R⋈S代表此操作, 下例:
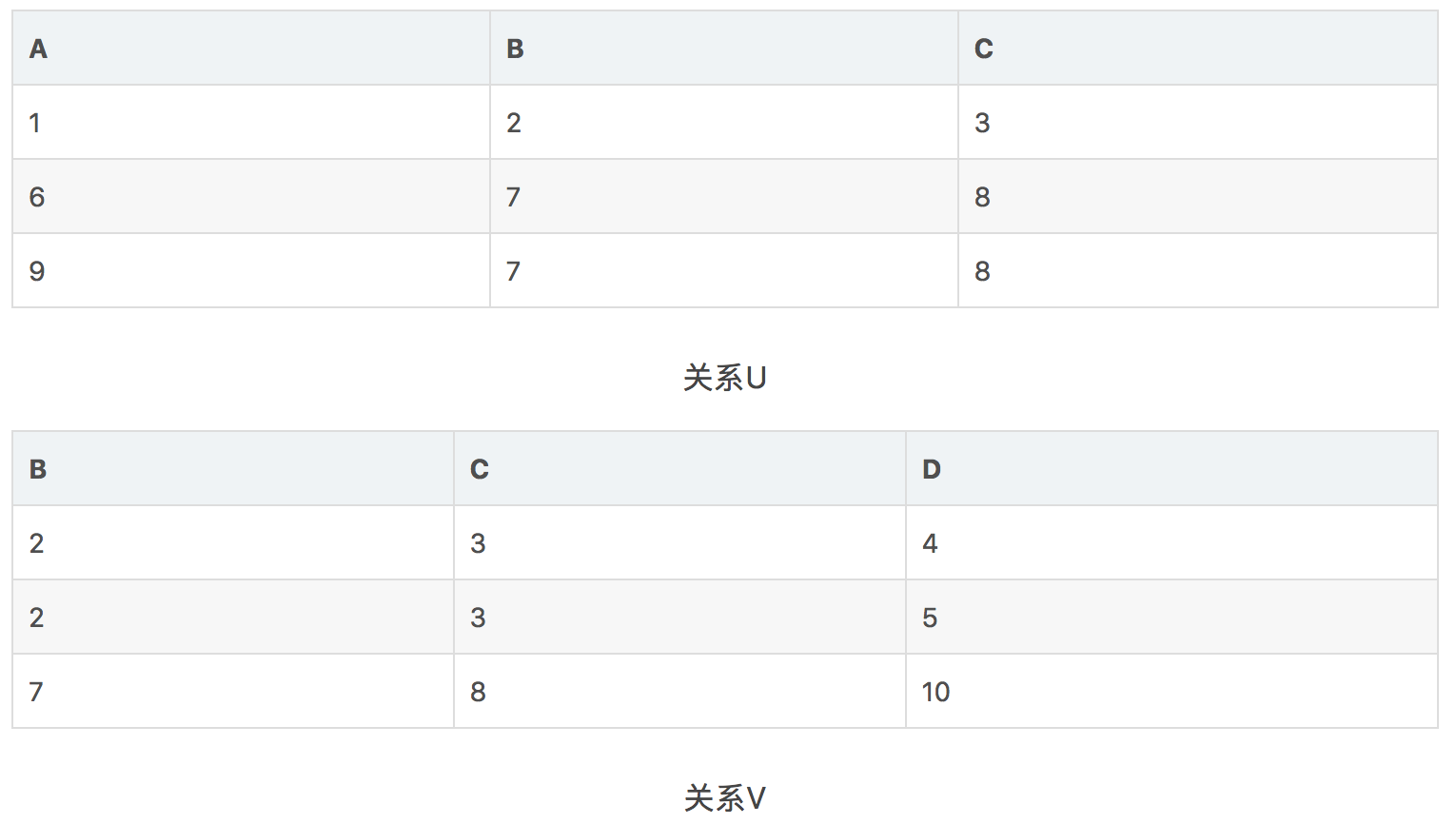
结果: U ⋈ V
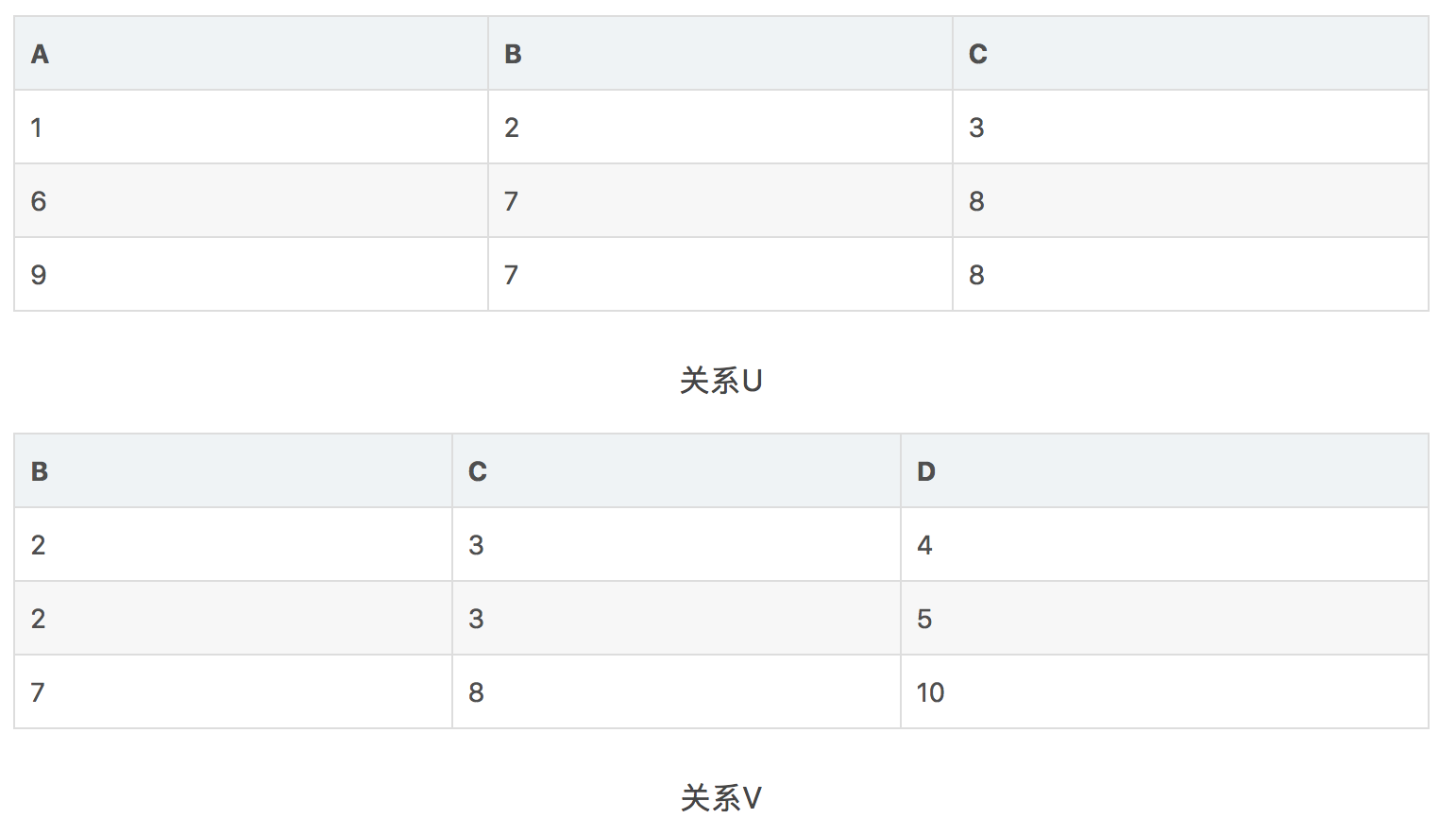
