剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制(138. 复制带随机指针的链表)
题目:
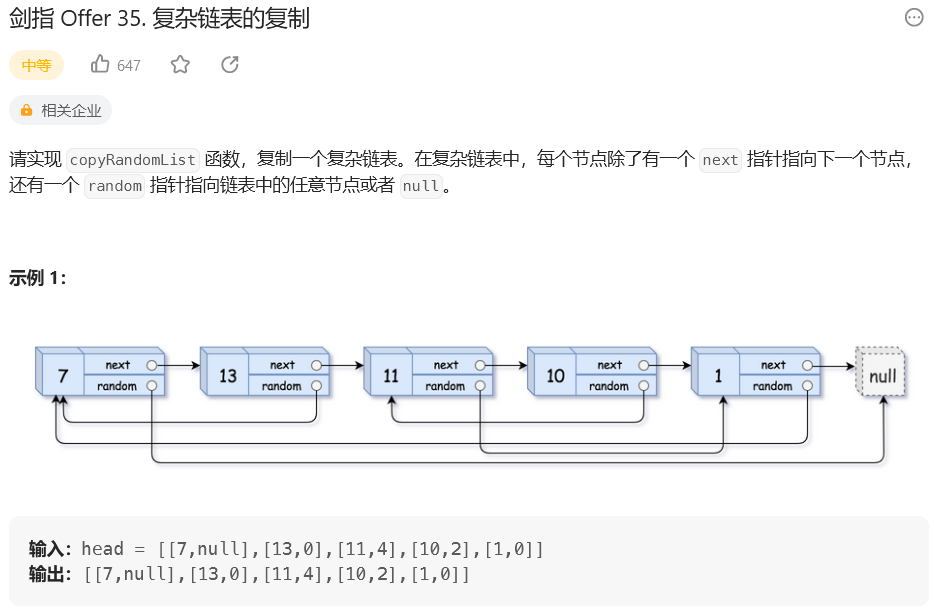
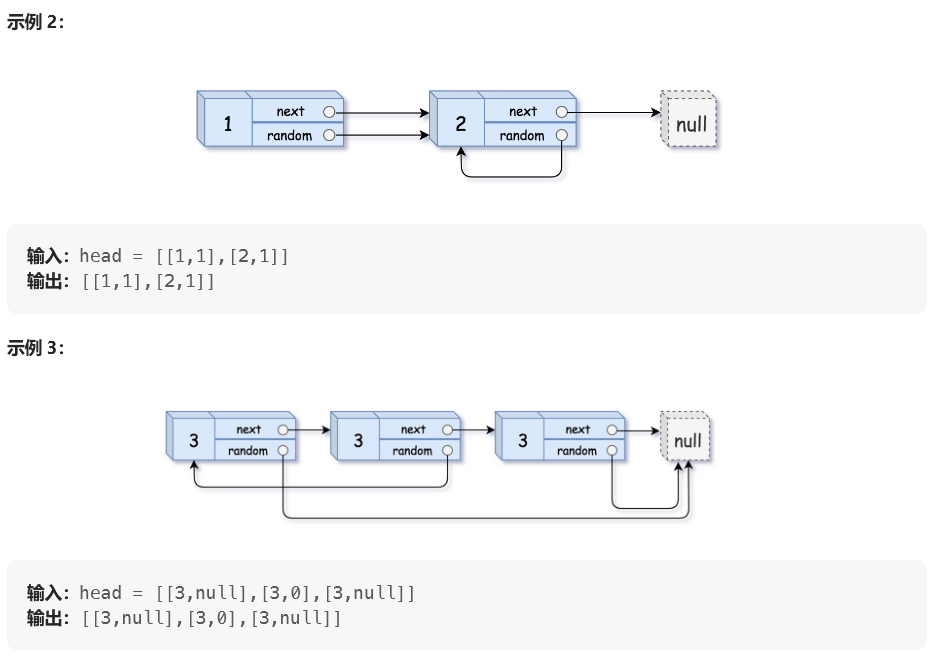
思路:
【1】回溯 + 哈希表(更简洁的说法应该是递归+哈希表),本质上是采用辅助空间来作为记录节点,用原本链表上的节点在哈希表中作为key指向value值的复制出来的链表的节点,这种相对简单易懂。
【2】迭代 + 节点拆分(这种的话可以参考如何将回溯变为双循环,然后其实又是利用一个循环在原本链表上增加节点来替代哈希表)
分为三步: 第一步:第一次循环在原本链表上复制出对应的复制结点,如A`(这种就是复制节点),A为原本节点 A->A`->B->B`->C->C` 第二步:第二次循环,填充复制结点的随机指向(这里因为原本的随机指向一下个就是复制的随机指向了) 第三步断开与原本之间的连接,抽出复制节点。
代码展示:
迭代+节点拆分的形式:
//时间0 ms击败100% //内存41.5 MB击败5.24% //时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。我们只需要遍历该链表三次。 //空间复杂度:O(1)。注意返回值不计入空间复杂度。 /*// Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) { Node nodeNew = new Node(node.val); nodeNew.next = node.next; node.next = nodeNew; } for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) { Node nodeNew = node.next; nodeNew.random = (node.random != null) ? node.random.next : null; } Node headNew = head.next; for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next) { Node nodeNew = node.next; node.next = node.next.next; nodeNew.next = (nodeNew.next != null) ? nodeNew.next.next : null; } return headNew; } }
回溯+哈希表的处理方式:
//时间0 ms击败100% //内存41.2 MB击败38.5% //时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。对于每个节点,我们至多访问其「后继节点」和「随机指针指向的节点」各一次,均摊每个点至多被访问两次。 //空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。为哈希表的空间开销。 /* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { Map<Node, Node> cachedNode = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } if (!cachedNode.containsKey(head)) { Node headNew = new Node(head.val); cachedNode.put(head, headNew); headNew.next = copyRandomList(head.next); headNew.random = copyRandomList(head.random); } return cachedNode.get(head); } }
利用双循环替代回溯:
//时间0 ms击败100% //内存41.3 MB击败21.57% //采用双循环来替代回溯,因为回溯本质上是利用的递归来进行处理,那么其次也是借助了辅助空间。 //然后采用第一次遍历仅简单的复制出链表的节点,第二次循环再填充进随机的指向即可。 //相对于回溯方式更加直观,空间也会相对节省,但是遍历的数量会有所上升,但时间复杂度不变因为O(N+N)其实还是O(N),空间复杂度也不变,但是调用栈的空间节省了,但是代码相对而言没有回溯的简洁。 /*// Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { Map<Node, Node> cachedNode = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } //第一次循环仅构建链表 Node temp = head; Node newList = null; while (temp != null){ Node headNew = new Node(temp.val); cachedNode.put(temp, headNew); if (newList == null){ newList = headNew; }else { newList.next = headNew; newList = newList.next; } temp = temp.next; } //第二次循环才开始填充随机指向 temp = head; newList = cachedNode.get(temp); while (temp != null){ if (temp.random != null) { newList.random = cachedNode.get(temp.random); } temp = temp.next; newList = newList.next; } return cachedNode.get(head); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号