微服务组件--注册中心Spring Cloud Eureka分析
Eureka核心功能点
【1】服务注册(register):Eureka Client会通过发送REST请求的方式向Eureka Server注册自己的服务,提供自身的元数据,比如ip地址、端口、运行状况指标的url、主页地址等信息。Eureka Server接收到注册请求后,就会把这些元数据信息存储在一个双层的Map中。
【2】服务续约(renew):在服务注册后,Eureka Client会维护一个心跳来持续通知Eureka Server,说明服务一直处于可用状态,防止被剔除。Eureka Client在默认的情况下会每隔30秒(eureka.instance.leaseRenewalIntervalInSeconds)发送一次心跳来进行服务续约。
【3】服务同步(replicate):Eureka Server之间会互相进行注册,构建Eureka Server集群,不同Eureka Server之间会进行服务同步,用来保证服务信息的一致性。
【4】获取服务(get registry):服务消费者(Eureka Client)在启动的时候,会发送一个REST请求给Eureka Server,获取上面注册的服务清单,并且缓存在Eureka Client本地,默认缓存30秒(eureka.client.registryFetchIntervalSeconds)。同时,为了性能考虑,EurekaServer也会维护一份只读的服务清单缓存,该缓存每隔30秒更新一次。
【5】服务调用:服务消费者在获取到服务清单后,就可以根据清单中的服务列表信息,查找到其他服务的地址,从而进行远程调用。Eureka有Region和Zone的概念,一个Region可以包含多个Zone,在进行服务调用时,优先访问处于同一个Zone中的服务提供者。
【6】服务下线(cancel):当Eureka Client需要关闭或重启时,就不希望在这个时间段内再有请求进来,所以,就需要提前先发送REST请求给Eureka Server,告诉Eureka Server自己要下线了,Eureka Server在收到请求后,就会把该服务状态置为下线(DOWN),并把该下线事件传播出去。
【7】服务剔除(evict):有时候,服务实例可能会因为网络故障等原因导致不能提供服务,而此时该实例也没有发送请求给Eureka Server来进行服务下线,所以,还需要有服务剔除的机制。Eureka Server在启动的时候会创建一个定时任务,每隔一段时间(默认60秒),从当前服务清单中把超时没有续约(默认90秒,eureka.instance.leaseExpirationDurationInSeconds)的服务剔除。180s被剔除
【8】自我保护:既然Eureka Server会定时剔除超时没有续约的服务,那就有可能出现一种场景,网络一段时间内发生了异常,所有的服务都没能够进行续约,Eureka Server就把所有的服务都剔除了,这样显然不太合理。所以,就有了自我保护机制,当短时间内,统计续约失败的比例,如果达到一定阈值,则会触发自我保护的机制,在该机制下,Eureka Server不会剔除任何的微服务,等到正常后,再退出自我保护机制。自我保护开关(eureka.server.enable-self-preservation: false)
常见的问题
【1】当eureka服务实例有注册或下线或有实例发生故障,内存注册表虽然会及时更新数据,但是客户端不一定能及时感知到,可能会过30秒才能感知到,因为客户端拉取注册表实例这里面有一个多级缓存机制。【实现的是最终一致性】
【2】还有服务剔除的不是默认90秒没心跳的实例,剔除的是180秒没心跳的实例(eureka的bug导致,注解有说明是因为加了两次过期时间,但是很小的BUG所有不修复了【在Lease结构里说明】)
【3】分析eureka服务下线的情况
1)图示
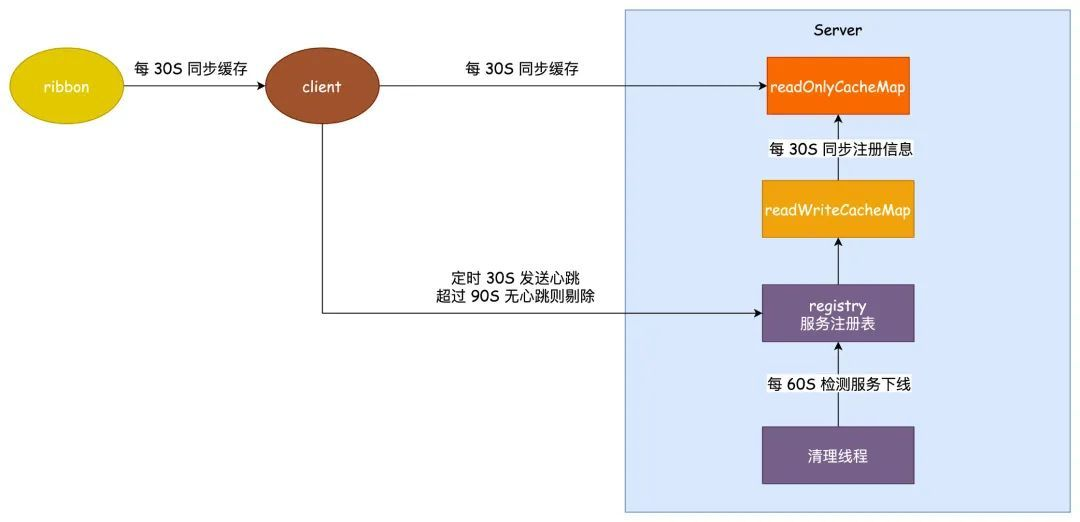
2)说明
1.客户端每个30s会发送心跳到服务端 2.ReadOnlyCacheMap和ReadWriteCacheMap每30s同步一次 3.客户端每隔30s同步一次ReadOnlyCacheMap 4.ribbon缓存每隔30s同步一次【有负载均衡的情况】 所以正常下线需要120s 而非正常下线,外加上服务剔除的180s+60s的定时任务,也就是360s【6min】 如果出现时间太长容易出现问题 1.修改 ribbon 同步缓存的时间为 3 秒:ribbon.ServerListRefreshInterval = 3000 2.修改客户端同步缓存时间为 3 秒 :eureka.client.registry-fetch-interval-seconds = 3 3.心跳间隔时间修改为 3 秒:eureka.instance.lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds = 3 4.超时剔除的时间改为 9 秒:eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds = 9 5.清理线程定时时间改为 5 秒执行一次:eureka.server.eviction-interval-timer-in-ms = 5000 6.同步到只读缓存的时间修改为 3 秒一次:eureka.server.response-cache-update-interval-ms = 3000 只读缓存其实是可以关闭的,通过修改参数eureka.server.use-read-only-response-cache = false可以做到 正常下线就是 3+3+3+3=12 秒,非正常下线再加 18+5 秒为 35 秒。 因为本质上服务剔除的是超时过期的,而lease可知过期时间实际上是两倍,也就是18s。考虑极端情况,18s刚好卡在定时任务的最后一刻,则是直接加上5s。 此外,这里的极端情况,也就是从某一次心跳之后开始不正常的。
源码精髓总结
【1】服务端多级缓存设计思想:
1)在拉取注册表的时候:
(1)首先从ReadOnlyCacheMap里查缓存的注册表。
(2)若没有,就找ReadWriteCacheMap里缓存的注册表。
(3)如果还没有,就从内存中获取实际的注册表数据。
2)在注册表发生变更的时候:
(1)会在内存中更新变更的注册表数据,同时过期掉ReadWriteCacheMap。
(2)此过程不会影响ReadOnlyCacheMap提供人家查询注册表。
(3)默认每30秒Eureka Server会将ReadWriteCacheMap更新到ReadOnlyCacheMap里
(4)默认每180秒Eureka Server会将ReadWriteCacheMap里是数据失效
(5)下次有服务拉取注册表,又会从内存中获取最新的数据了,同时填充 各级缓存
3)多级缓存机制的优点:
(1)尽可能保证了内存注册表数据不会出现频繁的读写冲突问题。
(2)并且进一步保证对Eureka Server的大量请求,都是快速从纯内存走,性能极高(可以稍微估计下对于一线互联网公司,内部上千个eureka client实例,每分钟对eureka大几千次的访问,一天就是上千万次的访问)
【2】TimedSupervisorTask定时任务的设计:
1)从整体上看,TimedSupervisorTask是固定间隔的周期性任务,一旦遇到超时就会将下一个周期的间隔时间调大,如果连续超时,那么每次间隔时间都会增大一倍,一直到达外部参数设定的上限为止,一旦新任务不再超时,间隔时间又会自动恢复为初始值,另外还有CAS来控制多线程同步。
【3】增量更新中哈希码检验的设计:
//里面的一致性哈希码,本质上就是校验数据 //如:服务器上全量块存的是【ABCDEFG】,此时它的哈希码便是全量块存的数据的哈希值,增量块存的是【FG】, //而我们客户端是【ABCD】,增量拉下来再合并,则为【ABCDFG】,得到的哈希值便会与全量哈希值不一致,代表了缺失一部分数据 //故检验不对就会全量拉取
【4】注册表的结构说明(这个仅是记录):
实例信息存放的map,这是个两层的ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String,Lease<InstanceInfo>>>,外层map的key是appName,也就是服务名,内层map的key是instanceId,也就是实例名 注册表map数据示例如下: { MICROSERVICE - PROVIDER - USER = { DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - user: 8002 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @2cd36af6, DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - user: 8001 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @600b7073 }, MICROSERVICE - PROVIDER - ORDER = { DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - order: 8002 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @2cd36af6, DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - order: 8001 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @600b7073 } }
Eureka服务端源码分析
【1】分析注解@EnableEurekaServer是如何开启eurekaServer服务注册功能
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.class) public @interface EnableEurekaServer {} //注释有说:这个注解是为了激活Eureka相关的配置类EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类 //但是却是导入了EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration类
【2】分析导入的EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration类
//注释说明:采用Marker的bean去激活EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类 //但实际上并没有做什么,直接去EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类看他是怎么处理的 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration { @Bean public Marker eurekaServerMarkerBean() { return new Marker(); } class Marker {} }
【3】分析EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class) //当发现了这里,便明白了,这个配置类要生效是必须要有Marker类的存在 //而且EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类本身是基于SpringBoot的SPI机制,自动导入的 @ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class,InstanceRegistryProperties.class }) @PropertySource("classpath:/eureka/server.properties") public class EurekaServerAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {...}
【4】分析EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类中的方法
//初始化集群节点集合 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes(PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, ServerCodecs serverCodecs, ReplicationClientAdditionalFilters replicationClientAdditionalFilters) { return new RefreshablePeerEurekaNodes(registry, this.eurekaServerConfig, this.eurekaClientConfig, serverCodecs, this.applicationInfoManager, replicationClientAdditionalFilters); } //初始化EurekaServer的相关配置 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) protected static class EurekaServerConfigBeanConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig(EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) { EurekaServerConfigBean server = new EurekaServerConfigBean(); if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) { // Set a sensible default if we are supposed to replicate server.setRegistrySyncRetries(5); } return server; } } //初始化一些接口,用于获取EurekaServer的信息 @Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "eureka.dashboard", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public EurekaController eurekaController() { return new EurekaController(this.applicationInfoManager); } //基于EurekaServer的配置,注册表,集群节点集合,以及服务实例初始化EurekaServer上下文 @Bean public EurekaServerContext eurekaServerContext(ServerCodecs serverCodecs, PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes) { return new DefaultEurekaServerContext(this.eurekaServerConfig, serverCodecs, registry, peerEurekaNodes, this.applicationInfoManager); } //初始化经过包装的Eureka原生启动类 @Bean public EurekaServerBootstrap eurekaServerBootstrap(PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, EurekaServerContext serverContext) { return new EurekaServerBootstrap(this.applicationInfoManager, this.eurekaClientConfig, this.eurekaServerConfig, registry, serverContext); } //初始化集群注册表 @Bean public PeerAwareInstanceRegistry peerAwareInstanceRegistry(ServerCodecs serverCodecs) { this.eurekaClient.getApplications(); // force initialization return new InstanceRegistry(this.eurekaServerConfig, this.eurekaClientConfig, serverCodecs, this.eurekaClient, this.instanceRegistryProperties.getExpectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews(), this.instanceRegistryProperties.getDefaultOpenForTrafficCount()); }