theta-连接(theta-joins)
theta指的是一些随机条件,用代表θ。对于两个关系,用公式表示为R⋈CS
其基本步骤为:
-
计算R和S的乘积
-
选出满足条件C的元组
给出如下表达式:
U ⋈A<D S
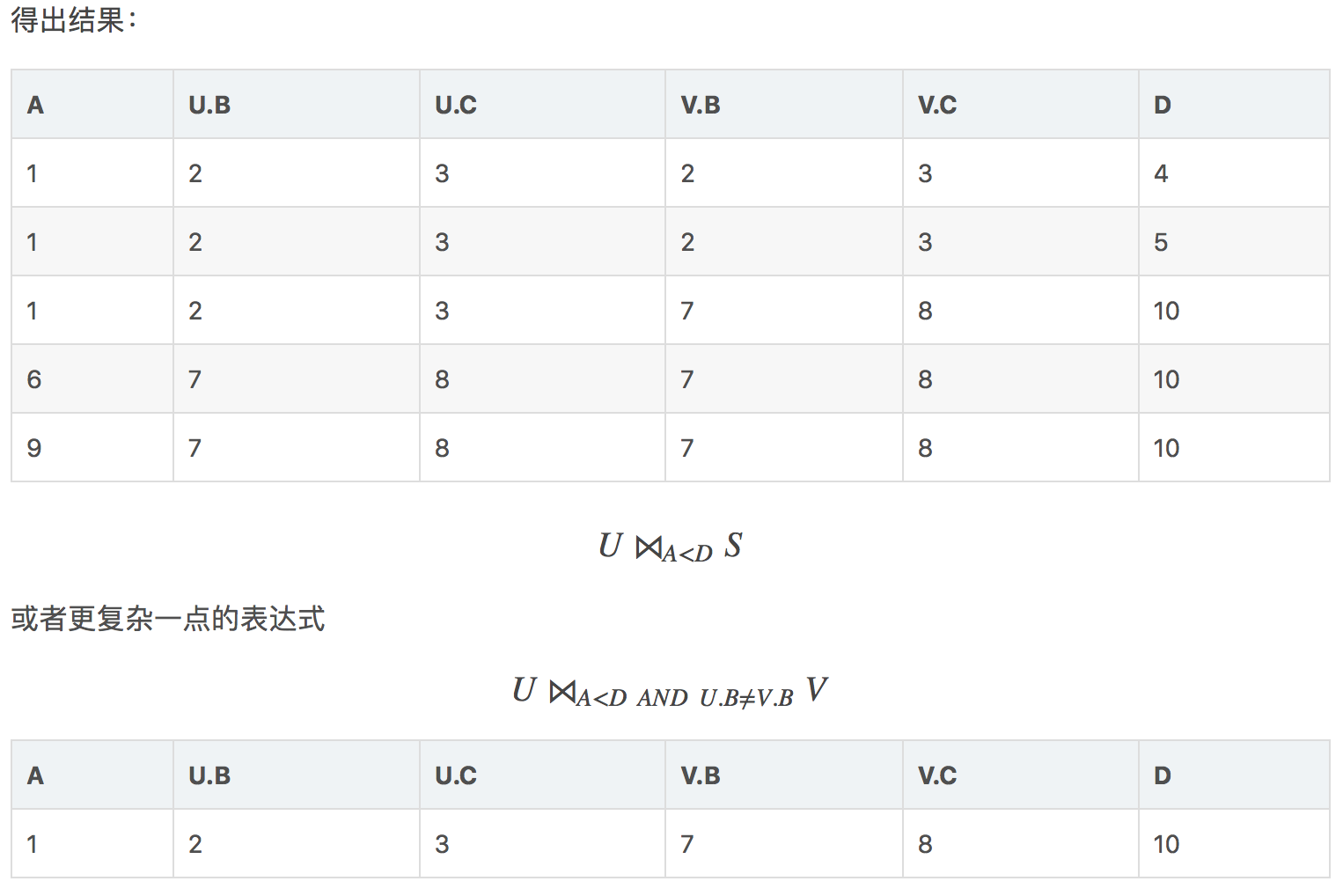
对操作进行组合以进行查询
举一例:
由Fox制作的长度为100分钟以上的电影的标题和年份是多少?
