剑指 Offer II 049. 从根节点到叶节点的路径数字之和(129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和)
题目:
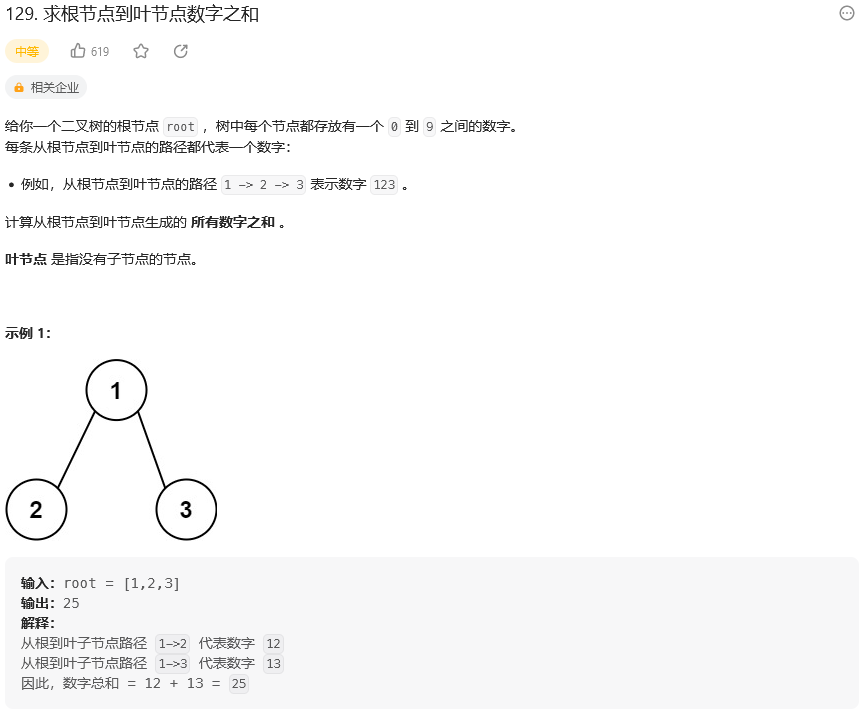
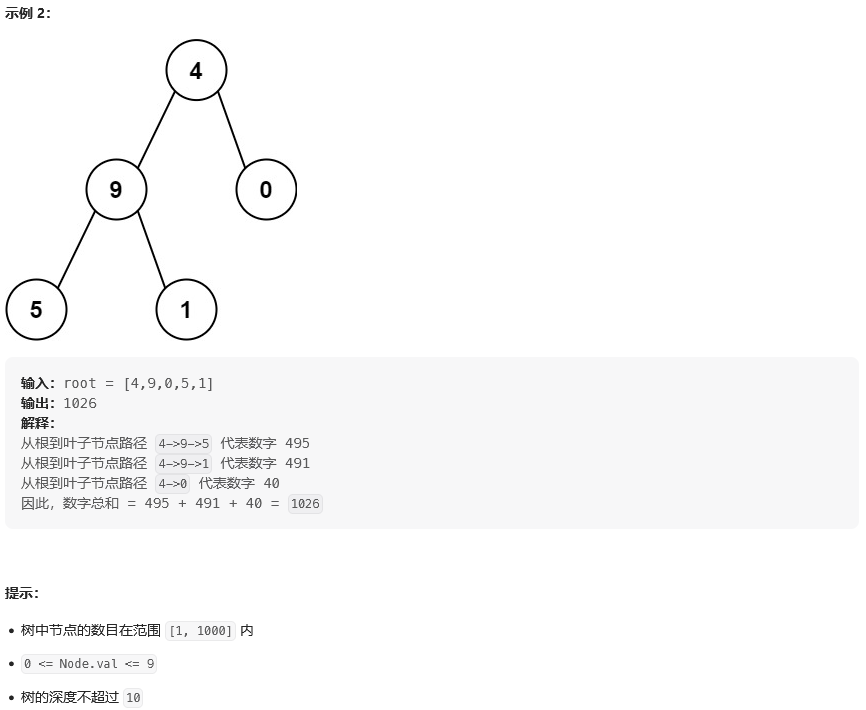

思路:
【1】这种情况其实递归的写法会比循环遍历的写法要好写的多,如每下一层就会把,之前的数值乘10,但同样要记住,当左右节点都为空的时候其实就不应该再往下叠一层。
代码展示:
//时间0 ms击败100% //内存39 MB击败67.82% /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val; return sumNumbersDfs(root,0); } public int sumNumbersDfs(TreeNode root,int sum) { sum = sum*10 + root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return sum; int count = 0; if (root.left != null) count += sumNumbersDfs(root.left,sum); if (root.right != null) count += sumNumbersDfs(root.right,sum); return count; } } //时间0 ms击败100% //内存38.9 MB击败84.73% //时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。对每个节点访问一次。 //空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点个数。 //空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间,递归栈的深度等于二叉树的高度, //最坏情况下,二叉树的高度等于节点个数,空间复杂度为 O(n)。 class Solution { public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) { return dfs(root, 0); } public int dfs(TreeNode root, int prevSum) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int sum = prevSum * 10 + root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { return sum; } else { return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum); } } }

