手写Spring3.x以上
一.准备工作
1.创建maven项目
2.创建配置类,加载容器类,启动类
public class CharkeyApplicationContext { private Class appConfig; public CharkeyApplicationContext(Class appConfig) { this.appConfig = appConfig; } public Object getBean(String name) { return null; } }
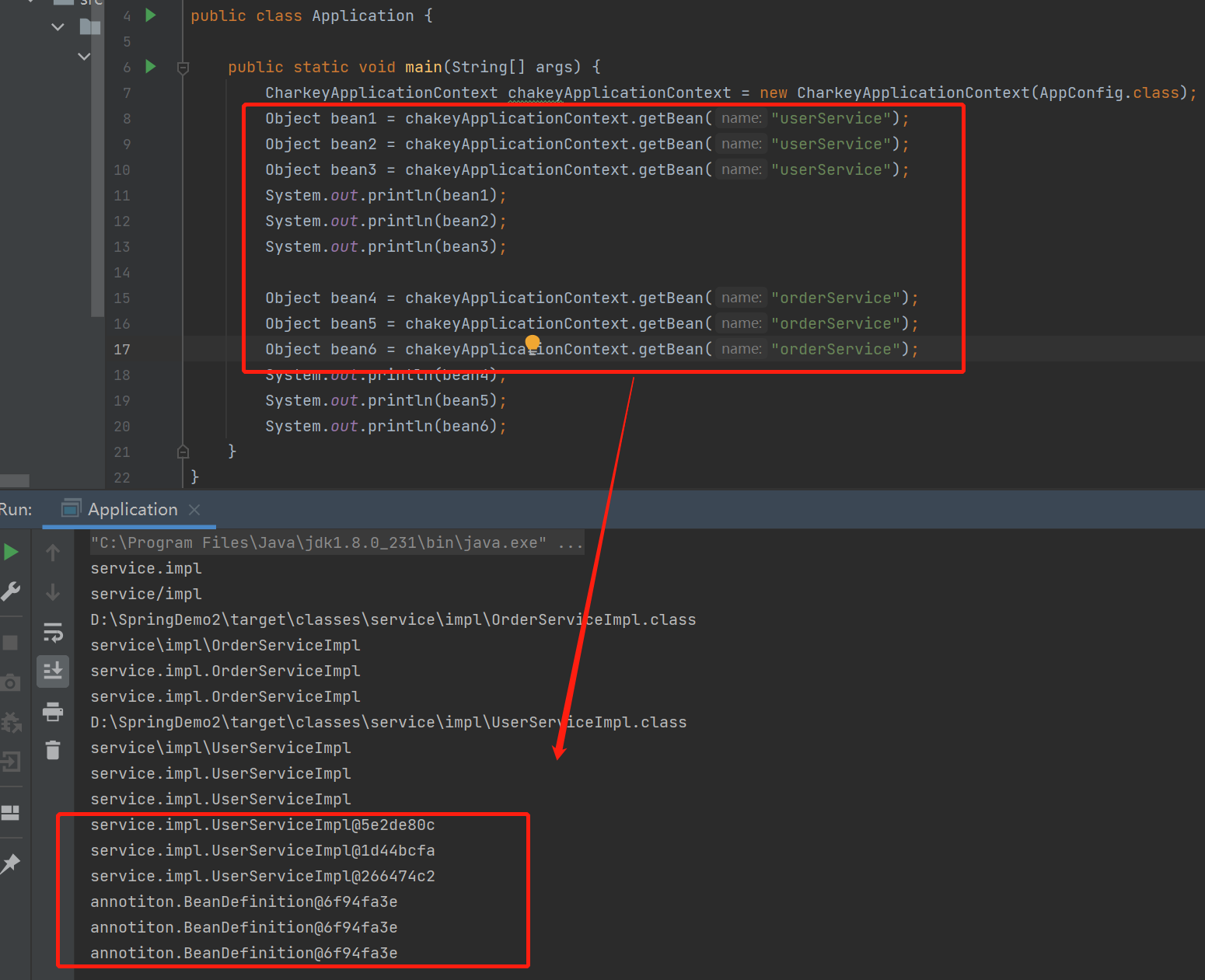
public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { CharkeyApplicationContext chakeyApplicationContext = new CharkeyApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); Object bean1 = chakeyApplicationContext.getBean("userService"); System.out.println(bean1); } }
二.IOC之扫描加载Bean对象
1.添加扫描Config类注解compentScan
2.添加compent注解标注扫描类
3.Bean加载到容器中
4.调用getBean
package annotiton; import java.lang.annotation.*; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Component { String value() default ""; }
package annotiton; import java.lang.annotation.*; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface ComponentScan { String value(); }
package annotiton; public class BeanDefinition { private Class clazz; private String scope;//单例 多例 public BeanDefinition() { } public BeanDefinition(Class clazz, String scope) { this.clazz = clazz; this.scope = scope; } public Class getClazz() { return clazz; } public void setClazz(Class clazz) { this.clazz = clazz; } public String getScope() { return scope; } public void setScope(String scope) { this.scope = scope; } }
@Component("orderService")
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
}
@Component("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
}
package config; import annotiton.ComponentScan; @ComponentScan("service.impl") public class AppConfig { }
package spring; import annotiton.BeanDefinition; import annotiton.Component; import annotiton.ComponentScan; import java.io.File; import java.net.URL; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; public class CharkeyApplicationContext { private Class appConfig; private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDifinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public CharkeyApplicationContext(Class configClass) { this.appConfig = appConfig; //扫描bean scan(configClass); } public Object getBean(String name) { BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDifinitionMap.get(name); return beanDefinition; } public void scan(Class app) { boolean annotationPresent = app.