Spring Security的RBAC数据模型嵌入
1.简介
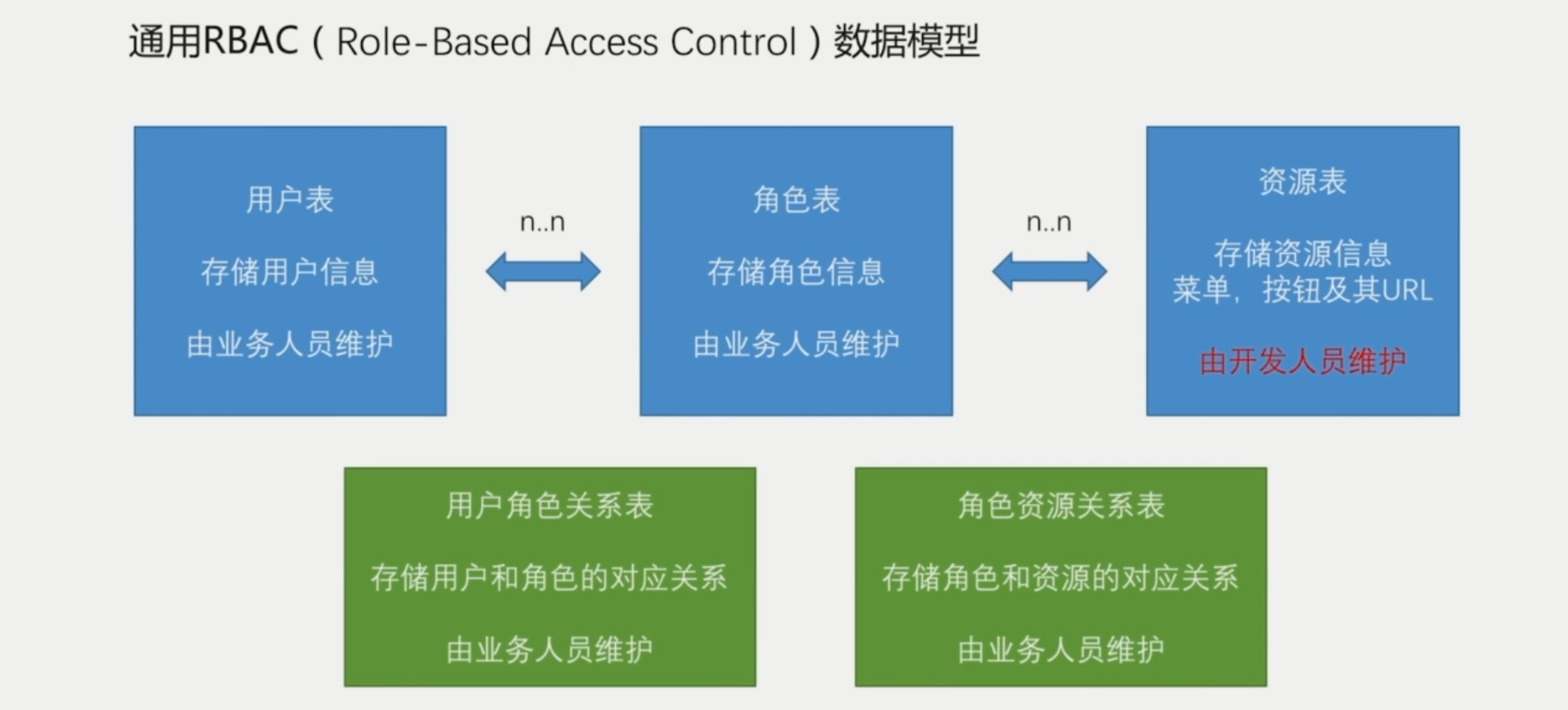
基于角色的权限访问控制(Role-Based Access Control)作为传统访问控制(自主访问,强制访问)的有前景的代替受到广泛的关注。在RBAC中,权限与角色相关联,用户通过成为适当角色的成员而得到这些角色的权限。这就极大地简化了权限的管理。在一个组织中,角色是为了完成各种工作而创造,用户则依据它的责任和资格来被指派相应的角色,用户可以很容易地从一个角色被指派到另一个角色。角色可依新的需求和系统的合并而赋予新的权限,而权限也可根据需要而从某角色中回收。角色与角色的关系可以建立起来以囊括更广泛的客观情况。
2.授权前台页面对接流程

3.代码相关
新建工程 authorize:
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.city.security</groupId>
<artifactId>city-security</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>city-security-authorize</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
RbacService
public interface RbacService {
boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication);
}
RbacServiceImpl
@Component("rbacService")
public class RbacServiceImpl implements RbacService {
@Autowired
private AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication) {
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
boolean hasPermission = false;
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
//说明我从数据库查到信息放到这个principal里面
String username = ((UserDetails) principal).getUsername();
//读取用户所拥有的权限
Set<String> urls = new HashSet<String>();
for (String url : urls) {
if(antPathMatcher.match(url,request.getRequestURI())){
hasPermission=true;
break;
}
}
}
return hasPermission;
}
}
修改DemoAuthorizeConifgProvider:
@Component
@Order(Integer.MAX_VALUE)//表示最后读取
public class DemoAuthorizeConifgProvider implements AuthorizeConfigProvider {
@Override
public void config(ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry config) {
System.out.println("---DemoAuthorizeConifgProvider------");
config.anyRequest().access("@rbacService.hasPermission(request,authentication)");
}
}
@Order修改顺序:
//配置permitAll的路径
@Component
@Order(Integer.MIN_VALUE)//最先读取
public class CityAuthorizeConfigProvider implements AuthorizeConfigProvider {
@Autowired
private SecurityProperties securityProperties;
@Override
public void config(ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry config) {
config.antMatchers(
"/static/**","/page/login","/page/failure","/page/mobilePage",
"/code/image","/code/sms","/authentication/mobile",securityProperties.getBrower().getSignUPUrl(),
"/user/register","/page/registerPage","/page/invalidSession","/page/logoutSuccess",securityProperties.getBrower().getSignOutUrl()
)
.permitAll();
}
}
4.基于方法的控制表达式
- 开启使用方法注解的配置
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
2.四种方法注解:@PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、@PreFilter和、PostFilter
- 用法
@PreAuthorize 注解适合进入方法前的权限验证
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
@GetMapping("/admin")
@ResponseBody
public Object admin(Principal principal) {
return principal;
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('ROLE_ADMIN','ROLE_USER') and principal.username.equals(#username)")
@GetMapping("/test/{username}")
@ResponseBody
public Object test(@PathVariable String username) {
return "Hello test";
}
@PostAuthorize 在方法执行后再进行权限验证,适合验证带有返回值的权限
// 这里的returnObject就代表返回的对象
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.username.equals(principal.username)")
@GetMapping("/demo2")
public Object demo2() {
User user = new User("lzc","lzc",AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_USER"));
return user;
}
@PreFilter可以对集合类型的参数进行过滤,@PostFilter可以对集合类型返回值进行过滤,用法跟上面两种方式类似。


