Javascript设计模式之我见:状态模式
大家好!本文介绍状态模式及其在Javascript中的应用。
模式介绍
定义
当一个对象的内在状态改变时允许改变其行为,这个对象看起来像是改变了其类。
状态模式主要解决的是控制一个对象状态的条件表达式过于复杂时的情况。把状态的判断逻辑转移到表示不同状态的一系列类中,可以把复杂的判断逻辑简化。
类图及说明
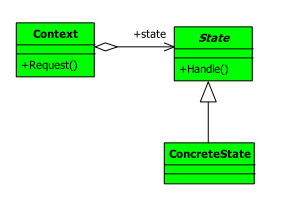
State:抽象状态
接口或抽象类,负责对象状态定义,并且封装环境角色以实现状态切换
ConcreState:具体状态
每一个具体状态必须完成两个职责:本状态的行为管理以及趋向状态处理。通俗地说,就是本状态下要做的事情,以及本状态如何过渡到其他状态。
Context:环境
定义客户端需要的接口,并且负责具体状态的切换。
应用场景
- 一个对象的行为取决于它的状态, 并且它必须在运行时刻根据状态改变它的行为。
- 代码中包含大量与对象状态有关的条件语句:一个操作中含有庞大的多分支的条件(if else(或switch case)语句,且这些分支依赖于该对象的状态。这个状态通常用一个或多个枚举常量表示。通常 , 有多个操作包含这一相同的条件结构。 State模式将每一个条件分支放入一个独立的类中。这使得你可以根据对象自身的情况将对象的状态作为一个对象,这一对象可以不依赖于其他对象而独立变化。
优点
- 避免了过多的 swith…case 或者 if..else 语句的使用,避免了程序的复杂性
- 很好的使用体现了开闭原则和单一职责原则,每个状态都是一个子类,你要增加状态就增加子类,你要修改状态,你只修改一个子类就可以了
- 封装性非常好,这也是状态模式的基本要求。状态变换放置到了类的内部来实现,外部的调用不用知道类内部如何实现状态和行为的变换。
缺点
- 具体状态类可能会有很多个,不好管理。
状态模式在Javascript中的应用
我的理解
- ConcreteState具体状态类有两个职责:处理本状态必须完成的任务;过渡到其他状态。
- 可以采自下而上的方法来实现状态类,即先实现ConcreteState类,然后再将ConcreteState类的共性提取出来,形成父类State。
类图及说明

User:使用者
使用者具有不同的状态,它创建Context类并将状态的逻辑委托给Context类处理。
示例
小时候大家应该都玩过魂斗罗游戏吧,魂斗罗吃了无敌道具后会变成刀枪不入,吃了火力增强道具后会变成杀人机器。让我们来看看它的状态是如何转换的。
状态图
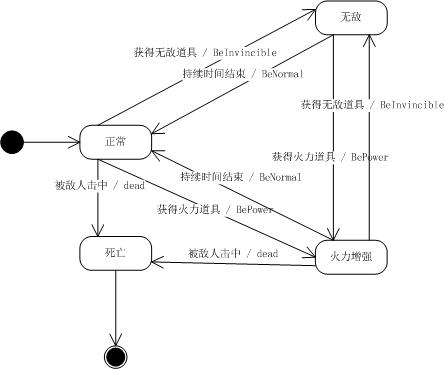
魂斗罗Warrior有NORMAL、INVINCIBLE、POWER、DEAD四个状态,每个状态都有beNormal、beInvincible、bePower、dead四个方法。有timeOver、getInvincible、getPower、beShotDead四个触发状态的事件。
类图
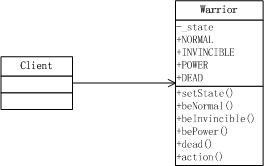
代码
代码中使用的库:YOOP
Warrior
var Warrior = YYC.Class({ Private: { _state: null }, Public: { //*事件标志 _getInvincible: false, _getPower: false, _timeOver: false, _beShotDead: false, setState: function (state) { this._state = state; }, //*状态方法 beNormal: function () { switch (this._state) { case Warrior.NORMAL_STATE: //本状态beNormal方法的逻辑。已经处于NORMAL状态,不用再转换为NORMAL状态了 console.log("恢复正常"); break; case Warrior.INVINCIBLE_STATE: //INVINCIBLE状态下beNormal方法的逻辑 console.log("恢复正常"); //从INVINCIBLE状态转换到NORMAL状态 this.setState(Warrior.NORMAL_STATE); break; case Warrior.POWER_STATE: //POWER状态下beNormal方法的逻辑 console.log("恢复正常"); //从POWER状态转换到NORMAL状态 this.setState(Warrior.NORMAL_STATE); break; case Warrior.DEAD_STATE: //不能起死回生 break; } }, beInvincible: function () { switch (this._state) { case Warrior.NORMAL_STATE: console.log("无敌"); this.setState(Warrior.INVINCIBLE_STATE); break; case Warrior.INVINCIBLE_STATE: console.log("无敌"); break; case Warrior.POWER_STATE: console.log("无敌"); this.setState(Warrior.INVINCIBLE_STATE); break; case Warrior.DEAD_STATE: break; } }, bePower: function () { switch (this._state) { case Warrior.NORMAL_STATE: console.log("火力增强"); this.setState(Warrior.POWER_STATE); break; case Warrior.INVINCIBLE_STATE: console.log("火力增强"); this.setState(Warrior.POWER_STATE); break; case Warrior.POWER_STATE: console.log("火力增强"); break; case Warrior.DEAD_STATE: break; } }, dead: function () { switch (this._state) { case Warrior.NORMAL_STATE: console.log("死亡"); this.setState(Warrior.DEAD_STATE); break; case Warrior.INVINCIBLE_STATE: //都无敌了当然不会死亡 break; case Warrior.POWER_STATE: console.log("死亡"); this.setState(Warrior.DEAD_STATE); break; case Warrior.DEAD_STATE: console.log("死亡"); break; } }, action: function () { //*此处进行触发状态的事件判断 if (this._timeOver) { this.beNormal(); } else if (this._getInvincible) { this.beInvincible(); } else if (this._getPower) { this.bePower(); } else if (this._beShotDead) { this.dead(); } } }, Static: { NORMAL_STATE: 1, INVINCIBLE_STATE: 2, POWER_STATE: 3, DEAD_STATE: 4 } });