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class); if (!annotationPresent) throw new RuntimeException("没有配置类"); ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) app.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class); String path = componentScan.value(); System.out.println(path); ClassLoader classLoader = CharkeyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader(); path = path.replace(".", "/"); System.out.println(path); URL resource = classLoader.getResource("service/impl");//"com/charkey/service" File file = new File(resource.getFile()); if (file.isDirectory()) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) { File file1 = files[i]; String absolutePath = file1.getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println(absolutePath); absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("service"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class")); System.out.println(absolutePath); absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("\\", "."); System.out.println(absolutePath); Class<?> clazz = null; try { clazz = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath); boolean isComponent = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class); if (!isComponent) continue; Component declaredAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class); String beanName = declaredAnnotation.value(); BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(); beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz); beanDifinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (clazz != null && clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) { System.out.println(absolutePath); } } } } }
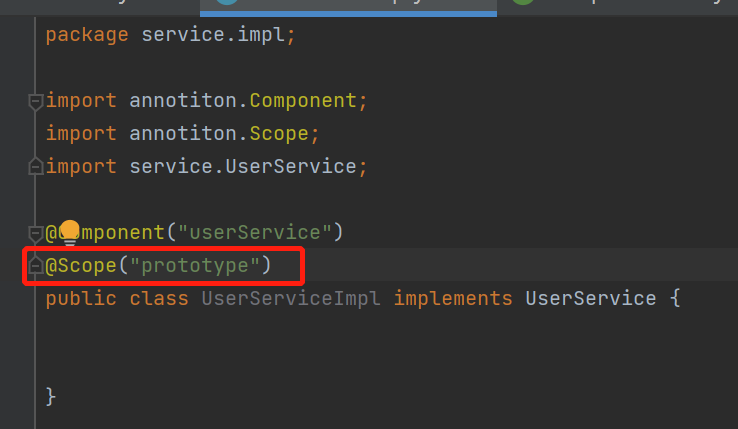
三.Scope注解实现可配置的单例,多例对象
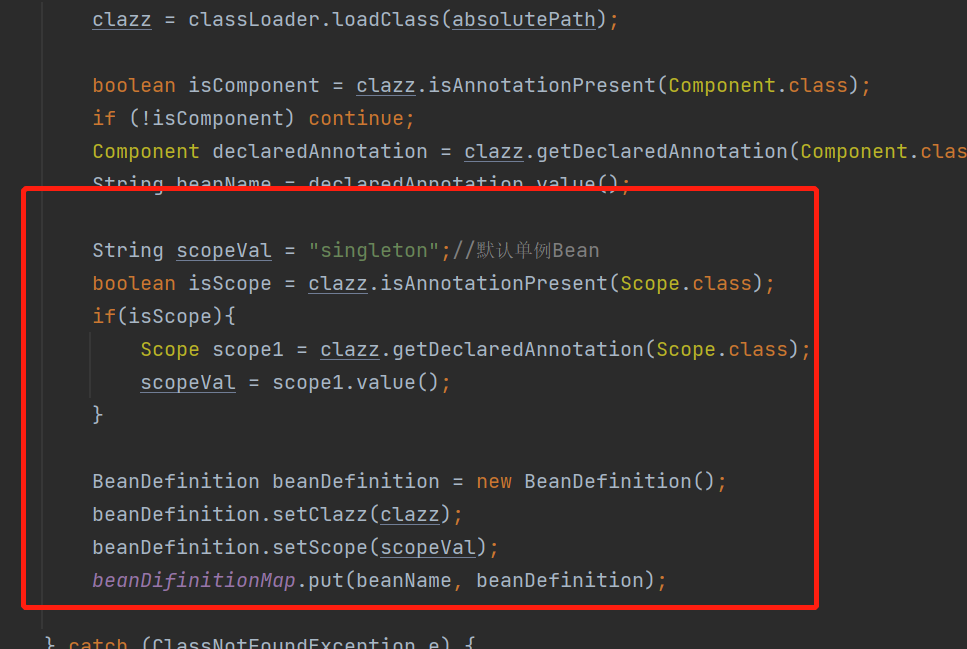
1.添加Scope注解,默认为singleton
2.被Compoent注解扫描的类被scope注解定义为Prototype视为多例,否则为单例
3.Bean加载到容器中
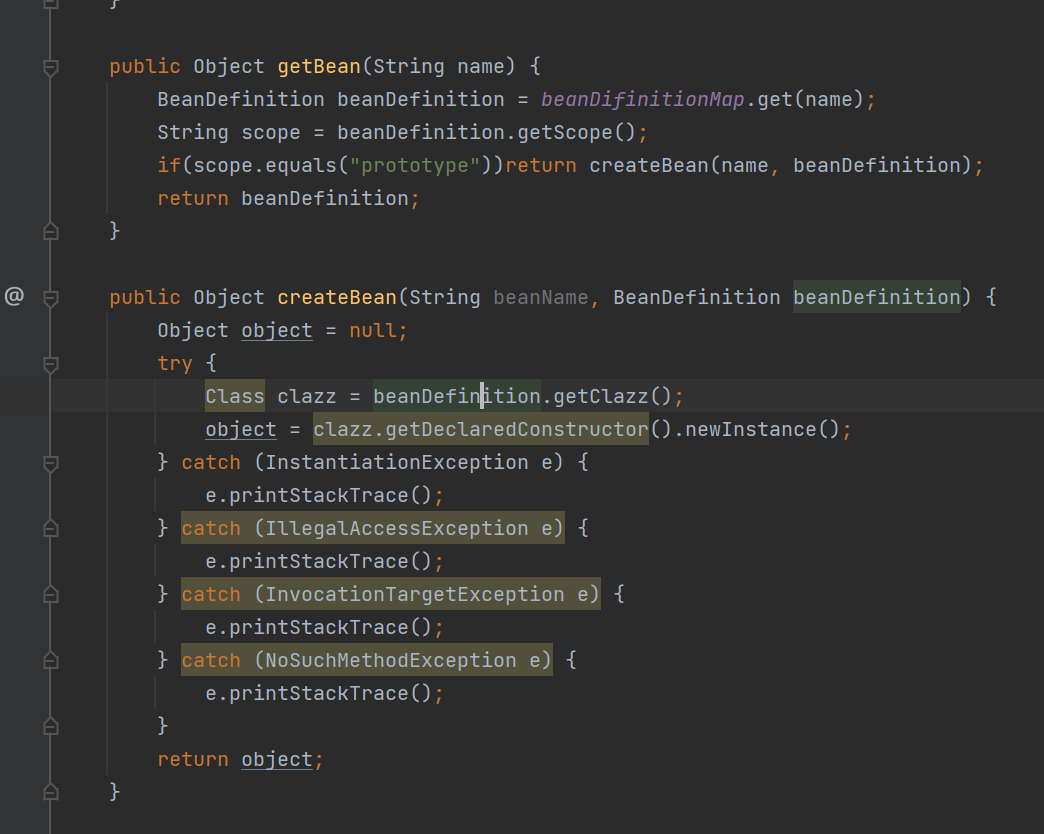
4.单例时从bean容器中取出,多例时创建新对象
package annotiton; import java.lang.annotation.*; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Scope { String value() default "singleton"; }
