92. 反转链表 II
题目:
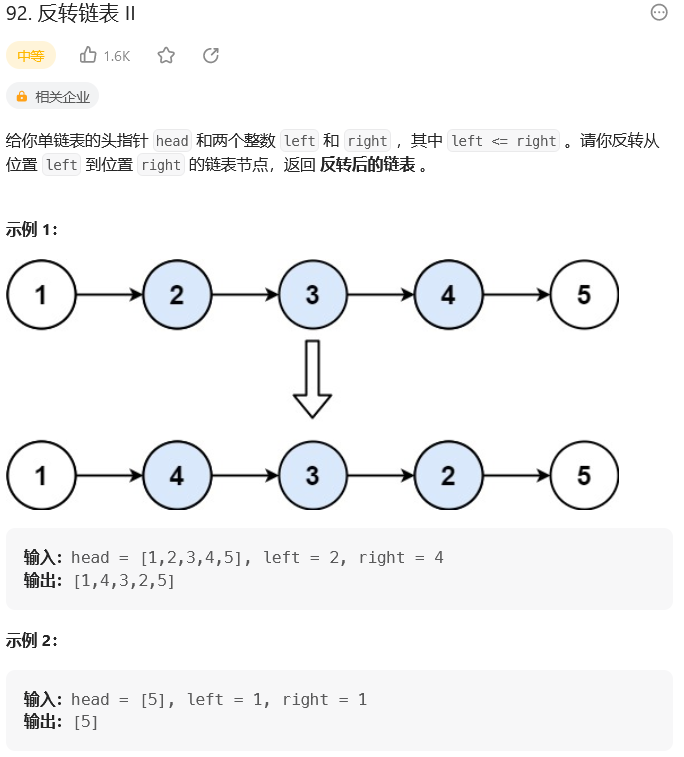

思路:
【1】采用分段处理的方式(这种方式时间复杂度为O(N+K),其中N为链表长度,K为反转长度)
【2】采用分段处理+头插法的方式(一趟扫描完成反转)
代码展示:
【1】采用分段处理的方式
// 采用分段处理的方式 //时间0 ms 击败 100% //内存39.3 MB 击败 11.47% //时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是链表总节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整个链表。 //空间复杂度:O(1)。只使用到常数个变量。 //逻辑说明: //将链表分成三段 : 左边不需要反转部分,中间需要反转部分,右边不需要反转部分 //其中左右两部分其实可以为空 //故需要构造一个 dummyNode 虚拟头节点(因为如果是从1开始反转就没有前驱点了) //所以设定前驱点 pre 是从 dummyNode 开始遍历,pre 是 left - 1 的节点 //然后 curr 是 right + 1 的节点 ,而 【left,right】 则是反转部分 //最后由 pre -> [right,left] -> curr 则是符合结果的部分 //返回 /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) { // 因为头节点有可能发生变化,使用虚拟头节点可以避免复杂的分类讨论 ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1); dummyNode.next = head; ListNode pre = dummyNode; // 第 1 步:从虚拟头节点走 left - 1 步,来到 left 节点的前一个节点 // 建议写在 for 循环里,语义清晰 for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) { pre = pre.next; } // 第 2 步:从 pre 再走 right - left + 1 步,来到 right 节点 ListNode rightNode = pre; for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) { rightNode = rightNode.next; } // 第 3 步:切断出一个子链表(截取链表) ListNode leftNode = pre.next; //这里取出边界的下一个节点,防止下面切断链接的时候丢失 ListNode curr = rightNode.next; // 注意:切断链接 pre.next = null; rightNode.next = null; // 第 4 步:同第 206 题,反转链表的子区间(相当于把这个链条抽出来进行反转后拼接回来) reverseLinkedList(leftNode); // 第 5 步:接回到原来的链表中 pre.next = rightNode; leftNode.next = curr; return dummyNode.next; } private void reverseLinkedList(ListNode head) { // 也可以使用递归反转一个链表 ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } } }
【2】采用分段处理+头插法的方式:
整体思想是:在需要反转的区间里,每遍历到一个节点,让这个新节点来到反转部分的起始位置。下面的图展示了整个流程
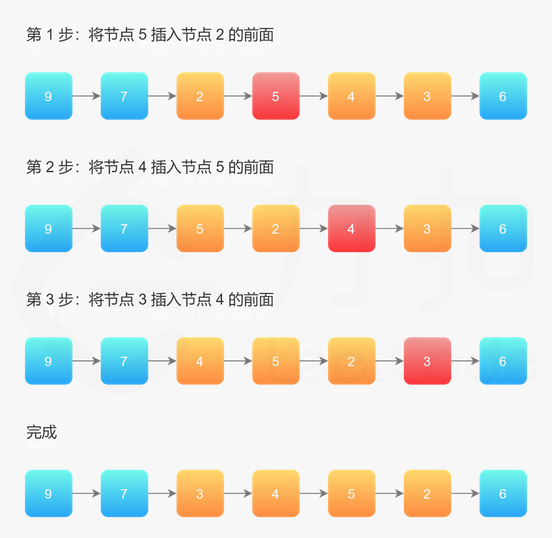
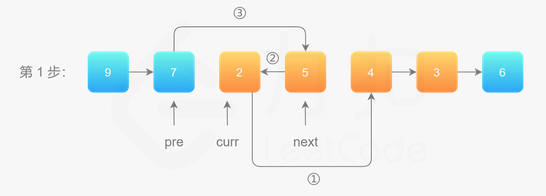
用三个指针变量 pre、curr、next 来记录反转的过程中需要的变量,它们的意义如下: 1)curr:指向待反转区域的第一个节点 left; 2)next:永远指向 curr 的下一个节点,循环过程中,curr 变化以后 next 会变化; 3)pre:永远指向待反转区域的第一个节点 left 的前一个节点,在循环过程中不变。
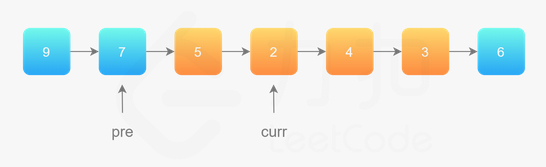
效果如下:
代码展示:
//时间0 ms 击败 100% //内存39.2 MB 击败 26.66% //时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是链表总节点数。最多只遍历了链表一次,就完成了反转。 //空间复杂度:O(1)。只使用到常数个变量。 /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) { // 设置 dummyNode 是这一类问题的一般做法 ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1); dummyNode.next = head; ListNode pre = dummyNode; for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) { pre = pre.next; } ListNode cur = pre.next; ListNode next; for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) { next = cur.next; cur.next = next.next; next.next = pre.next; pre.next = next; } return dummyNode.next; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号