选择排序
选择排序
选择排序(Select Sort)是以中简单直观的排序算法。它的基本思想是:
对于一个给定的未排序序列,经过第一轮比较后得到最小的元素,然后将该元素和序列中的第一个元素进行交换;
然后在从剩余的序列中选择的最小的元素和第二个元素交换位置;
重复该过程,直到需要比较的元素只有一个为止。
选择排序说明
下面以数列{20,40,30,10,60,50}为例,演示它的选择排序过程(如下图)。
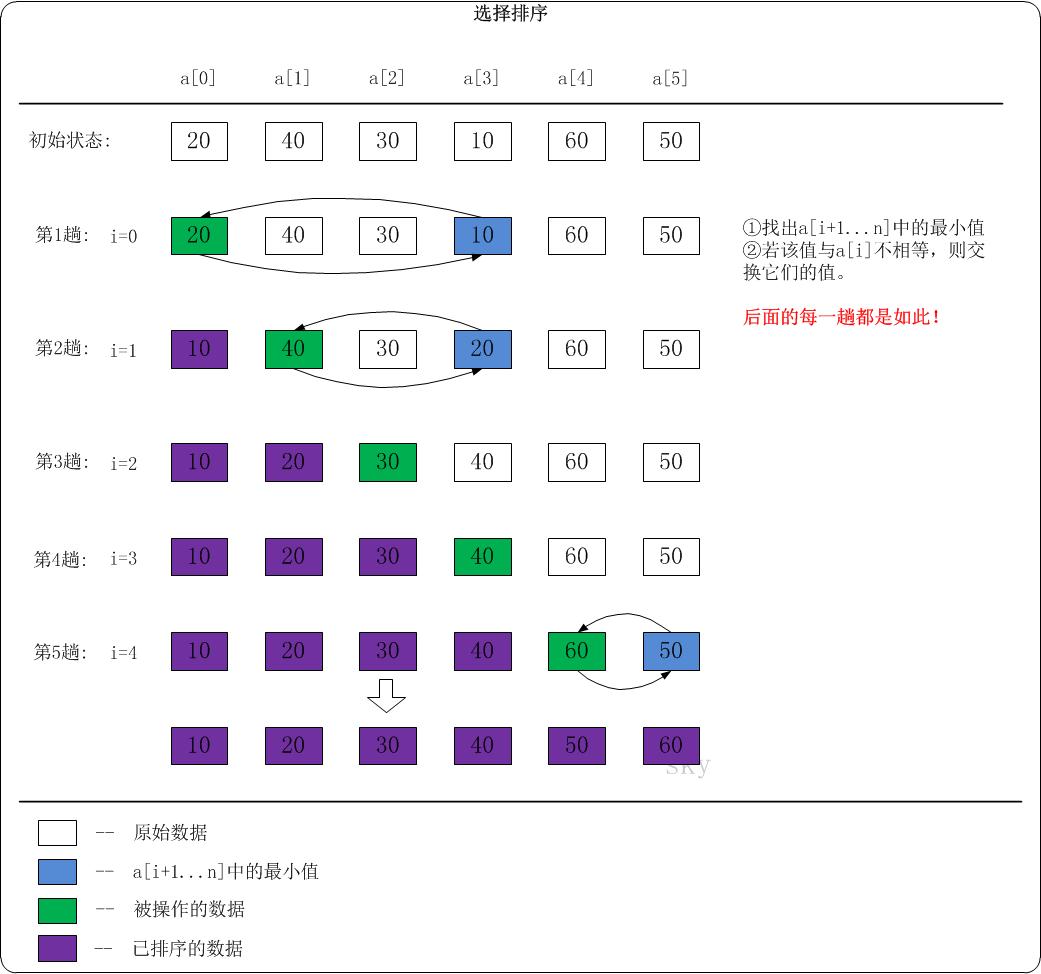
排序流程
第1趟:i=0。找出a[1...5]中的最小值a[3]=10,然后将a[0]和a[3]互换。 数列变化:20,40,30,10,60,50 -- > 10,40,30,20,60,50
第2趟:i=1。找出a[2...5]中的最小值a[3]=20,然后将a[1]和a[3]互换。 数列变化:10,40,30,20,60,50 -- > 10,20,30,40,60,50
第3趟:i=2。找出a[3...5]中的最小值,由于该最小值大于a[2],该趟不做任何处理。
第4趟:i=3。找出a[4...5]中的最小值,由于该最小值大于a[3],该趟不做任何处理。
第5趟:i=4。交换a[4]和a[5]的数据。 数列变化:10,20,30,40,60,50 -- > 10,20,30,40,50,60
代码实现
/**
* SelectSort
*/
public class SelectSort {
public static void selectSort(int[] array) {
int len = array.length;
if (len <= 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int pos = 0;
for (int j = i; j < len; j++) {
if (array[j] < min) {
min = array[j];
pos = j;
}
}
swap(array, i, pos);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] array, int pos1, int pos2) {
int tmp = array[pos1];
array[pos1] = array[pos2];
array[pos2] = tmp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {20,40,30,10,60,50};
selectSort(a);
System.out.printf("after sort:");
for (int i=0; i<a.length; i++)
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
}
选择排序的时间复杂度和稳定性
选择排序的时间复杂度是O(N^2)。
假设被排序的数列中有N个数。遍历一趟的时间复杂度是O(N),需要遍历多少次呢?N-1!因此,选择排序的时间复杂度是O(N^2)。
选择排序稳定性
选择排序是稳定的算法,它满足稳定算法的定义。



