剑指 Offer II 081. 允许重复选择元素的组合(39. 组合总和)
题目:

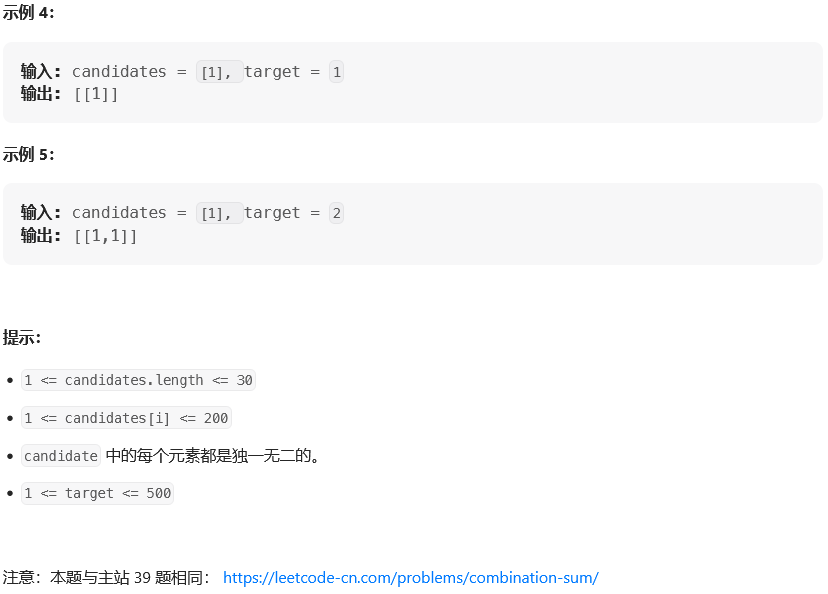
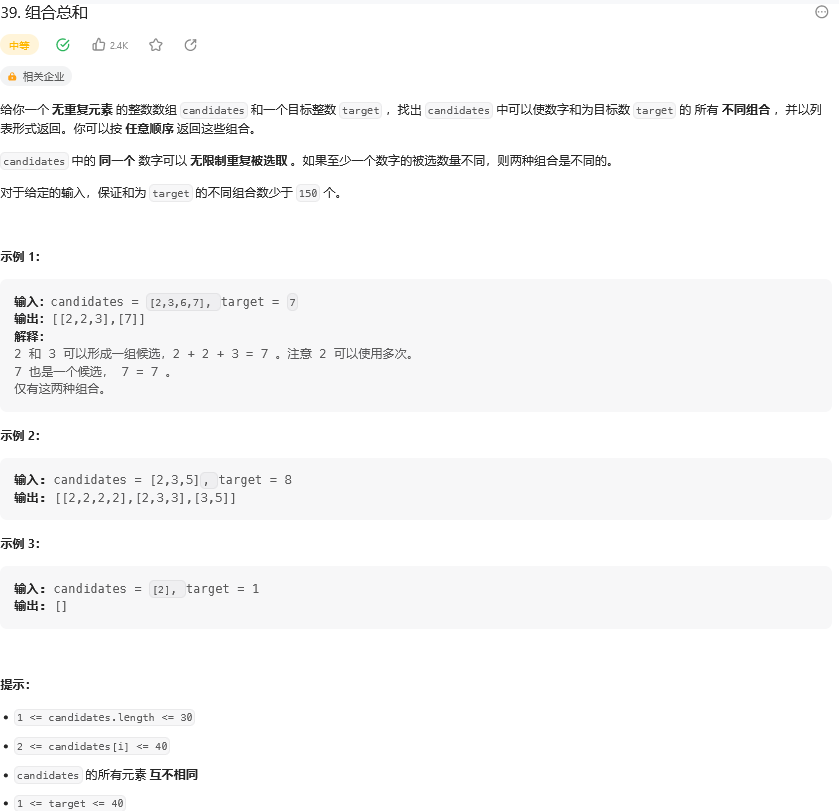
思路:
【1】回溯算法 + 剪枝的方式,一般而言这种最好是画出树形图,如candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7], target = 7 为例:
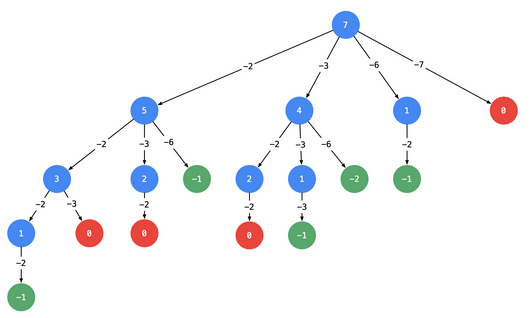
【2】其次,根据题目可知是组合(即 [2, 2, 3] 与 [2, 3, 2] 视为相同列表,这表示了我们要去重),去重的方式可以采用指针的方式,如[2, 3, 6, 7],当指针指向2的时候可以使用2, 3, 6, 7。当指针指向3时候只能使用3, 6, 7,指向6的时候只能使用6, 7,这样就不会达到会出现2, 3, 2这种情况,从而去重。
【3】此外,剪枝的话需要进行排序,由于无序的话其实最多只能判断该节点是否要纳入路径而不是将一堆不合适的全部去除。
代码展示:
回溯算法 + 剪枝的方式:
//时间2 ms击败77.56% //内存41.8 MB击败58.57% import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Deque; import java.util.List; public class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (len == 0) { return res; } Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>(); dfs(candidates, 0, len, target, path, res); return res; } /** * @param candidates 候选数组 * @param begin 搜索起点 * @param len 冗余变量,是 candidates 里的属性,可以不传 * @param target 每减去一个元素,目标值变小 * @param path 从根结点到叶子结点的路径,是一个栈 * @param res 结果集列表 */ private void dfs(int[] candidates, int begin, int len, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) { // target 为负数和 0 的时候不再产生新的孩子结点 if (target < 0) { return; } if (target == 0) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } // 重点理解这里从 begin 开始搜索的语意 for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) { path.addLast(candidates[i]); // 注意:由于每一个元素可以重复使用,下一轮搜索的起点依然是 i,这里非常容易弄错 dfs(candidates, i, len, target - candidates[i], path, res); // 状态重置 path.removeLast(); } } } //剪枝优化 //时间2 ms击败96.66% //内存41.9 MB击败49.83% import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Deque; import java.util.List; public class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (len == 0) { return res; } // 排序是剪枝的前提 Arrays.sort(candidates); Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>(); dfs(candidates, 0, len, target, path, res); return res; } private void dfs(int[] candidates, int begin, int len, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) { // 由于进入更深层的时候,小于 0 的部分被剪枝,因此递归终止条件值只判断等于 0 的情况 if (target == 0) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) { // 重点理解这里剪枝,前提是候选数组已经有序, if (target - candidates[i] < 0) { break; } path.addLast(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, i, len, target - candidates[i], path, res); path.removeLast(); } } }

