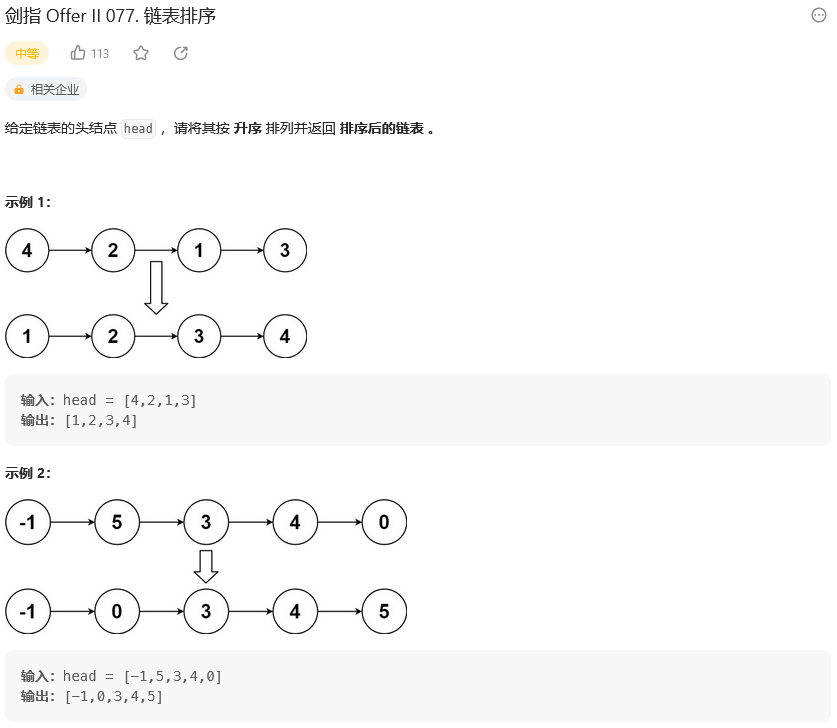
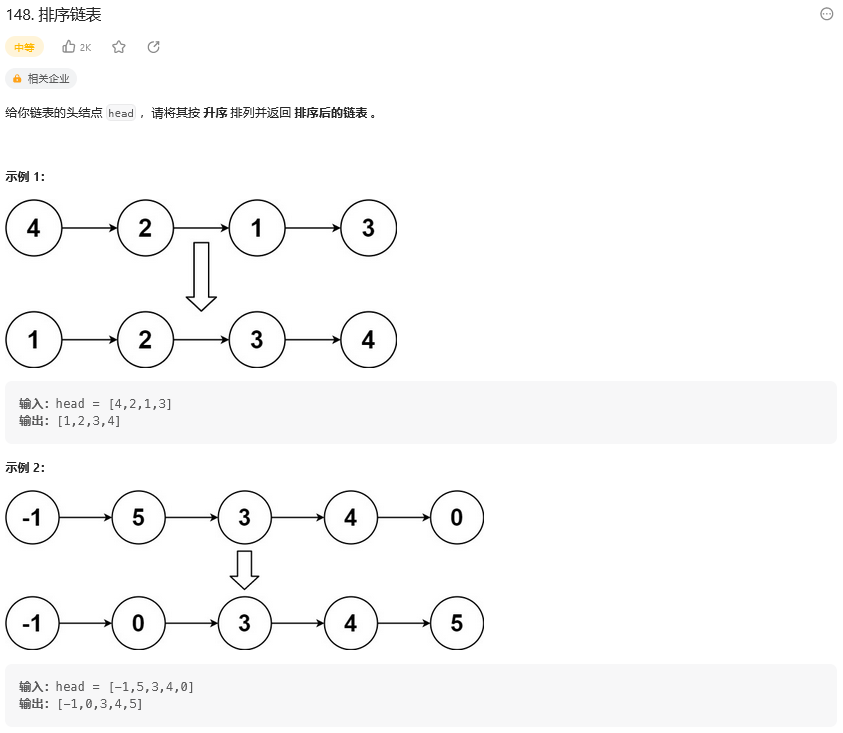
剑指 Offer II 077. 链表排序(148. 排序链表)
题目:


思路:
【0】首先题目限制了O(nlogn)的时间复杂度,这个大家应该都会有印象,毕竟大部分排序算法都是这个复杂度,其次空间复杂度为O(1),也就是说,最多借助常量值的辅助变量。而归并排序基于分治算法。最容易想到的实现方式是自顶向下的递归实现,考虑到递归调用的栈空间,自顶向下归并排序的空间复杂度是 O(logn)。如果要达到 O(1) 的空间复杂度,则需要使用自底向上的实现方式。
【1】自顶向下归并排序的方式
【2】自底向上归并排序的方式
代码展示:
自顶向下归并排序的方式:
//时间7 ms击败45.80% //内存49.3 MB击败29.37% //时间复杂度:O(nlogn),其中 n 是链表的长度。 //空间复杂度:O(logn),其中 n 是链表的长度。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间。 /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { return sortList(head, null); } public ListNode sortList(ListNode head, ListNode tail) { if (head == null) { return head; } if (head.next == tail) { head.next = null; return head; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != tail) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; if (fast != tail) { fast = fast.next; } } ListNode mid = slow; ListNode list1 = sortList(head, mid); ListNode list2 = sortList(mid, tail); ListNode sorted = merge(list1, list2); return sorted; } public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } }
自底向上归并排序的方式:
//时间11 ms击败24.72% //内存49 MB击败60.54% //时间复杂度:O(nlogn),其中 n 是链表的长度。 //空间复杂度:O(1)。 class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null) { return head; } int length = 0; ListNode node = head; while (node != null) { length++; node = node.next; } ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head); for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1) { ListNode prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next; while (curr != null) { ListNode head1 = curr; for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr.next != null; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode head2 = curr.next; curr.next = null; curr = head2; for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next != null; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode next = null; if (curr != null) { next = curr.next; curr.next = null; } ListNode merged = merge(head1, head2); prev.next = merged; while (prev.next != null) { prev = prev.next; } curr = next; } } return dummyHead.next; } public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号