【5】分析EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类导入的EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration类
//因为实现了SmartLifecycle接口,会在初始化完成后根据isAutoStartup()的返回值确认是否调用start()方法 //故查看EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration类#start()方法 @Override public void start() { new Thread(() -> { try { //初始化EurekaServer,同时启动Eureka Server eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext); log.info("Started Eureka Server"); //发送Eureka注册事件 publish(new EurekaRegistryAvailableEvent(getEurekaServerConfig())); // 设置启动的状态为true EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.running = true; // 发送Eureka Start事件,其他还有各种事件,我们可以监听这种时间,然后做一些特定的业务需求 publish(new EurekaServerStartedEvent(getEurekaServerConfig())); } catch (Exception ex) {...} }).start(); } //初始化EurekaServer的运行环境和上下文 //EurekaServerBootstrap类#contextInitialized方法 public void contextInitialized(ServletContext context) { try { //初始化运行环境 initEurekaEnvironment(); //初始化上下文 initEurekaServerContext(); context.setAttribute(EurekaServerContext.class.getName(), this.serverContext); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RuntimeException(...); } }
【6】分析初始化上下文initEurekaServerContext方法做了什么【进行了服务同步,服务剔除的启动】
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception { // For backward compatibility JsonXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(), XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH); XmlXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(), XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH); if (isAws(this.applicationInfoManager.getInfo())) { this.awsBinder = new AwsBinderDelegate(this.eurekaServerConfig, this.eurekaClientConfig, this.registry, this.applicationInfoManager); this.awsBinder.start(); } //初始化eureka server上下文 EurekaServerContextHolder.initialize(this.serverContext); log.info("Initialized server context"); // Copy registry from neighboring eureka node // 从相邻的eureka节点复制注册表 int registryCount = this.registry.syncUp(); // 默认每30秒发送心跳,1分钟就是2次 // 修改eureka状态为up // 同时,这里面会开启一个定时任务,用于清理60秒没有心跳的客户端。自动下线 // 根据属性值可知是PeerAwareInstanceRegistry类 this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount); // Register all monitoring statistics. EurekaMonitors.registerAllStats(); } //返回了一个EurekaServerContextHolder【其实就是将serverContext设置进入到里面当做属性值】 public static synchronized void initialize(EurekaServerContext serverContext) { holder = new EurekaServerContextHolder(serverContext); }
【7】服务同步的逻辑
//进行服务同步 @Override public int syncUp() { // Copy entire entry from neighboring DS node int count = 0; //从配置文件中拿到注册的节点 for (int i = 0; ((i < serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetries()) && (count == 0)); i++) { if (i > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetryWaitMs()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { break; } } //调用节点的http请求获取所有的服务实例 Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications(); for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) { for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) { try { if (isRegisterable(instance)) { //将其他节点的实例注册到本节点 register(instance, instance.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs(), true); count++; } } catch (Throwable t) {...} } } } return count; }
【8】服务剔除的逻辑
//进行服务剔除 @Override public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) { // Renewals happen every 30 seconds and for a minute it should be a factor of 2. // 计算每分钟最大续约数 this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count; // 每分钟最小续约数 updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); this.startupTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (count > 0) { this.peerInstancesTransferEmptyOnStartup = false; } DataCenterInfo.Name selfName = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getDataCenterInfo().getName(); boolean isAws = Name.Amazon == selfName; if (isAws && serverConfig.shouldPrimeAwsReplicaConnections()) { primeAwsReplicas(applicationInfoManager); } logger.info("Changing status to UP"); // 设置实例的状态为UP applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP); // 开启定时任务,默认60秒执行一次,用于清理60秒之内没有续约的实例 super.postInit(); } protected void updateRenewsPerMinThreshold() { this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews * (60.0 / serverConfig.getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds()) * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold()); } protected void postInit() { renewsLastMin.start(); if (evictionTaskRef.get() != null) { evictionTaskRef.get().cancel(); } evictionTaskRef.set(new EvictionTask()); //服务剔除任务 //evictionIntervalTimerInMs = 60 * 1000,即每60s执行一次,且延迟60s evictionTimer.schedule(evictionTaskRef.get(), serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs(), serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs()); } //EvictionTask类#run方法 @Override public void run() { try { long compensationTimeMs = getCompensationTimeMs(); logger.info("Running the evict task with compensationTime {}ms", compensationTimeMs); evict(compensationTimeMs); } catch (Throwable e) {...} } //剔除逻辑 public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) { logger.debug("Running the evict task"); if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) { logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled."); return; } // We collect first all expired items, to evict them in random order. For large eviction sets, // if we do not that, we might wipe out whole apps before self preservation kicks in. By randomizing it, // the impact should be evenly distributed across all applications. List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>(); for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) { Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue(); if (leaseMap != null) { for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) { Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue(); if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) { expiredLeases.add(lease); } } } } // To compensate for GC pauses or drifting local time, we need to use current registry size as a base for // triggering self-preservation. Without that we would wipe out full registry. int registrySize = (int) getLocalRegistrySize(); int registrySizeThreshold = (int) (registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold()); int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold; int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); if (toEvict > 0) { logger.info("Evicting {} items (expired={}, evictionLimit={})", toEvict, expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); for (int i = 0; i < toEvict; i++) { // Pick a random item (Knuth shuffle algorithm) int next = i + random.nextInt(expiredLeases.size() - i); Collections.swap(expiredLeases, i, next); Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = expiredLeases.get(i); String appName = lease.getHolder().getAppName(); String id = lease.getHolder().getId(); EXPIRED.increment(); logger.warn("DS: Registry: expired lease for {}/{}", appName, id); internalCancel(appName, id, false); } } }
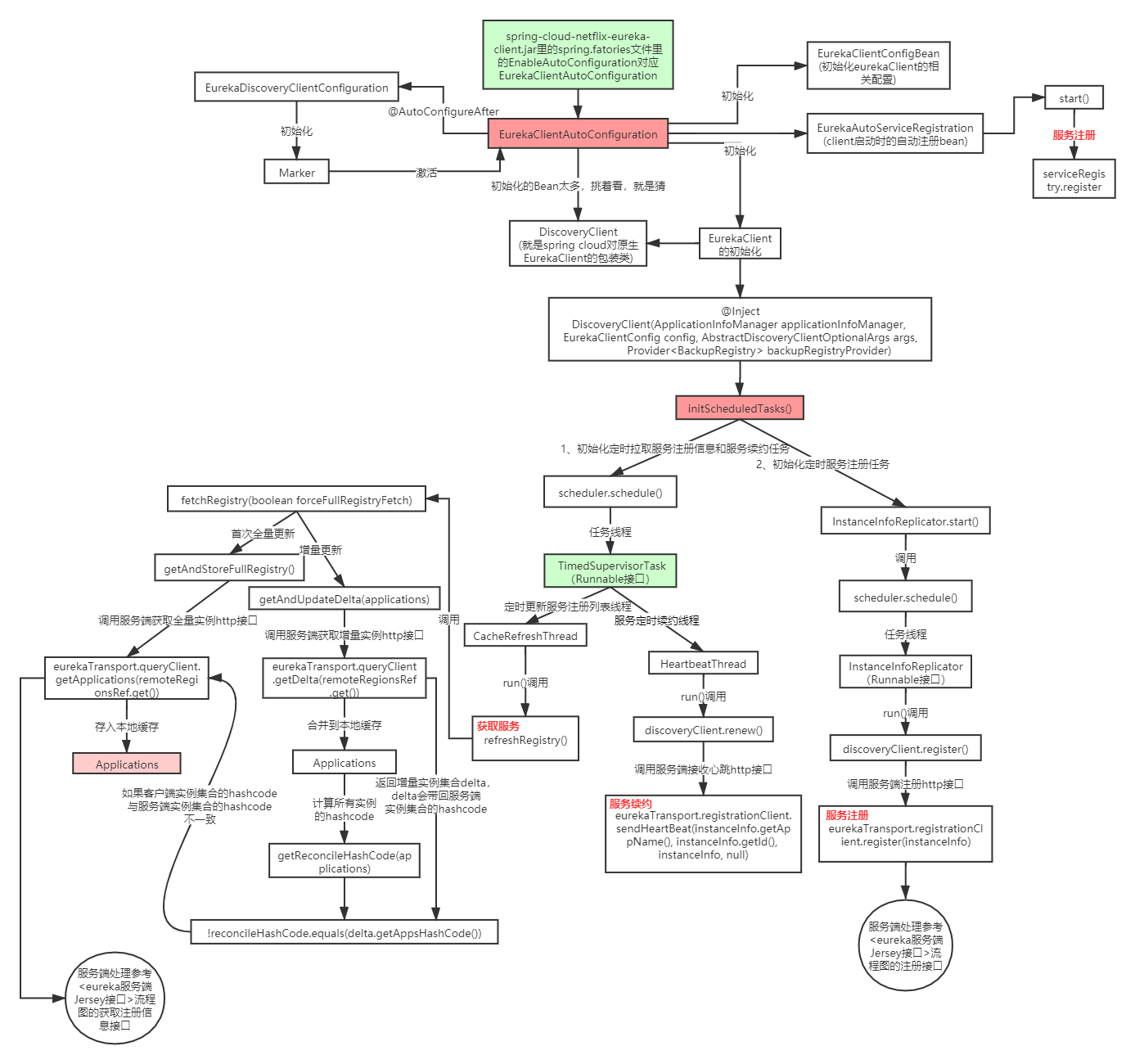
Eureka客户端源码分析
【1】根据SpringBoot自动装配先找出所有会调用的类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.eureka.RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.reactive.EurekaReactiveDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerEurekaAutoConfiguration org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