package spring; import annotiton.BeanDefinition; import annotiton.Component; import annotiton.ComponentScan; import annotiton.Scope; import java.io.File; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.net.URL; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; public class CharkeyApplicationContext { private Class appConfig; private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDifinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public CharkeyApplicationContext(Class configClass) { this.appConfig = appConfig; //扫描bean scan(configClass); } public Object getBean(String name) { BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDifinitionMap.get(name); String scope = beanDefinition.getScope(); if(scope.equals("prototype"))return createBean(name, beanDefinition); return beanDefinition; } public Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) { Object object = null; try { Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz(); object = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return object; } public void scan(Class app) { boolean annotationPresent = app.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class); if (!annotationPresent) throw new RuntimeException("没有配置类"); ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) app.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class); String path = componentScan.value(); System.out.println(path); ClassLoader classLoader = CharkeyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader(); path = path.replace(".", "/"); System.out.println(path); URL resource = classLoader.getResource("service/impl");//"com/charkey/service" File file = new File(resource.getFile()); if (file.isDirectory()) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) { File file1 = files[i]; String absolutePath = file1.getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println(absolutePath); absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("service"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class")); System.out.println(absolutePath); absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("\\", "."); System.out.println(absolutePath); Class<?> clazz = null; try { clazz = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath); boolean isComponent = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class); if (!isComponent) continue; Component declaredAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class); String beanName = declaredAnnotation.value(); String scopeVal = "singleton";//默认单例Bean boolean isScope = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class); if(isScope){ Scope