剑指 Offer II 080. 含有 k 个元素的组合(77. 组合)
题目:
思路:
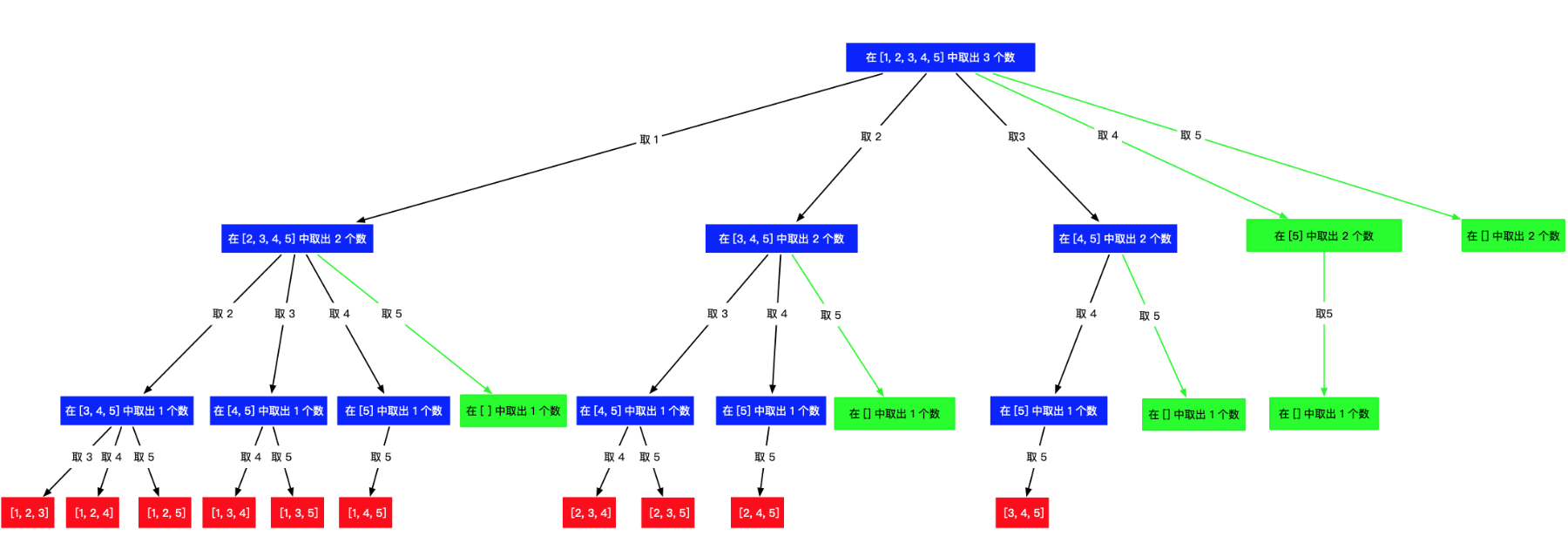
【1】利用回溯的方式:
【2】非递归(字典序法)实现组合型枚举(未理解)
代码展示:
非递归(字典序法)实现组合型枚举的方式:
//时间6 ms击败57.94% //内存42.8 MB击败45.2% class Solution { List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); // 初始化 // 将 temp 中 [0, k - 1] 每个位置 i 设置为 i + 1,即 [0, k - 1] 存 [1, k] // 末尾加一位 n + 1 作为哨兵 for (int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) { temp.add(i); } temp.add(n + 1); int j = 0; while (j < k) { ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp.subList(0, k))); j = 0; // 寻找第一个 temp[j] + 1 != temp[j + 1] 的位置 t // 我们需要把 [0, t - 1] 区间内的每个位置重置成 [1, t] while (j < k && temp.get(j) + 1 == temp.get(j + 1)) { temp.set(j, j + 1); ++j; } // j 是第一个 temp[j] + 1 != temp[j + 1] 的位置 temp.set(j, temp.get(j) + 1); } return ans; } }
利用回溯的方式:
//时间24 ms击败10.8% //内存43.1 MB击败13.83% //回溯的方式是利用了树的概念,通过选或者不选来决定是否纳入到集合数组中 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (k <= 0 || n < k) { return res; } Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>(); dfs(n, k, 1, path, res); return res; } private void dfs(int n, int k, int begin, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (path.size() == k) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = begin; i <= n; i++) { path.addLast(i); dfs(n, k, i + 1, path, res); path.removeLast(); } } } //剪枝的优化 //时间1 ms击败99.98% //内存42.9 MB击败26.69% //在回溯过程中剪枝是很重要的,因为可以大大的节约运行的时间 //首先剪枝的有,当剩下的数据不足以组成一个想要的集合的时候,其实这部分就没有必要继续浪费时间的遍历下去 //所以剪枝过程就是:把 i <= n 改成 i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1 ; class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (k <= 0 || n < k) { return res; } Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>(); dfs(n, k, 1, path, res); return res; } private void dfs(int n, int k, int begin, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (path.size() == k) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = begin; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++) { path.addLast(i); dfs(n, k, i + 1, path, res); path.removeLast(); } } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号