【2】找到对应的自动装配类EurekaClientAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @EnableConfigurationProperties @ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class) @Import(DiscoveryClientOptionalArgsConfiguration.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) @ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled @AutoConfigureBefore({ NoopDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class, CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class, ServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration.class }) @AutoConfigureAfter(name = { "org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshAutoConfiguration", "org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration", "org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration" }) public class EurekaClientAutoConfiguration { //初始化EurekaClient的相关配置 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClientConfig.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public EurekaClientConfigBean eurekaClientConfigBean(ConfigurableEnvironment env) { EurekaClientConfigBean client = new EurekaClientConfigBean(); if ("bootstrap".equals(this.env.getProperty("spring.config.name"))) { // We don't register during bootstrap by default, but there will be another // chance later. client.setRegisterWithEureka(false); } return client; } //Client启动时的自动注册Bean @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public EurekaAutoServiceRegistration eurekaAutoServiceRegistration( ApplicationContext context, EurekaServiceRegistry registry, EurekaRegistration registration) { return new EurekaAutoServiceRegistration(context, registry, registration); } //EurekaClient配置类 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnMissingRefreshScope protected static class EurekaClientConfiguration { @Autowired private ApplicationContext context; @Autowired private AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs<?> optionalArgs; @Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown") @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClient.class,search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public EurekaClient eurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager manager, EurekaClientConfig config) { return new CloudEurekaClient(manager, config, this.optionalArgs, this.context); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ApplicationInfoManager.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public ApplicationInfoManager eurekaApplicationInfoManager(EurekaInstanceConfig config) { InstanceInfo instanceInfo = new InstanceInfoFactory().create(config); return new ApplicationInfoManager(config, instanceInfo); } @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public EurekaRegistration eurekaRegistration(EurekaClient eurekaClient, CloudEurekaInstanceConfig instanceConfig, ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, @Autowired( required = false) ObjectProvider<HealthCheckHandler> healthCheckHandler) { return EurekaRegistration.builder(instanceConfig).with(applicationInfoManager) .with(eurekaClient).with(healthCheckHandler).build(); } } .... }
【2.1】分析注解@AutoConfigureAfter导入的EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration类做了什么
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @EnableConfigurationProperties @ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) @ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled @ConditionalOnBlockingDiscoveryEnabled public class EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration { //基于EurekaClientAutoConfiguration的启动标志 @Deprecated @Bean public Marker eurekaDiscoverClientMarker() { return new Marker(); } //将EurekaClient包装成EurekaDiscoveryClient @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public EurekaDiscoveryClient discoveryClient(EurekaClient client, EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) { return new EurekaDiscoveryClient(client, clientConfig); } //心跳检测的处理配置 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.healthcheck.enabled",matchIfMissing = false) protected static class EurekaHealthCheckHandlerConfiguration { @Autowired(required = false) private StatusAggregator statusAggregator = new SimpleStatusAggregator(); @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(HealthCheckHandler.class) public EurekaHealthCheckHandler eurekaHealthCheckHandler() { return new EurekaHealthCheckHandler(this.statusAggregator); } } @Deprecated class Marker { } //定义了Client配置重刷的监听器 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass(RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent.class) protected static class EurekaClientConfigurationRefresher implements ApplicationListener<RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent> { .... } } //看得出来包装也只是将配置和客户端放在了一起 public EurekaDiscoveryClient(EurekaClient eurekaClient, EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) { this.clientConfig = clientConfig; this.eurekaClient = eurekaClient; }
【3】分析EurekaClient的相关配置EurekaClientConfigBean类
//仅列举了部分 @ConfigurationProperties(EurekaClientConfigBean.PREFIX) public class EurekaClientConfigBean implements EurekaClientConfig, Ordered { //客户端配置前缀 public static final String PREFIX = "eureka.client"; //public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "/eureka"; //默认的注册地址 public static final String DEFAULT_URL = "http://localhost:8761" + DEFAULT_PREFIX + "/"; //默认域 public static final String DEFAULT_ZONE = "defaultZone"; private static final int MINUTES = 60; //多长时间从注册中心服务端拉取一次服务信息,单位秒;这个就是主动拉取注册中心上所有服务的实例信息 private int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = 30; //多长时间复制实例变化到eureka服务端,单位秒;这个配置是复制实例信息到注册中心 private int instanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds = 30; //实例初始化复制信息到eureka服务端的间隔时间,所以可以看到,其实实例的初始化阶段不是立即复制实例信息到注册中心的,单位秒 private int initialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds = 40; //eureka服务端的变化,多长时间,客户端会获取一次eureka服务的信息 private int eurekaServiceUrlPollIntervalSeconds = 5 * MINUTES; //eureka server的代理端口 private String proxyPort; //eureka server的代理host name private String proxyHost; //账号 private String proxyUserName; //密码 private String proxyPassword; //从server读取所需的超时时间 private int eurekaServerReadTimeoutSeconds = 8; //连接server的超时时间 private int eurekaServerConnectTimeoutSeconds = 5; //被允许连接到所有server host的总连接数 private int eurekaServerTotalConnections = 200; // 被允许连接到每一个server host的总连接数 private int eurekaServerTotalConnectionsPerHost = 50; //连接到server的http连接的空闲超时时间,超时会被清理掉 private int eurekaConnectionIdleTimeoutSeconds = 30; //heartbeatExecutor 心跳的线程数 private int heartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize = 2; //客户端初始化阶段强制注册,默认关闭 private boolean shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit = false; ... }
【4】分析EurekaClientConfiguration配置类里面生成的EurekaClient的Bean
//CloudEurekaClient类【继承DiscoveryClient类】#构造方法 public CloudEurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs<?> args, ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) { super(applicationInfoManager, config, args); this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager; this.publisher = publisher; this.eurekaTransportField = ReflectionUtils.findField(DiscoveryClient.class, "eurekaTransport"); ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.eurekaTransportField); } //DiscoveryClient类【继承EurekaClient(原生的EurekaClient)】#构造方法 public DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, final EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args) { this(applicationInfoManager, config, args, ResolverUtils::randomize); } public DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, final EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, EndpointRandomizer randomizer) { //主要是这个this指向,毕竟里面的都是方法传参 this(applicationInfoManager, config, args, new Provider<BackupRegistry>() { private volatile BackupRegistry backupRegistryInstance; @Override public synchronized BackupRegistry get() { if (backupRegistryInstance == null) { String backupRegistryClassName = config.getBackupRegistryImpl(); if (null != backupRegistryClassName) { try { backupRegistryInstance = (BackupRegistry) Class.forName(backupRegistryClassName).newInstance(); logger.info("Enabled backup registry of type {}", backupRegistryInstance.getClass()); } catch (InstantiationException e) {..} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {..} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {...} } if (backupRegistryInstance == null) { logger.warn("Using default backup registry implementation which does not do anything."); backupRegistryInstance = new NotImplementedRegistryImpl(); } } return backupRegistryInstance; } }, randomizer); }
