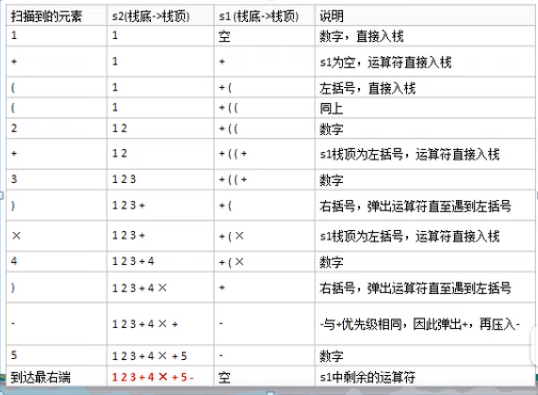
中缀转后缀(逆波兰)
中缀转后缀(逆波兰)
具体步骤如下:
-
初始化两个栈:运算符栈s1和储存中间结果的栈s2;
-
从左至右扫描中缀表达式;
-
遇到操作数时,将其压s2;
-
遇到运算符时,比较其与s1栈项运算符的优先级:
- 如果s1为空,或栈顶运算符为左括号“(", 则直接将此运算符入栈;
- 否则,若优先级比栈顶运算符的高,也将运算符压入s1;
- 否则,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并压入到s2中,再次转到第一步与s1中新的栈顶运算符相比较;
-
遇到括号时:
- 如果是左括号“(”,则直接压入s1
- 如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出s1栈项的运算符,并压入s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃
-
重复步骤2至5,直到表达式的最右边
-
将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并压入s2
-
依次弹出s2中的元素并输出,结果的逆序即为中缀表达式对应的后缀表达式
例如:中缀表达式 1+((2+3)*4)-5 =>转成后缀表达式 123+4x+5-
代码实现(只考虑正整数)
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String suffixExpression = "30 4 + 5 * 6 -";
// List<String> list = getListString(suffixExpression);
// int res = calculate(list);
// System.out.println("计算的结果是:"+ res);
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";
List<String> list1 = change(expression);
System.out.println("中缀表达式为"+list1);
List<String> list2 = change2(list1);
System.out.println("后缀表达式为"+list2);
System.out.println("输出的结果是"+calculate(list2));
}
//中缀转后缀
//1.1+((2+3)*4)-5 =>转成123+4x+5-
//2.因为直接对str.,进行操作,不方便,因此先将"1+((2+3)x4)-5" =》中缀的表达式对应的List
//即"1+((2+3)x4)-5" => ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5]
public static List<String> change(String middle){
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
String str;
char c;
do {
if ((c = middle.charAt(i)) < 48 || (c = middle.charAt(i)) > 57){
list.add(c+"");
i++;
}else {
str = "";
while (i < middle.length() && (c = middle.charAt(i)) >= 48 && (c = middle.charAt(i)) <= 57){
str += c;
i++;
}
list.add(str);
}
}while (i < middle.length());
return list;
}
//3.将得到的中缀表达式对应的List =>后缀表达式对应的List
// 即ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] =》 ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,-]
public static List<String> change2(List<String> list){
Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>();
//说明:因为s2这个栈,在整个转换过程中,没有pop操作,而且后面我们还需要逆序输出
//因此比较麻烦,这里我们就不用Stack<String> 直接使用List<String> s2
//Stack<String> stack2 = new Stack<>();
List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>();
for (String item : list){
if (item.matches("\\d+")){
s2.add(item);
}else if (item.equals("(")){
s1.push(item);
}else if (item.equals(")")){
while (!s1.peek().equals("(")){
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.pop();//弹出"("
}else {
//当item的优先级小于等于s1栈顶运算符,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并加入到s2中,再次转到(4.1)与s1中新的栈顶运算符相比较
while (s1.size()!=0&&Operation.getValue(s1.peek())>=Operation.getValue(item)){
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.push(item);
}
}
//将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并加入s2
while (s1.size()!=0){
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
return s2;
}
public static int calculate(List<String> ls){
Stack<String> stack =new Stack<String>();
for (String item : ls){
if (item.matches("\\d+")){
stack.push(item);
}else {
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = 0;
if (item.equals("+")){
res = num1 + num2;
} else if (item.equals("-")){
res = num2 - num1;
}else if (item.equals("*")){
res = num2 * num1;
}else if (item.equals("/")){
res = num2 / num1;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
stack.push(res + "");
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
//比较优先级
class Operation{
private static int ADD = 1;
private static int SUB = 1;
private static int MUL = 2;
private static int DIV = 2;
public static int getValue(String operation){
int result = 0;
switch (operation){
case "+":
result = ADD;
break;
case "-":
result = SUB;
break;
case "*":
result = MUL;
break;
case "/":
result = DIV;
break;
}
return result;
}
}