scope1 = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class); scopeVal = scope1.value(); } BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(); beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz); beanDefinition.setScope(scopeVal); beanDifinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (clazz != null && clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) { System.out.println(absolutePath); } } } } }
四.使用Autowired控制反转以及依赖注入
1.添加Autowired注解,增加requied属性
2.模拟DI创建bean容器
3.在创建bean时,把bean中的被autowired定义的属性加载
package annotiton; import java.lang.annotation.*; @Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Autowired { boolean value() default true; }
package spring;
import annotiton.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
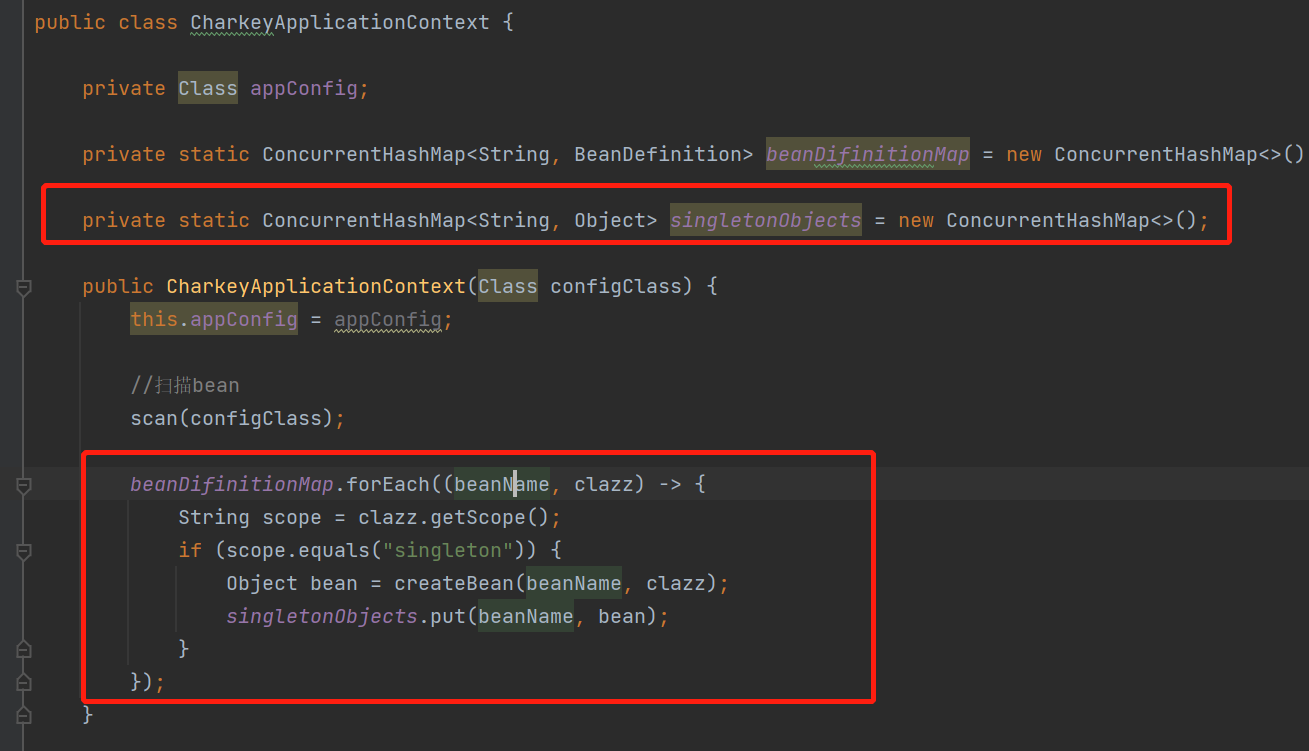
public class CharkeyApplicationContext {
private Class appConfig;
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDifinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public CharkeyApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.appConfig = appConfig;
//扫描bean
scan(configClass);
beanDifinitionMap.forEach((beanName, clazz) -> {
String scope = clazz.getScope();
if (scope.equals("singleton")) {
Object bean = createBean(beanName, clazz);
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
});
}
public Object getBean(String name) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDifinitionMap.get(name);
String scope = beanDefinition.getScope();
if(scope.equals("prototype"))return createBean(name, beanDefinition);
return singletonObjects.get(name);
}
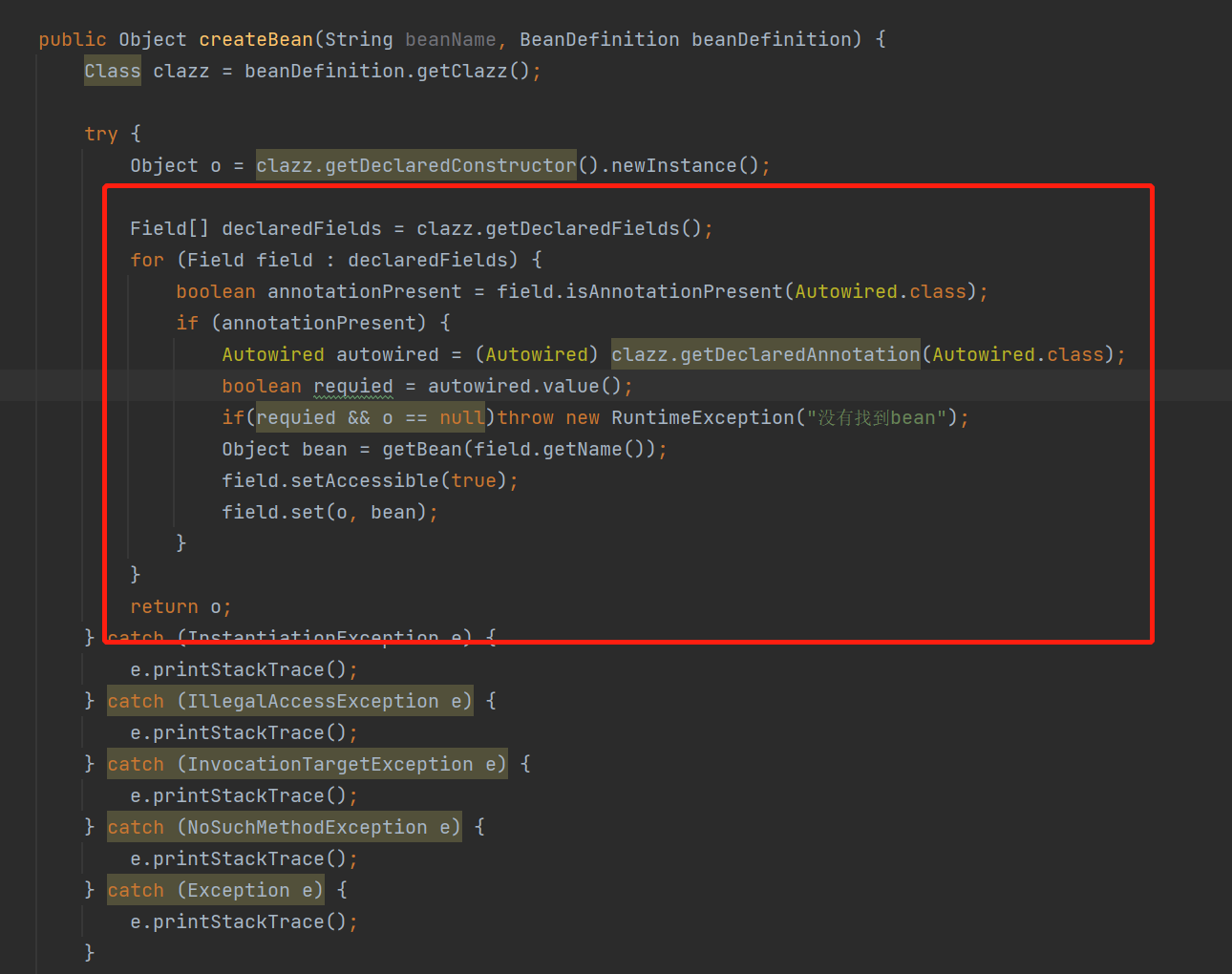
public Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
try {
Object o = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
boolean annotationPresent = field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class);
if (annotationPresent) {
Autowired autowired = (Autowired) clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Autowired.class);
boolean requied = autowired.value();
if(requied && o == null)throw new RuntimeException("没有找到bean");
Object bean = getBean(field.getName());
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(o, bean);
}
}
return o;
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public void scan(Class app) {
boolean annotationPresent = app.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class);
