格网DEM生成不规则三角网TIN
🚀概述
在GIS(地理信息科学)中,地形有两种表达方式,一种是格网DEM,一种是不规则三角网TIN。一般情况下规则格网DEM用的比较多,因为可以将高程当作像素,将其存储为图片类型的数据(例如.tif)。但是规则格网存储的数据量大,按规则取点,并不能最大程度的保证地形特征,所以很多情况下需要将其表达为不规则三角网,也就是TIN。
🌈详论
1️⃣数据准备
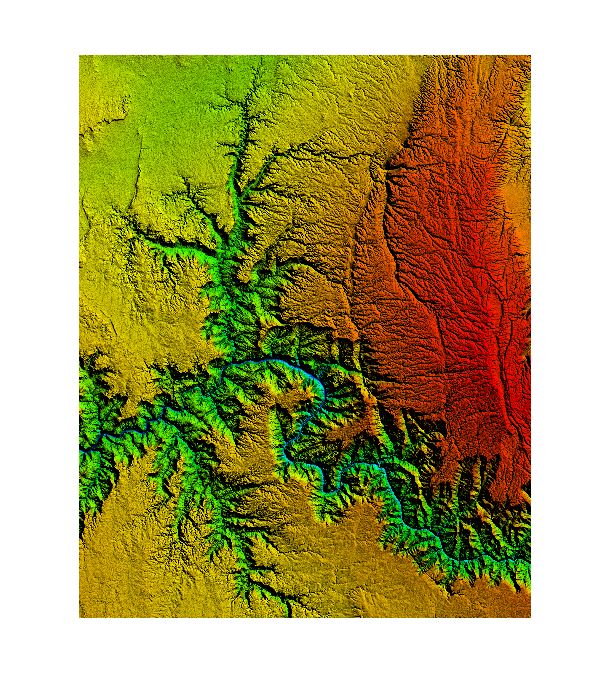
下载SRTM30的DEM数据,找到美国大峡谷附近的地形,通过UTM投影,将其转换成30米的平面坐标的DEM(.tif格式)。通过Global Mapper打开,显示的效果如下:
2️⃣转换算法
格网DEM本身也可以看作是一个三角网,每个方格由两个三角形组成,N个方格据组成了一个地形格网。所以在参考文献一中提到了一种保留重要点法,将格网DEM中认为不重要的点去除掉,剩下的点构建成不规则三角网即可。那么怎么直到有的点重要,有的点不重要呢?参考文献一中提到了一种约束:
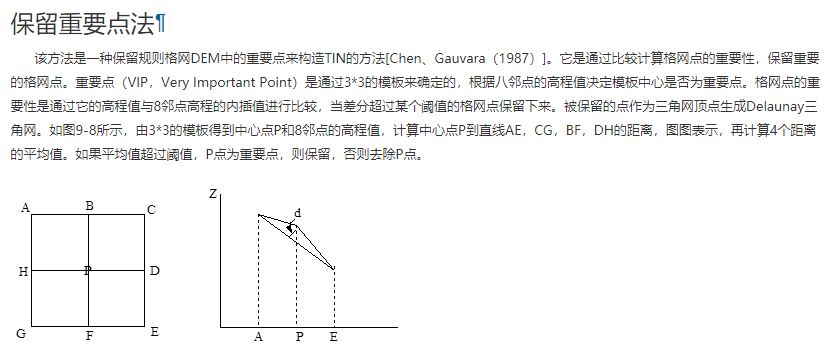
可以看到这类似于图像处理中的滤波操作,通过比较每个高程点与周围的平均高差,如果大于一个阈值,则为重要点,否则为不重要点。其中的关键点就是求空间点与直线的距离,具体算法可参看这篇文章《空间点与直线距离算法》。
3️⃣TIN构建
经过保留重要点法过滤之后,剩下的点就要进行构网了。一般来说最好构建成Delaunay三角网(因为Delaunay三角网具有很多最优特性)。Delaunay三角网的构建算法也挺复杂,不过可以通过计算几何算法库CGAL来构建。
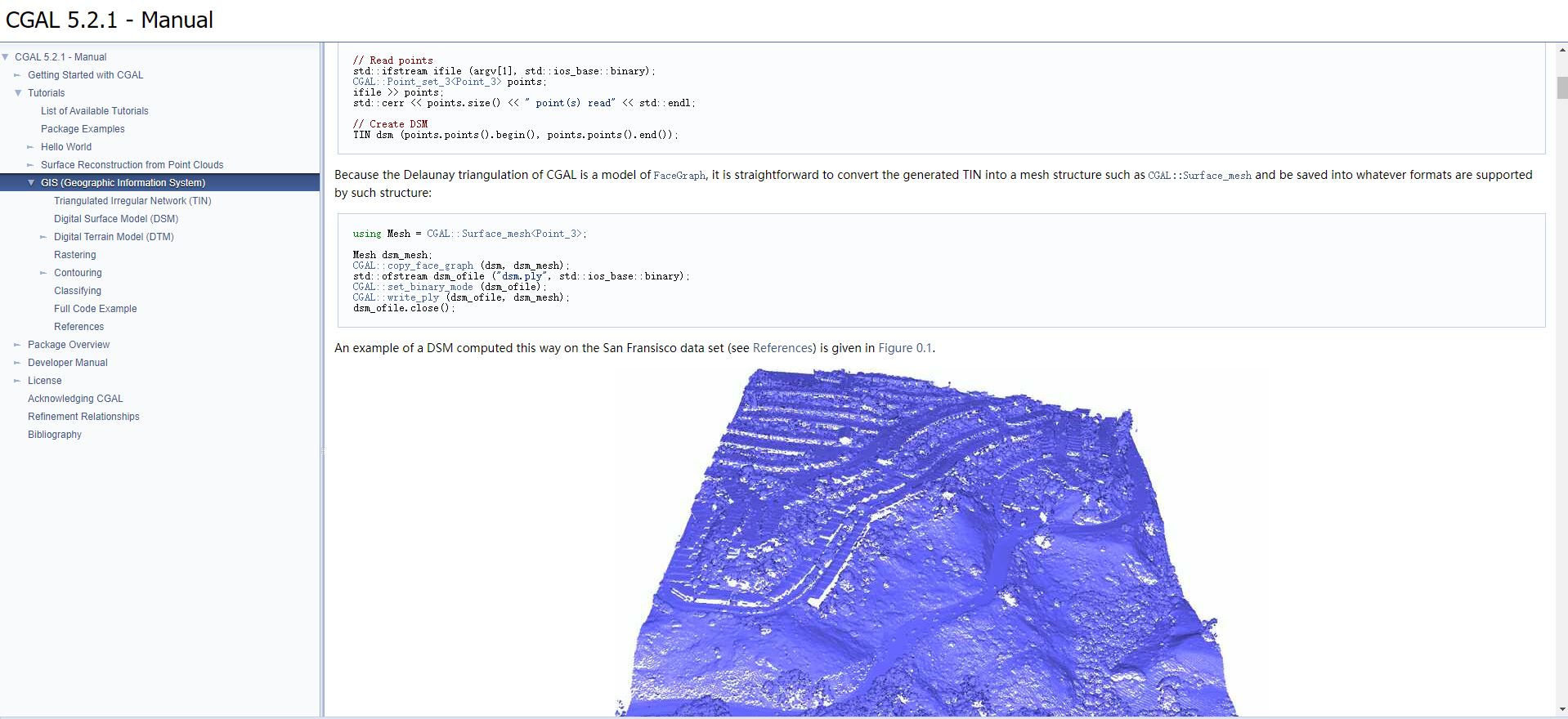
查阅CGAL的文档,发现CGAL居然已经有了GIS专题,里面有许多与地形处理相关的示例。其中一个示例就是通过点集生成了Delaunay三角网,并且生成了.ply文件。.ply文件正好是一种三维数据格式,能够被很多三维软件打开。
4️⃣具体实现
解决了两个关键算法,具体实现就很简单了:引入GDAL数据来处理地形数据(.tif),遍历每个像素点(高程点)做滤波操作,通过CGAL来构建TIN:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <Vec3.hpp>
#include <threeCGAL.h>
#include <gdal_priv.h>
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Projection_traits_xy_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Delaunay_triangulation_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Triangulation_vertex_base_with_info_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Triangulation_face_base_with_info_2.h>
#include <CGAL/boost/graph/graph_traits_Delaunay_triangulation_2.h>
#include <CGAL/boost/graph/copy_face_graph.h>
#include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/border.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/remesh.h>
using Kernel = CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel;
using Projection_traits = CGAL::Projection_traits_xy_3<Kernel>;
using Point_2 = Kernel::Point_2;
using Point_3 = Kernel::Point_3;
using Segment_3 = Kernel::Segment_3;
// Triangulated Irregular Network
using TIN = CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_2<Projection_traits>;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