【5】分析DiscoveryClient的构造方法
@Inject DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider, EndpointRandomizer endpointRandomizer) { if (args != null) { this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = args.healthCheckHandlerProvider; this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = args.healthCheckCallbackProvider; this.eventListeners.addAll(args.getEventListeners()); this.preRegistrationHandler = args.preRegistrationHandler; } else { this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = null; this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = null; this.preRegistrationHandler = null; } this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager; InstanceInfo myInfo = applicationInfoManager.getInfo(); clientConfig = config; staticClientConfig = clientConfig; transportConfig = config.getTransportConfig(); instanceInfo = myInfo; if (myInfo != null) { appPathIdentifier = instanceInfo.getAppName() + "/" + instanceInfo.getId(); } else {...} this.backupRegistryProvider = backupRegistryProvider; this.endpointRandomizer = endpointRandomizer; this.urlRandomizer = new EndpointUtils.InstanceInfoBasedUrlRandomizer(instanceInfo); localRegionApps.set(new Applications()); fetchRegistryGeneration = new AtomicLong(0); remoteRegionsToFetch = new AtomicReference<String>(clientConfig.fetchRegistryForRemoteRegions()); remoteRegionsRef = new AtomicReference<>(remoteRegionsToFetch.get() == null ? null : remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(",")); if (config.shouldFetchRegistry()) { this.registryStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRY_PREFIX + "lastUpdateSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L}); } else { this.registryStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC; } if (config.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) { this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRATION_PREFIX + "lastHeartbeatSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L}); } else { this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC; } //从这里开始初始化Eureka Client if (!config.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && !config.shouldFetchRegistry()) { logger.info("Client configured to neither register nor query for data."); scheduler = null; heartbeatExecutor = null; cacheRefreshExecutor = null; eurekaTransport = null; instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(config), clientConfig.getRegion()); // This is a bit of hack to allow for existing code using DiscoveryManager.getInstance() // to work with DI'd DiscoveryClient DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this); DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config); initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis(); logger.info("Discovery Client initialized at timestamp {} with initial instances count: {}", initTimestampMs, this.getApplications().size()); return; // no need to setup up an network tasks and we are done } try { // default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2, new ThreadFactoryBuilder() .setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d") .setDaemon(true) .build()); //心跳的线程池 heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), new ThreadFactoryBuilder() .setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d") .setDaemon(true) .build() ); // use direct handoff //缓存重刷的线程池 cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), new ThreadFactoryBuilder() .setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d") .setDaemon(true) .build() ); // use direct handoff eurekaTransport = new EurekaTransport(); scheduleServerEndpointTask(eurekaTransport, args); AzToRegionMapper azToRegionMapper; if (clientConfig.shouldUseDnsForFetchingServiceUrls()) { azToRegionMapper = new DNSBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig); } else { azToRegionMapper = new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig); } if (null != remoteRegionsToFetch.get()) { azToRegionMapper.setRegionsToFetch(remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(",")); } instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(azToRegionMapper, clientConfig.getRegion()); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize DiscoveryClient!", e); } if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry() && !fetchRegistry(false)) { fetchRegistryFromBackup(); } // call and execute the pre registration handler before all background tasks (inc registration) is started if (this.preRegistrationHandler != null) { this.preRegistrationHandler.beforeRegistration(); } if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && clientConfig.shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit()) { try { if (!register() ) { throw new IllegalStateException("Registration error at startup. Invalid server response."); } } catch (Throwable th) {...} } // finally, init the schedule tasks (e.g. cluster resolvers, heartbeat, instanceInfo replicator, fetch //最核心代码,初始化定时任务 initScheduledTasks(); try { Monitors.registerObject(this); } catch (Throwable e) {...} DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this); DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config); initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis(); }
【6】核心逻辑initScheduledTasks初始化定时任务,是做了什么
/** * Initializes all scheduled tasks. */ private void initScheduledTasks() { //获取服务注册列表信息 if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) { //服务注册列表更新的周期时间 //默认是30 int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds(); int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound(); //定时更新服务注册列表 //这里的延时任务明显是只调用一次,具体在分析他的任务的run方法 scheduler.schedule( new TimedSupervisorTask( "cacheRefresh", scheduler, cacheRefreshExecutor, registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS, expBackOffBound, new CacheRefreshThread() //该线程执行更新的具体逻辑 ), registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) { //服务续约的周期时间 int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs(); int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound(); //应用启动可见此日志,内容是:Starting heartbeat executor: renew interval is: 30 logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs); // Heartbeat timer // 服务定时续约 scheduler.schedule( new TimedSupervisorTask( "heartbeat", scheduler, heartbeatExecutor, renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS, expBackOffBound, new HeartbeatThread() //该线程执行续约的具体逻辑 ), renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //这个Runable中含有服务注册的逻辑 instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator( this, instanceInfo, clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(), 2); // burstSize statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() { @Override public String getId() { return "statusChangeListener"; } @Override public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) { if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() || InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) { // log at warn level if DOWN was involved logger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent); } else { logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent); } instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate(); } }; if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) { applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener); } //服务注册 instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds()); } else { logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration"); } }