if (!annotationPresent) throw new RuntimeException("没有配置类");
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) app.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScan.value();
System.out.println(path);
ClassLoader classLoader = CharkeyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
path = path.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println(path);
URL resource = classLoader.getResource("service/impl");//"com/charkey/service"
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
File file1 = files[i];
String absolutePath = file1.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println(absolutePath);
absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("service"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
System.out.println(absolutePath);
absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("\\", ".");
System.out.println(absolutePath);
Class<?> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath);
boolean isComponent = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class);
if (!isComponent) continue;
Component declaredAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = declaredAnnotation.value();
String scopeVal = "singleton";//默认单例Bean
boolean isScope = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class);
if(isScope){
Scope scope1 = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
scopeVal = scope1.value();
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
beanDefinition.setScope(scopeVal);
beanDifinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (clazz != null && clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
System.out.println(absolutePath);
}
}
}
}
}
五. Bean的生命周期
1.创建InitializingBean接口,定义初始化方法
2.修饰到需要初始化的Compent类上
3.创建Bean时,触发初始化方法
package annotiton; public interface InitializingBean { void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception; }

package service.impl; import annotiton.Autowired; import annotiton.Component; import annotiton.InitializingBean; import annotiton.Scope; import service.OrderService; import service.UserService; @Component("userService") @Scope("prototype") public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService, InitializingBean { @Autowired private OrderService orderService; private String name; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void testAutowired(){ System.out.println(orderService); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("bean初始化。。。"); //System.out.println(getName()); } }