GDALAllRegister();
string demPath = "D:/Work/DEM2TIN/DEM.tif";
string tinPath = "D:/Work/DEM2TIN/Tin.ply";
GDALDataset* img = (GDALDataset *)GDALOpen(demPath.c_str(), GA_ReadOnly);
if (!img)
{
cout << "Can't Open Image!" << endl;
return 1;
}
int imgWidth = img->GetRasterXSize(); //图像宽度
int imgHeight = img->GetRasterYSize(); //图像高度
int bandNum = img->GetRasterCount(); //波段数
//int depth = GDALGetDataTypeSize(img->GetRasterBand(1)->GetRasterDataType()) / 8; //图像深度
int depth = sizeof(float); //图像深度
double padfTransform[6];
img->GetGeoTransform(padfTransform);
double dx = padfTransform[1];
double startx = padfTransform[0] + 0.5 * dx;
double dy = -padfTransform[5];
double starty = padfTransform[3] - imgHeight * dy + 0.5 * dy;
//申请buf
int bufWidth = imgWidth;
int bufHeight = imgHeight;
size_t imgBufNum = (size_t)bufWidth * bufHeight * bandNum;
size_t imgBufOffset = (size_t)bufWidth * (bufHeight - 1) * bandNum;
float *pblock = new float[imgBufNum];
//读取
img->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, bufWidth, bufHeight, pblock + imgBufOffset, bufWidth, bufHeight,
GDT_Float32, bandNum, nullptr, bandNum*depth, -bufWidth * bandNum*depth, depth);
CGAL::Point_set_3<Point_3> points;
double zThreshold = 5;
//
for (int yi = 0; yi < imgHeight; yi++)
{
for (int xi = 0; xi < imgWidth; xi++)
{
//将四个角点的约束加入,保证与DEM范围一致
if ((xi == 0 && yi == 0) || (xi == imgWidth - 1 && yi == 0) ||
(xi == imgWidth - 1 && yi == imgHeight - 1) || (xi == 0 && yi == imgHeight - 1))
{
double gx1 = startx + dx * xi;
double gy1 = starty + dy * yi;
size_t m11 = (size_t)(imgWidth)* yi + xi;
tinyCG::Vec3d P(gx1, gy1, pblock[m11]);
points.insert(Point_3(P.x(), P.y(), P.z()));
}
else
{
double gx0 = startx + dx * (xi - 1);
double gy0 = starty + dy * (yi - 1);
double gx1 = startx + dx * xi;
double gy1 = starty + dy * yi;
double gx2 = startx + dx * (xi + 1);
double gy2 = starty + dy * (yi + 1);
size_t m00 = (size_t)imgWidth * (yi - 1) + xi - 1;