【6.1】定时任务TimedSupervisorTask类的设计
//TimedSupervisorTask类#run方法 //这里存在一个设计的亮点 public class TimedSupervisorTask extends TimerTask { ... public TimedSupervisorTask(String name, ScheduledExecutorService scheduler, ThreadPoolExecutor executor, int timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int expBackOffBound, Runnable task) { this.scheduler = scheduler; this.executor = executor; this.timeoutMillis = timeUnit.toMillis(timeout); this.task = task; //可以看出任务还是需要根据传入来的 this.delay = new AtomicLong(timeoutMillis); this.maxDelay = timeoutMillis * expBackOffBound; // Initialize the counters and register. successCounter = Monitors.newCounter("success"); timeoutCounter = Monitors.newCounter("timeouts"); rejectedCounter = Monitors.newCounter("rejectedExecutions"); throwableCounter = Monitors.newCounter("throwables"); threadPoolLevelGauge = new LongGauge(MonitorConfig.builder("threadPoolUsed").build()); Monitors.registerObject(name, this); } @Override public void run() { Future<?> future = null; try { future = executor.submit(task); threadPoolLevelGauge.set((long) executor.getActiveCount()); //设置了超时时间 future.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // block until done or timeout //出现任务不超时的情况又会将延迟时间重置(这里主要是配合下面捕捉异常的超时翻倍情况) delay.set(timeoutMillis); threadPoolLevelGauge.set((long) executor.getActiveCount()); successCounter.increment(); } catch (TimeoutException e) { logger.warn("task supervisor timed out", e); //出现超时的记录 timeoutCounter.increment(); //将超时时间翻倍(在最大的任务时间内),主动延迟 long currentDelay = delay.get(); long newDelay = Math.min(maxDelay, currentDelay * 2); //设置为最新的值,考虑到多线程,所以用了CAS delay.compareAndSet(currentDelay, newDelay); } catch (RejectedExecutionException e) { //一旦线程池的阻塞队列中放满了待处理任务,触发了拒绝策略,就会将调度器停掉 if (executor.isShutdown() || scheduler.isShutdown()) { logger.warn("task supervisor shutting down, reject the task", e); } else { logger.warn("task supervisor rejected the task", e); } //被拒绝的次数 rejectedCounter.increment(); } catch (Throwable e) { if (executor.isShutdown() || scheduler.isShutdown()) { logger.warn("task supervisor shutting down, can't accept the task"); } else { logger.warn("task supervisor threw an exception", e); } throwableCounter.increment(); } finally { if (future != null) { //这里任务要么执行完毕,要么发生异常,都用cancel方法来清理任务; future.cancel(true); } //只要调度器没有停止,就再指定等待时间之后在执行一次同样的任务 //任务里面又塞入这个任务 if (!scheduler.isShutdown()) { //假设外部调用时传入的超时时间为30秒(构造方法的入参timeout),最大间隔时间为50秒(构造方法的入参expBackOffBound) //如果最近一次任务没有超时,那么就在30秒后开始新任务, //如果最近一次任务超时了,那么就在50秒后开始新任务(异常处理中有个乘以二的操作,乘以二后的60秒超过了最大间隔50秒) scheduler.schedule(this, delay.get(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } } }
【6.2】分析更新服务注册列表任务 CacheRefreshThread【获取服务逻辑】
//DiscoveryClient类的内置类 class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable { public void run() { refreshRegistry(); } } //DiscoveryClient类#refreshRegistry方法 @VisibleForTesting void refreshRegistry() { try { boolean isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries = isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries(); boolean remoteRegionsModified = false; // This makes sure that a dynamic change to remote regions to fetch is honored. String latestRemoteRegions = clientConfig.fetchRegistryForRemoteRegions(); //不做aws环境的配置这个if逻辑不会执行 if (null != latestRemoteRegions) { String currentRemoteRegions = remoteRegionsToFetch.get(); if (!latestRemoteRegions.equals(currentRemoteRegions)) { // Both remoteRegionsToFetch and AzToRegionMapper.regionsToFetch need to be in sync synchronized (instanceRegionChecker.getAzToRegionMapper()) { if (remoteRegionsToFetch.compareAndSet(currentRemoteRegions, latestRemoteRegions)) { String[] remoteRegions = latestRemoteRegions.split(","); remoteRegionsRef.set(remoteRegions); instanceRegionChecker.getAzToRegionMapper().setRegionsToFetch(remoteRegions); remoteRegionsModified = true; } else {....} } } else { // Just refresh mapping to reflect any DNS/Property change instanceRegionChecker.getAzToRegionMapper().refreshMapping(); } } //获取注册信息方法 boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified); if (success) { registrySize = localRegionApps.get().size(); lastSuccessfulRegistryFetchTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {...省略日志内容...} } catch (Throwable e) {...} } private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) { Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start(); try { // 如果增量被禁用,或者是第一次,那么获取所有应用程序 // 取出本地缓存之前获取的服务列表信息 Applications applications = getApplications(); //是否禁用增量更新 if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta() || (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress())) || forceFullRegistryFetch //是否第一次拉取 || (applications == null) || (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0) || (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta { //全量获取 getAndStoreFullRegistry(); } else { //增量获取 getAndUpdateDelta(applications); } //更新本地缓存 applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode()); logTotalInstances(); } catch (Throwable e) { return false; } finally { if (tracer != null) { tracer.stop(); } } // Notify about cache refresh before updating the instance remote status //将本地缓存更新的事件广播给所有已注册的监听器,注意该方法已被CloudEurekaClient类重写 onCacheRefreshed(); // Update remote status based on refreshed data held in the cache //检查刚刚更新的缓存中,有来自Eureka server的服务列表,其中包含了当前应用的状态, //当前实例的成员变量lastRemoteInstanceStatus,记录的是最后一次更新的当前应用状态, //上述两种状态在updateInstanceRemoteStatus方法中作比较 ,如果不一致,就更新lastRemoteInstanceStatus,并且广播对应的事件 updateInstanceRemoteStatus(); // registry was fetched successfully, so return true return true; } @Override public Applications getApplications() { return localRegionApps.get(); }
【6.2.1】分析全量更新
private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable { long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get(); Applications apps = null; //由于并没有配置特别关注的region信息,因此会调用eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications方法从服务端获取服务列表 EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null ? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get()) : eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get()); if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) { //返回对象就是服务列表 apps = httpResponse.getEntity(); } logger.info("The response status is {}", httpResponse.getStatusCode()); if (apps == null) {...} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) { //考虑到多线程同步,只有CAS成功的线程,才会把自己从Eureka server获取的数据来替换本地缓存 localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps)); } else {...} } //EurekaHttpClientDecorator类#getApplications方法 @Override public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplications(final String... regions) { //这里面涉及到配置是否重试 return execute(new RequestExecutor<Applications>() { @Override public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> execute(EurekaHttpClient delegate) { //调用AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient类 return delegate.getApplications(regions); } @Override public RequestType getRequestType() { return RequestType.GetApplications; } }); } @Override public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplications(String... regions) { //取增量数据的path是"apps/delta" return getApplicationsInternal("apps/", regions); } //具体的请求响应处理都在此方法中 private EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplicationsInternal(String urlPath, String[] regions) { ClientResponse response = null; String regionsParamValue = null; try { //jersey、resource这些关键词都预示着这是个restful请求 WebResource webResource = jerseyClient.resource(serviceUrl).path(urlPath); if (regions != null && regions.length > 0) { regionsParamValue = StringUtil.join(regions); webResource = webResource.queryParam("regions", regionsParamValue); } Builder requestBuilder = webResource.getRequestBuilder(); addExtraHeaders(requestBuilder); //发起网络请求,将响应封装成ClientResponse实例 response = requestBuilder.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_TYPE).get(ClientResponse.class); Applications applications = null; if (response.getStatus() == Status.OK.getStatusCode() && response.hasEntity()) { //取得全部应用信息 applications = response.getEntity(Applications.class); } return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatus(), Applications.class) .headers(headersOf(response)) .entity(applications) .build(); } finally { if (response != null) { response.close(); } } } //总结:获取全量数据,是通过jersey-client库的API向Eureka server发起restful请求http://localhost:8761/eureka/apps实现的,并将响应的服务列表数据放在一个成员变量中作为本地缓存