场景类
function _resetFlag(warrior) { warrior._getInvincible = false; warrior._getPower = false; warrior._timeOver = false; warrior._beShotDead = false; } function _getInvincible(warrior) { _resetFlag(warrior); warrior._getInvincible = true; } function _getPower(warrior) { _resetFlag(warrior); warrior._getPower = true; } function _beShotDead(warrior) { _resetFlag(warrior); warrior._beShotDead = true; } function main() { var warrior = new Warrior(); //初始状态为Normal warrior.setState(Warrior.NORMAL); //获得无敌道具,进入无敌状态 _getInvincible(warrior); warrior.action(); //获得火力增强道具,进入火力增强状态 _getPower(warrior); warrior.action(); //被击中,进入死亡状态 _beShotDead(warrior); warrior.action(); }
运行结果

示例分析
我们来看看这段程序的问题。
- 实现类Warrior用了大量的switch...case判断,增加了大量代码,可读性和可维护性差。
- 扩展性差。
如果要增加1个状态,则beNormal、beInvincible、bePower、dead方法中都要增加判断条件,这不符合开闭原则。
使用状态模式
类图
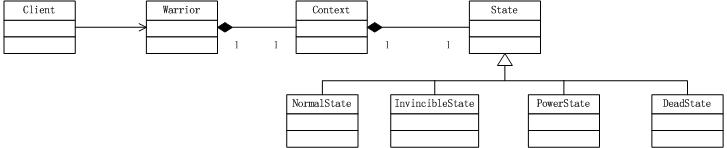
代码
State
var State = YYC.AClass({ Public: { setContext: function (context) { this.P_context = context; } }, Protected: { P_context: null }, Abstract: { beNormal: function () { }, beInvincible: function () { }, bePower: function () { }, dead: function () { } } });
NormalState
var NormalState = YYC.Class(State, { Public: { //*在具体状态类中进行触发状态的事件判断 beNormal: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.timeOver) { //本状态逻辑 console.log("恢复正常"); } }, beInvincible: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.getInvincible) { //过度到无敌状态的逻辑 this.P_context.setState(Context.InvincibleState); this.P_context.beInvincible(); } }, bePower: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.getPower) { //过度到火力增强状态的逻辑 this.P_context.setState(Context.PowerState); this.P_context.bePower(); } }, dead: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.beShotDead) { //过度到死亡状态的逻辑 this.P_context.setState(Context.DeadState); this.P_context.dead(); } } } });
InvincibleState
var InvincibleState = YYC.Class(State, { Public: { beNormal: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.timeOver) { this.P_context.setState(Context.NormalState); this.P_context.beNormal(); } }, beInvincible: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.getInvincible) { console.log("无敌"); } }, bePower: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.getPower) { this.P_context.setState(Context.PowerState); this.P_context.bePower(); } }, dead: function () { //都无敌了当然不会死亡 } } });
PowerState
var PowerState = YYC.Class(State, { Public: { beNormal: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.timeOver) { this.P_context.setState(Context.NormalState); this.P_context.beNormal(); } }, beInvincible: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.getInvincible) { this.P_context.setState(Context.InvincibleState); this.P_context.beInvincible(); } }, bePower: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.getPower) { console.log("火力增强"); } }, dead: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.beShotDead) { this.P_context.setState(Context.DeadState); this.P_context.dead(); } } } });
DeadState
var DeadState = YYC.Class(State, { Public: { beNormal: function () { //不能起死回生 }, beInvincible: function () { //挂都挂了,还怎么无敌 }, bePower: function () { //挂都挂了,还怎么火力增强 }, dead: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.beShotDead) { console.log("死亡"); } } } });