size_t m01 = (size_t)imgWidth * (yi - 1) + xi;
size_t m02 = (size_t)imgWidth * (yi - 1) + xi + 1;
size_t m10 = (size_t)imgWidth* yi + xi - 1;
size_t m11 = (size_t)imgWidth* yi + xi;
size_t m12 = (size_t)imgWidth* yi + xi + 1;
size_t m20 = (size_t)imgWidth * (yi + 1) + xi - 1;
size_t m21 = (size_t)imgWidth * (yi + 1) + xi;
size_t m22 = (size_t)imgWidth * (yi + 1) + xi + 1;
tinyCG::Vec3d P(gx1, gy1, pblock[m11]);
double zMeanDistance = 0;
int counter = 0;
if(m00 < imgBufNum && m22 < imgBufNum)
{
tinyCG::Vec3d A(gx0, gy0, pblock[m00]);
tinyCG::Vec3d E(gx2, gy2, pblock[m22]);
zMeanDistance = zMeanDistance + tinyCG::threeCGAL::CalDistancePointAndLine(P, A, E);
counter++;
}
if (m02 < imgBufNum && m20 < imgBufNum)
{
tinyCG::Vec3d C(gx2, gy0, pblock[m02]);
tinyCG::Vec3d G(gx0, gy2, pblock[m20]);
zMeanDistance = zMeanDistance + tinyCG::threeCGAL::CalDistancePointAndLine(P, C, G);
counter++;
}
if (m01 < imgBufNum && m21 < imgBufNum)
{
tinyCG::Vec3d B(gx1, gy0, pblock[m01]);
tinyCG::Vec3d F(gx1, gy2, pblock[m21]);
zMeanDistance = zMeanDistance + tinyCG::threeCGAL::CalDistancePointAndLine(P, B, F);
counter++;
}
if (m12 < imgBufNum && m10 < imgBufNum)
{
tinyCG::Vec3d D(gx2, gy1, pblock[m12]);
tinyCG::Vec3d H(gx0, gy1, pblock[m10]);
zMeanDistance = zMeanDistance + tinyCG::threeCGAL::CalDistancePointAndLine(P, D, H);
counter++;
}
zMeanDistance = zMeanDistance / counter;
if (zMeanDistance > zThreshold)
{
points.insert(Point_3(P.x(), P.y(), P.z()));
}
}
}
}
delete[] pblock;
pblock = nullptr;
GDALClose(img);
// Create DSM
TIN dsm (points.points().begin(), points.points().end());
using Mesh = CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point_3>;
Mesh dsm_mesh;
CGAL::copy_face_graph (dsm, dsm_mesh);
std::ofstream dsm_ofile (tinPath, std::ios_base::binary);
CGAL::set_binary_mode (dsm_ofile);
CGAL::write_ply (dsm_ofile, dsm_mesh);
dsm_ofile.close();
return 0;
}
5️⃣实验结果
将最终生成的三维模型文件.ply通过MeshLab打开,渲染效果如下:

通过Global Mapper还可以看到具体的三角构网效果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号