【6.2.2】分析增量更新
//分析增量更新 //里面的一致性哈希码,本质上就是校验数据 //如:服务器上全量块存的是【ABCDEFG】,此时它的哈希码便是全量块存的数据的哈希值,增量块存的是【FG】, //而我们客户端是【ABCD】,增量拉下来再合并,则为【ABCDFG】,得到的哈希值便会与全量哈希值不一致,代表了缺失一部分数据 //故检验不对就会全量拉取 private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable { long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get(); Applications delta = null; //增量信息是通过eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta方法完成的 EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get()); if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) { //delta中保存了Eureka server返回的增量更新 delta = httpResponse.getEntity(); } //如果没有 if (delta == null) { //如果增量信息为空,就直接发起一次全量更新 getAndStoreFullRegistry(); } //考虑到多线程同步问题,这里通过CAS来确保请求发起到现在是线程安全的, //如果这期间fetchRegistryGeneration变了,就表示其他线程也做了类似操作,因此放弃本次响应的数据 else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) { logger.debug("Got delta update with apps hashcode {}", delta.getAppsHashCode()); String reconcileHashCode = ""; if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) { try { //用Eureka返回的增量数据和本地数据做合并操作 updateDelta(delta); //用合并了增量数据之后的本地数据来生成一致性哈希码 reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications); } finally { fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock(); } } else {...} //Eureka server在返回增量更新数据时,也会返回服务端的一致性哈希码, //理论上每次本地缓存数据经历了多次增量更新后,计算出的一致性哈希码应该是和服务端一致的, //如果发现不一致,就证明本地缓存的服务列表信息和Eureka server不一致了,需要做一次全量更新 if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) { //一致性哈希码不同,就在reconcileAndLogDifference方法中做全量更新 reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall } } else {...} } //updateDelta方法将增量更新数据和本地数据做合并 private void updateDelta(Applications delta) { int deltaCount = 0; //遍历所有服务 for (Application app : delta.getRegisteredApplications()) { //遍历当前服务的所有实例 for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) { //取出缓存的所有服务列表,用于合并 Applications applications = getApplications(); String instanceRegion = instanceRegionChecker.getInstanceRegion(instance); //判断正在处理的实例和当前应用是否在同一个region if (!instanceRegionChecker.isLocalRegion(instanceRegion)) { //如果不是同一个region,接下来合并的数据就换成专门为其他region准备的缓存 Applications remoteApps = remoteRegionVsApps.get(instanceRegion); if (null == remoteApps) { remoteApps = new Applications(); remoteRegionVsApps.put(instanceRegion, remoteApps); } applications = remoteApps; } ++deltaCount; //对新增的实例的处理 if (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) { Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()); if (existingApp == null) { applications.addApplication(app); } logger.debug("Added instance {} to the existing apps in region {}", instance.getId(), instanceRegion); applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance); } //对修改实例的处理 else if (ActionType.MODIFIED.equals(instance.getActionType())) { Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()); if (existingApp == null) { applications.addApplication(app); } logger.debug("Modified instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId()); applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance); } //对删除实例的处理 else if (ActionType.DELETED.equals(instance.getActionType())) { Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()); if (existingApp != null) { logger.debug("Deleted instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId()); existingApp.removeInstance(instance); /* * We find all instance list from application(The status of instance status is not only the status is UP but also other status) * if instance list is empty, we remove the application. */ if (existingApp.getInstancesAsIsFromEureka().isEmpty()) { applications.removeApplication(existingApp); } } } } } logger.debug("The total number of instances fetched by the delta processor : {}", deltaCount); getApplications().setVersion(delta.getVersion()); //整理数据,使得后续使用过程中,这些应用的实例总是以相同顺序返回 getApplications().shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances()); //和当前应用不在同一个region的应用,其实例数据也要整理 for (Applications applications : remoteRegionVsApps.values()) { applications.setVersion(delta.getVersion()); applications.shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances()); } }
【6.3】分析服务定时续约任务 HeartbeatThread(也就是心跳机制)
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable { public void run() { if (renew()) { lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } } boolean renew() { EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse; try { //发送心跳请求 httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null); logger.debug(PREFIX + "{} - Heartbeat status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode()); if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode()) { REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment(); logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - Re-registering apps/{}", appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName()); long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime(); boolean success = register(); if (success) { instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp); } return success; } return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode(); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e); return false; } }
【7】分析服务注册的instanceInfoReplicator.start方法
public void start(int initialDelayMs) { if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) { instanceInfo.setIsDirty(); // for initial register Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, initialDelayMs, TimeUnit.SECONDS); scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next); } } //InstanceInfoReplicator类#run方法 public void run() { try { discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo(); Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime(); if (dirtyTimestamp != null) { //服务注册 discoveryClient.register(); instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp); } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t); } finally { Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS); scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next); } } boolean register() throws Throwable { logger.info(PREFIX + "{}: registering service...", appPathIdentifier); EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse; try { //发起注册请求 httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn(PREFIX + "{} - registration failed {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e); throw e; } return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NO_CONTENT.getStatusCode(); }
【8】Eureka Server服务端Jersey接口部分分析
【8.1】服务端Jersey接口处理类ApplicationResource
@Produces({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public class ApplicationResource {
...