六. 监听Bean的初始化前、初始化、初始化后
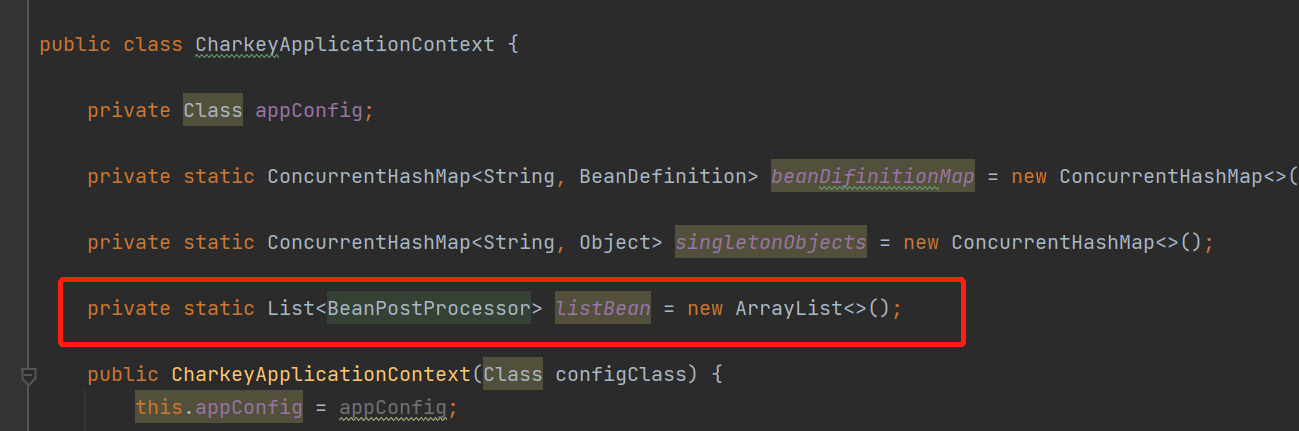
1.Bean生命周期接口及实现 BeanPostProcessor 和 MyBeanPostInitialization,并在MyBeanPostInitialization添加Compent
2.扫描时将BeanPostProcessor 放到容器中
3.创建Bean时,从容器中取出BeanPostProcessor ,并执行初始化方法
package annotiton; public interface BeanPostProcessor { Object postProcessorBeforeInintion(String beanName, Object bean); Object postProcessorAfterInintion(String beanName, Object bean); }
package service.impl; import annotiton.BeanPostProcessor; import annotiton.Component; import service.OrderService; @Component public class MyBeanPostInitialization implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessorBeforeInintion(String beanName, Object bean) { if (beanName.equals("orderService")) { OrderService orderService = (OrderService) bean; System.out.println("Bean开始初始化。。。"); orderService.setName("charkey"); } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessorAfterInintion(String beanName, Object bean) { if (beanName.equals("orderService")) { OrderService orderService = (OrderService) bean; System.out.println("Bean初始化结束。。。name为。。。" + orderService.getName()); } return bean; } }
扫描
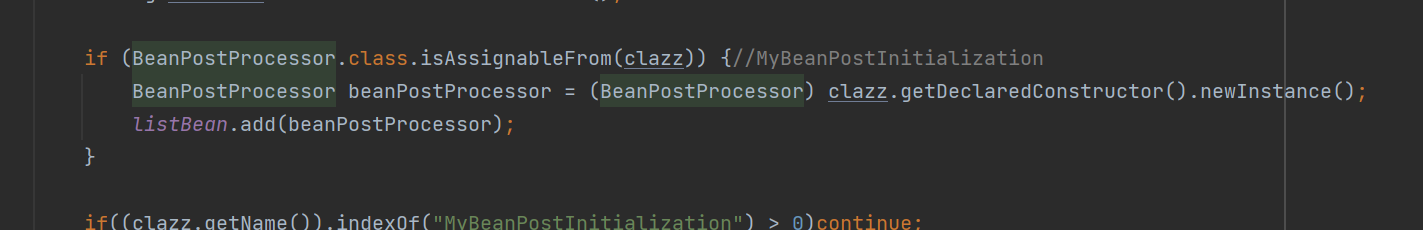

package spring; import annotiton.*; import java.io.File; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.net.URL; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; public class CharkeyApplicationContext { private Class appConfig; private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDifinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static List<BeanPostProcessor> listBean = new ArrayList<>(); public CharkeyApplicationContext(Class configClass) { this.appConfig = appConfig; //扫描bean scan(configClass); beanDifinitionMap.forEach((beanName, clazz) -> { String scope = clazz.getScope(); if (scope.equals("singleton")) { Object bean = createBean(beanName, clazz); singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean); } }); } public Object getBean(String name) { BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDifinitionMap.get(name); String scope = beanDefinition.getScope(); if (scope.equals("prototype")) return createBean(name, beanDefinition); return