Context
var Context = YYC.Class({ Init: function (warrior) { this.warrior = warrior; }, Private: { _state: null }, Public: { warrior: null, setState: function (state) { this._state = state; //把当前的上下文通知到当前状态类对象中 this._state.setContext(this); }, beNormal: function () { this._state.beNormal(); }, beInvincible: function () { this._state.beInvincible(); }, bePower: function () { this._state.bePower(); }, dead: function () { this._state.dead(); } }, Static: { NormalState: new NormalState(), InvincibleState: new InvincibleState(), PowerState: new PowerState(), DeadState: new DeadState() } });
Warrior
var Warrior = YYC.Class({ Init: function () { this._context = new Context(this); //设置初始状态 this._context.setState(Context.NormalState); }, Private: { _context: null }, Public: { //*事件标志 getInvincible: false, getPower: false, timeOver: false, beShotDead: false, action: function () { this._context.beNormal(); this._context.beInvincible(); this._context.bePower(); this._context.dead(); } } });
场景类Client
function _resetFlag(warrior) { warrior.getInvincible = false; warrior.getPower = false; warrior.imeOver = false; warrior.beShotDead = false; } function _getInvincible(warrior) { _resetFlag(warrior); warrior.getInvincible = true; } function _getPower(warrior) { _resetFlag(warrior); warrior.getPower = true; } function _beShotDead(warrior) { _resetFlag(warrior); warrior.beShotDead = true; } function main() { var warrior = new Warrior(); //获得无敌道具,进入无敌状态 _getInvincible(warrior); warrior.action(); //获得火力增强道具,进入火力增强状态 _getPower(warrior); warrior.action(); //被击中,进入死亡状态 _beShotDead(warrior); warrior.action(); }
运行结果

示例分析
将触发状态的事件判断移到Warrior类中
目前是在具体状态类中进行触发状态的事件判断,这样造成了重复判断。可以将判断提出来,放到Warrior类的action中进行判断:
Warrior
action: function () { if (this.timeOver) { this._context.beNormal(); } else if (this.getInvincible) { this._context.beInvincible(); } else if (this.getPower) { this._context.bePower(); } else if (this.beShotDead) { this._context.dead(); } }
NormalState(其它三个具体状态类做相同的重构)
var NormalState = YYC.Class(State, { Public: { beNormal: function () { //本状态逻辑 console.log("恢复正常"); }, beInvincible: function () { //过度到无敌状态的逻辑 this.P_context.setState(Context.InvincibleState); this.P_context.beInvincible(); }, bePower: function () { //过度到火力增强状态的逻辑 this.P_context.setState(Context.PowerState); this.P_context.bePower(); }, dead: function () { //过度到死亡状态的逻辑 this.P_context.setState(Context.DeadState); this.P_context.dead(); } } });
局限性
如果不同状态转换为同一状态的触发事件不同,那么就不能把触发状态的事件移到Warrior类中,而需要在具体状态类中判断。
例如,现在从NORMAL状态转换到POWER状态的触发事件为“获得火力增强道具”,而从INVINCIBLE状态转换到POWER状态的触发事件为“持续时间结束且获得火力增强道具”:
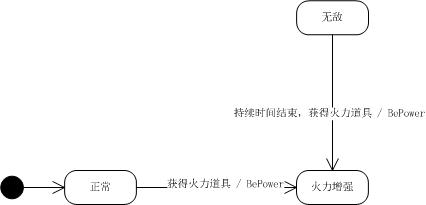
那么就不能在Warrior中进行统一的事件判断了,而应该在具体状态类NormalState、InvincibleState类中判断:
NormalState
bePower: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.getPower) { this.P_context.setState(Context.PowerState); this.P_context.bePower(); } },
InvincibleState
bePower: function () { if (this.P_context.warrior.timeOver && this.P_context.warrior.getPower) { this.P_context.setState(Context.PowerState); this.P_context.bePower(); } },
结论
不同状态转换为同一状态的触发事件相同,则可以将触发状态的事件判断放到调用Context的类中;否则将触发状态的事件判断放到具体状态类中。
参考资料



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号