//注册一个实例的信息
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
logger.debug("Registering instance {} (replication={})", info.getId(), isReplication);
// validate that the instanceinfo contains all the necessary required fields
// 参数校验,不符合验证规则的,返回400状态码,
if (isBlank(info.getId())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing instanceId").build();
} else if (isBlank(info.getHostName())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing hostname").build();
} else if (isBlank(info.getIPAddr())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing ip address").build();
} else if (isBlank(info.getAppName())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing appName").build();
} else if (!appName.equals(info.getAppName())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Mismatched appName, expecting " + appName + " but was " + info.getAppName()).build();
} else if (info.getDataCenterInfo() == null) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing dataCenterInfo").build();
} else if (info.getDataCenterInfo().getName() == null) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing dataCenterInfo Name").build();
}
// handle cases where clients may be registering with bad DataCenterInfo with missing data
DataCenterInfo dataCenterInfo = info.getDataCenterInfo();
if (dataCenterInfo instanceof UniqueIdentifier) {
String dataCenterInfoId = ((UniqueIdentifier) dataCenterInfo).getId();
if (isBlank(dataCenterInfoId)) {
boolean experimental = "true".equalsIgnoreCase(serverConfig.getExperimental("registration.validation.dataCenterInfoId"));
if (experimental) {
String entity = "DataCenterInfo of type " + dataCenterInfo.getClass() + " must contain a valid id";
return Response.status(400).entity(entity).build();
} else if (dataCenterInfo instanceof AmazonInfo) {
AmazonInfo amazonInfo = (AmazonInfo) dataCenterInfo;
String effectiveId = amazonInfo.get(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId);
if (effectiveId == null) {
amazonInfo.getMetadata().put(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId.getName(), info.getId());
}
} else {
logger.warn("Registering DataCenterInfo of type {} without an appropriate id", dataCenterInfo.getClass());
}
}
}
// 重点在这里,进行注册
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible
}
}
【8.1.1】注册方法分析
@Override public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) { int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS; if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) { leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs(); } super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication); replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication); } //AbstractInstanceRegistry类#register方法 public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) { try { // 上只读锁 read.lock(); // 从本地MAP里面获取当前实例的信息 //注册表的结构 Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName()); // 增加注册次数到监控信息里面去。 REGISTER.increment(isReplication); if (gMap == null) { // 如果第一次进来,那么gMap为空,则创建一个ConcurrentHashMap放入到registry里面去 final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>(); // putIfAbsent方法主要是在向ConcurrentHashMap中添加键—值对的时候,它会先判断该键值对是否已经存在。 // 如果不存在(新的entry),那么会向map中添加该键值对,并返回null。 // 如果已经存在,那么不会覆盖已有的值,直接返回已经存在的值。 gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap); if (gMap == null) { // 表明map中确实不存在,则设置gMap为最新创建的那个 gMap = gNewMap; } } // 从MAP中查询已经存在的Lease信息 (比如第二次来) Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId()); // 当Lease的对象不为空时。 if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) { // 当instance已经存在是,和客户端的instance的信息做比较,时间最新的那个,为有效instance信息 Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp(); Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp(); if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) { registrant = existingLease.getHolder(); } } else { // 这里只有当existinglease不存在时,才会进来。 像那种恢复心跳,信息过期的,都不会进入这里。 // Eureka‐Server的自我保护机制做的操作,为每分钟最大续约数+2 ,同时重新计算每分钟最小续约数 synchronized (lock) { if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) { // Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1; updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); } } } // 构建一个最新的Lease信息 Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration); if (existingLease != null) { // 当原来存在Lease的信息时,设置他的serviceUpTimestamp, 保证服务开启的时间一直是第一次的那个 lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp()); } // 放入本地Map中 gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease); // 添加到最近的注册队列里面去,以时间戳作为Key, 名称作为value,主要是为了运维界面的统计数据。 synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) { recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>( System.currentTimeMillis(), registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")")); } // 分析instanceStatus if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) { logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the " + "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId()); if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) { logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId()); overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus()); } } InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId()); if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) { logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap); registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap); } // Set the status based on the overridden status rules InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication); registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus); // 得到instanceStatus,判断是否是UP状态, if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) { lease.serviceUp(); } // 设置注册类型为添加 registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED); // 租约变更记录队列,记录了实例的每次变化, 用于注册信息的增量获取、 recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease)); registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp(); // 清理缓存 ,传入的参数为key invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress()); } finally { read.unlock(); } }
【8.1.1】分析Lease结构
public class Lease<T> { enum Action { Register, Cancel, Renew }; //租约过期的时间常量,默认90秒,也就说90秒没有心跳过来,那么这边将会自动剔除该节点 public static final int DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS = 90; 这个租约是属于谁的, 目前占用这个属性的是 private T holder; //租约是啥时候过期的,当服务下线的时候,会过来更新这个时间戳registrationTimestamp : 租约的注册时间 private long evictionTimestamp; private long registrationTimestamp; //服务启动时间 ,当客户端在注册的时候,instanceInfo的status 为UP的时候,则更新这个时间戳 private long serviceUpTimestamp; //最后更新时间,每次续约的时候,都会更新这个时间戳,在判断实例是否过期时,需要用到这个属性。 private volatile long lastUpdateTimestamp; //过期时间,毫秒单位 private long duration; public Lease(T r, int durationInSecs) { holder = r; registrationTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); lastUpdateTimestamp = registrationTimestamp; duration = (durationInSecs * 1000); } //更新的时候设置过期时间为当前时间+90S public void renew() { lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration; } public void cancel() { if (evictionTimestamp <= 0) { evictionTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } public void serviceUp() { if (serviceUpTimestamp == 0) { serviceUpTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } public void setServiceUpTimestamp(long serviceUpTimestamp) { this.serviceUpTimestamp = serviceUpTimestamp; } public boolean isExpired() { return isExpired(0l); } //这里面存在的问题是过期时间+90S //实际上也就是在更新时候的180s之后才算过期 public boolean isExpired(long additionalLeaseMs) { return (evictionTimestamp > 0 || System.currentTimeMillis() > (lastUpdateTimestamp + duration + additionalLeaseMs)); } public long getRegistrationTimestamp() { return registrationTimestamp; } public long getLastRenewalTimestamp() { return lastUpdateTimestamp; } public long getEvictionTimestamp() { return evictionTimestamp; } public long getServiceUpTimestamp() { return serviceUpTimestamp; } public T getHolder() { return holder; } }
【8.2】客户端Jersey接口处理类ApplicationsResource
@Path("/{version}/apps")
@Produces({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public class ApplicationsResource {
...
private final EurekaServerConfig serverConfig;
private final PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry;
private final ResponseCache responseCache;
@Inject
ApplicationsResource(EurekaServerContext eurekaServer) {
this.serverConfig = eurekaServer.getServerConfig();
this.registry = eurekaServer.getRegistry();
this.responseCache = registry.getResponseCache();
}
public ApplicationsResource() {
this(EurekaServerContextHolder.getInstance().getServerContext());
}
//获取关于特定{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Application}的信息。
@Path("{appId}")
public ApplicationResource getApplicationResource(
@PathParam("version") String version,
@PathParam("appId") String appId) {
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
return new ApplicationResource(appId, serverConfig, registry);
}
//获取关于所有{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Applications}的信息。
@GET
public Response getContainers(@PathParam("version") String version,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding,
@HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept,
@Context UriInfo uriInfo,
@Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty();
String[] regions = null;
if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) {
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL.increment();
} else {
regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(",");
Arrays.sort(regions); // So we don't have different caches for same regions queried in different order.