singletonObjects.get(name); } public Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) { Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz(); try { Object o = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : declaredFields) { boolean annotationPresent = field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class); if (annotationPresent) { Autowired autowired = (Autowired) clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Autowired.class); if (autowired == null) continue; boolean requied = autowired.value(); if (requied && o == null) throw new RuntimeException("没有找到bean"); Object bean = getBean(field.getName()); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(o, bean); } } //初始化前执行 for (BeanPostProcessor processor : listBean) { processor.postProcessorBeforeInintion(beanName,o); } //初始化执行 if (o instanceof InitializingBean) { ((InitializingBean) o).afterPropertiesSet(); } //初始化前执行 for (BeanPostProcessor processor : listBean) { processor.postProcessorAfterInintion(beanName,o); } return o; } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } public void scan(Class app) { boolean annotationPresent = app.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class); if (!annotationPresent) throw new RuntimeException("没有配置类"); ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) app.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class); String path = componentScan.value(); System.out.println(path); ClassLoader classLoader = CharkeyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader(); path = path.replace(".", "/"); System.out.println(path); URL resource = classLoader.getResource("service/impl");//"com/charkey/service" File file = new File(resource.getFile()); if (file.isDirectory()) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) { File file1 = files[i]; String absolutePath = file1.getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println(absolutePath); absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("service"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class")); System.out.println(absolutePath); absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("\\", "."); System.out.println(absolutePath); Class<?