- 首先,查的是标题和年份,用的是projection
- 由Fox制作的且100分钟以上,用的selection
先进行selection,然后进行projection,用公式可以表示为
πtitle,year( σlength≥100(Movies) ⋂ studioName=′Fox′(Movies) )
或者,可以这样写:
πtitle,year(σlength≥100 AND studioName=′Fox′(Movies))
命名和重命名
使用ρS(A1,A2,...,An)(R),来重命名R,内部的元组是一样的,只是关系名和属性名改变了,如果不想改变属性名,那么只需要ρS(R)即可
以上述的关系为例,在笛卡尔乘积部分,合并时存在相同的属性名,需要加前缀进行区分,由此,我们可以使用重命名方法: 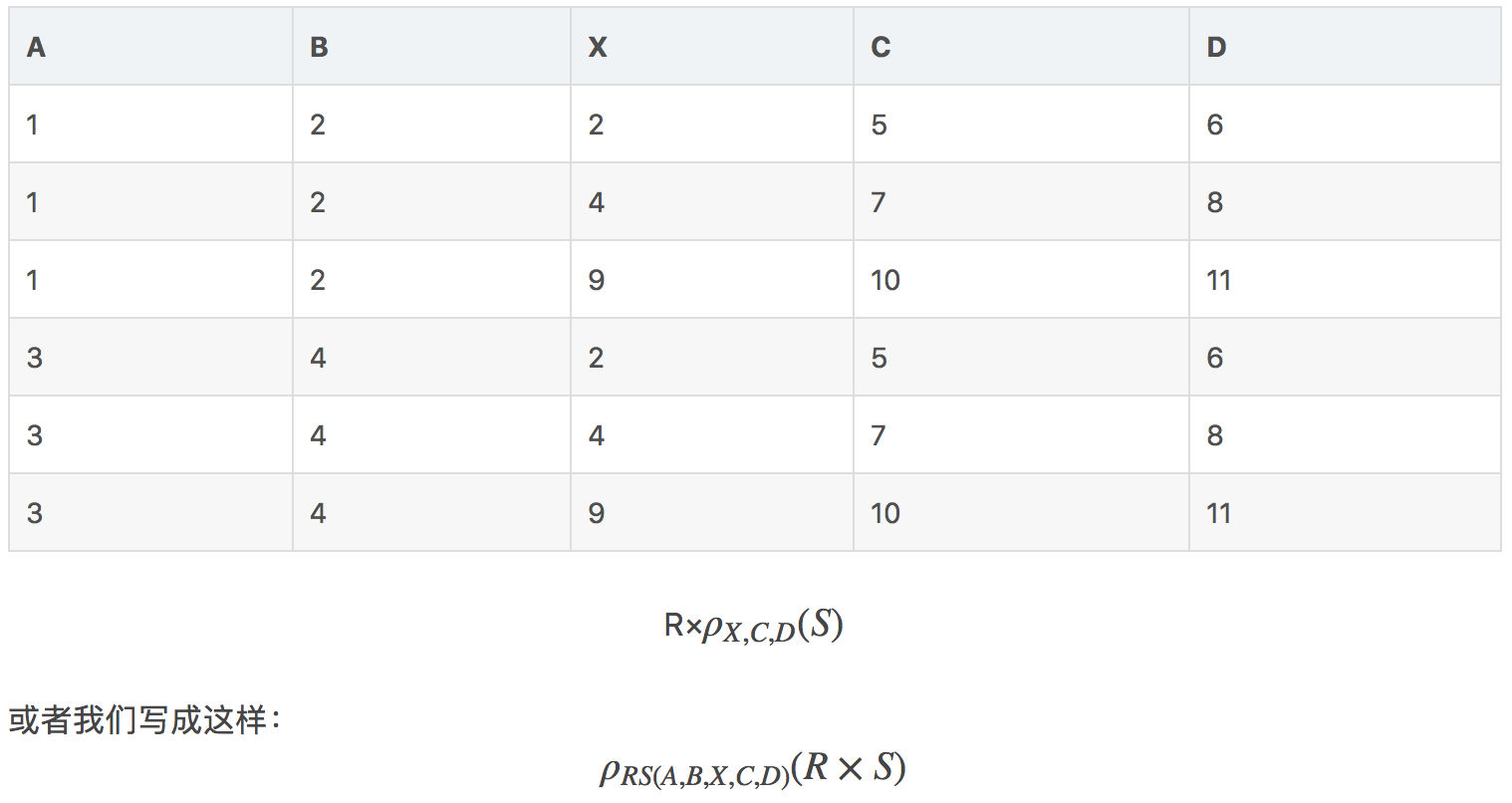


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号