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment();
}
// Check if the server allows the access to the registry. The server can
// restrict access if it is not
// ready to serve traffic depending on various reasons.
if (!registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested)) {
return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build();
}
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
KeyType keyType = Key.KeyType.JSON;
String returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON;
if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains(HEADER_JSON_VALUE)) {
keyType = Key.KeyType.XML;
returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML;
}
//获取服务实例对应的缓存key
Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application,
ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS,
keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions
);
Response response;
//是否压缩
if (acceptEncoding != null && acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) {
response = Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey))
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType)
.build();
} else {
//从缓存里获取服务实例注册信息
response = Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
}
return response;
}
//在{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Applications}中获取关于所有增量更改的信息。
@Path("delta")
@GET
public Response getContainerDifferential(
@PathParam("version") String version,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding,
@HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept,
@Context UriInfo uriInfo, @Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty();
// If the delta flag is disabled in discovery or if the lease expiration
// has been disabled, redirect clients to get all instances
if ((serverConfig.shouldDisableDelta()) || (!registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested))) {
return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build();
}
String[] regions = null;
if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) {
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_DELTA.increment();
} else {
regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(",");
Arrays.sort(regions); // So we don't have different caches for same regions queried in different order.
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_DELTA_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment();
}
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
KeyType keyType = Key.KeyType.JSON;
String returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON;
if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains(HEADER_JSON_VALUE)) {
keyType = Key.KeyType.XML;
returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML;
}
Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application,
ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS_DELTA,
keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions
);
if (acceptEncoding != null
&& acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) {
return Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey))
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType)
.build();
} else {
return Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
}
}
}
【8.2.1】ApplicationsResource类的getContainers方法分析
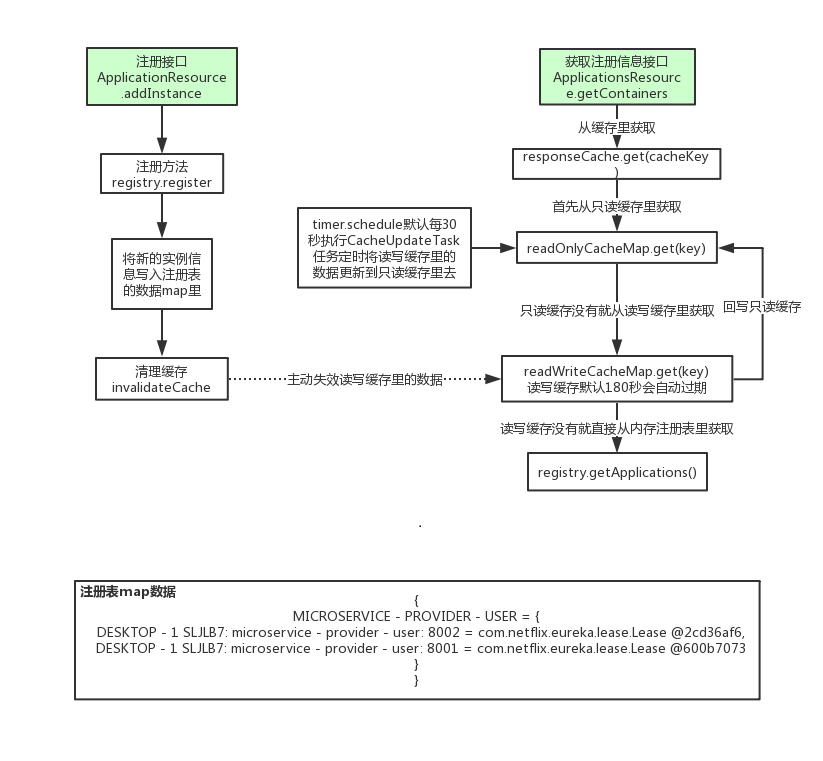
//获取关于所有{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Applications}的信息。 @GET public Response getContainers(@PathParam("version") String version, @HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader, @HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding, @HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept, @Context UriInfo uriInfo, @Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) { boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty(); String[] regions = null; if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) { EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL.increment(); } else { regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(","); Arrays.sort(regions); // So we don't have different caches for same regions queried in different order. EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment(); } // Check if the server allows the access to the registry. The server can // restrict access if it is not // ready to serve traffic depending on various reasons. if (!registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested)) { return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build(); } CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version)); KeyType keyType = Key.KeyType.JSON; String returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON; if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains(HEADER_JSON_VALUE)) { keyType = Key.KeyType.XML; returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML; } //获取服务实例对应的缓存key Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application, ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS, keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions ); Response response; //是否压缩 if (acceptEncoding != null && acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) { response = Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey)) .header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE) .header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType) .build(); } else { //从缓存里获取服务实例注册信息,从ResponseCacheImpl类中获取 response = Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey)) .build(); } return response; } //分析responseCache.get方法 //ResponseCacheImpl类#get方法 public String get(final Key key) { return get(key, shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache); } @VisibleForTesting String get(final Key key, boolean useReadOnlyCache) { Value payload = getValue(key, useReadOnlyCache); if (payload == null || payload.getPayload().equals(EMPTY_PAYLOAD)) { return null; } else { return payload.getPayload(); } } //精髓设计的点,利用了读写分离,有种CopyOnWrite的思维 //private final ConcurrentMap<Key, Value> readOnlyCacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Key, Value>(); //private final LoadingCache<Key, Value> readWriteCacheMap; @VisibleForTesting Value getValue(final Key key, boolean useReadOnlyCache) { Value payload = null; try { //只读缓存的开启 if (useReadOnlyCache) { final Value currentPayload = readOnlyCacheMap.get(key); //只读缓存拿不到才去读写缓存里面拿 if (currentPayload != null) { payload = currentPayload; } else { payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key); readOnlyCacheMap.put(key, payload); } } else { payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key); } } catch (Throwable t) {...} return payload; } //ResponseCacheImpl类#构造方法 ResponseCacheImpl(EurekaServerConfig serverConfig, ServerCodecs serverCodecs, AbstractInstanceRegistry registry) { this.serverConfig = serverConfig; this.serverCodecs = serverCodecs; this.shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache = serverConfig.shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache(); this.registry = registry; long responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs = serverConfig.getResponseCacheUpdateIntervalMs(); this.readWriteCacheMap = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().initialCapacity(serverConfig.getInitialCapacityOfResponseCache()) //读写缓存默认180秒会自动定时过期 .expireAfterWrite(serverConfig.getResponseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .removalListener(new RemovalListener<Key, Value>() { @Override public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Key, Value> notification) { Key removedKey = notification.getKey(); if (removedKey.hasRegions()) { Key cloneWithNoRegions = removedKey.cloneWithoutRegions(); regionSpecificKeys.remove(cloneWithNoRegions, removedKey); } } }) .build(new CacheLoader<Key, Value>() { @Override public Value load(Key key) throws Exception { if (key.hasRegions()) { Key cloneWithNoRegions = key.cloneWithoutRegions(); regionSpecificKeys.put(cloneWithNoRegions, key); } //从内存注册表中获取 Value value = generatePayload(key); return value; } }); if (shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache) { //默认30秒用读写缓存的数据更新只读缓存的数据 timer.schedule(getCacheUpdateTask(), new Date(((System.currentTimeMillis() / responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs) * responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs) + responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs), responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs); } try { Monitors.registerObject(this); } catch (Throwable e) {...} }
Eureka服务端源码分析图

Eureka服务端Jersey接口分析图
Eureka客户端源码分析图


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号