> clazz = null; try { clazz = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath); boolean isComponent = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class); if (!isComponent) continue; Component declaredAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class); String beanName = declaredAnnotation.value(); if (BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {//MyBeanPostInitialization BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); listBean.add(beanPostProcessor); } if((clazz.getName()).indexOf("MyBeanPostInitialization") > 0)continue; if((beanName == null || beanName.equals("")) ){ beanName = clazz.getName().substring(clazz.getName().lastIndexOf(".")+1); beanName = Character.toLowerCase(beanName.charAt(0)) + (beanName.length() > 1 ? beanName.substring(1) :""); beanName = beanName.replace("Impl",""); } String scopeVal = "singleton";//默认单例Bean boolean isScope = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class); if (isScope) { Scope scope1 = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class); scopeVal = scope1.value(); } BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(); beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz); beanDefinition.setScope(scopeVal); beanDifinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (clazz != null && clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) { System.out.println(absolutePath); } } } } }
五.实现AOP
在Bean初始化完成后,配置JDK的Proxy对象并返回
package service.impl; import annotiton.BeanPostProcessor; import annotiton.Component; import service.OrderService; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; @Component public class MyBeanPostInitialization implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessorBeforeInintion(String beanName, Object bean) { if (beanName.equals("orderService")) { OrderService orderService = (OrderService) bean; System.out.println("Bean开始初始化。。。"); orderService.setName("charkey"); } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessorAfterInintion(String beanName, Object bean) { if (beanName.equals("orderService")) { OrderService orderService = (OrderService) bean; System.out.println("Bean初始化结束。。。name为。。。" + orderService.getName()); Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(MyBeanPostInitialization.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("执行test方法前AOP执行逻辑。。。。。"); return method.invoke(bean, args); } }); return proxyInstance; } return bean; } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号