4412 GPIO读 和 ioremap控制GPIO寄存器
一、配置GPIO读
在视频14的基础上做
1.利用拨码开关来实现GPIO输入
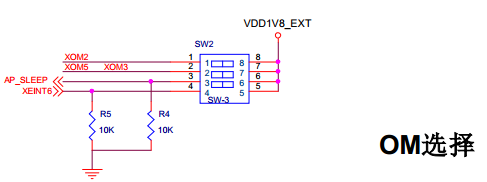


所以AP_SLEEP对应GPC0_3,然后在drivers/gpio/gpio-exynos4.c中对应EXYNOS4_GPC0(0)
XEINT6→GPX0_6→EXYNOS4_GPX0(6)
读寄存器手册分析流程:
- 设置寄存器为输入 GPC0CON
- 读寄存器值 GPC0DAT
- 不上拉,不下拉 GPC0PUD
2.GPIO的输入需要哪些函数,从arch\arm\plat-samsung\gpio-config.c中找
- 申请gpio_request
- 读寄存器gpio_get_value
- 设置GPIO为输入模式s3c_gpio_cfgpin S3C_GPIO_INPUT
- 设置上拉下拉s3c_gpio_setpull S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE
- 释放GPIO gpio_free
3.平台文件中设备注册
在文件arch/arm/mach-exynos/mach-itop4412.c中:
struct platform_device s3c_device_read_gpio_ctl = {
.name = "read_gpio_ctl",
.id = -1,
};
&s3c_device_read_gpio_ctl,
在init_lcd_type函数中request了GPIO。所以在get_lcd_type需要释放GPIO
gpio_free(EXYNOS4_GPC0(3));
gpio_free(EXYNOS4_GPX0(6));
4.Makefile修改

TARGET_NAME = read_gpio APP_NAME = app_read_gpio obj-m += $(TARGET_NAME).o KDIR := /home/topeet/chen/kernel-3.0/iTop4412_Kernel_3.0 PWD ?= $(shell pwd) all:app make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules app:$(APP_NAME) arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc $(APP_NAME).c -o $(APP_NAME) -static clean: rm -rf *.o *.ko *.mod.c *.symvers *.order \ .$(TARGET_NAME)* $(APP_NAME)
5.驱动的修改

#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> /*驱动注册的头文件,包含驱动的结构体和注册和卸载的函数*/ #include <linux/platform_device.h> /*注册杂项设备头文件*/ #include <linux/miscdevice.h> /*注册设备节点的文件结构体*/ #include <linux/fs.h> /*Linux中申请GPIO的头文件*/ #include <linux/gpio.h> /*三星平台的GPIO配置函数头文件*/ /*三星平台EXYNOS系列平台,GPIO配置参数宏定义头文件*/ #include <plat/gpio-cfg.h> #include <mach/gpio.h> /*三星平台4412平台,GPIO宏定义头文件*/ #include <mach/gpio-exynos4.h> #define DRIVER_NAME "read_gpio_ctl" #define DEVICE_NAME "read_gpio_ctl" MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("TOPEET"); static long read_gpio_ioctl( struct file *files, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) { printk("cmd is %d,arg is %d\n",cmd,arg); if(cmd > 1){ printk(KERN_EMERG "cmd is 0 or 1\n"); } if(arg > 1){ printk(KERN_EMERG "arg is only 1\n"); } //if cmd is 0, return GPC(3)>>switch3 //if cmd is 1, return GPX(6)>>switch4 if(cmd == 0) { return gpio_get_value(EXYNOS4_GPC0(3)); } if(cmd == 1) { return gpio_get_value(EXYNOS4_GPX0(6)); } return 0; } static int read_gpio_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_EMERG "read_gpio release\n"); return 0; } static int read_gpio_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_EMERG "read_gpio open\n"); return 0; } static struct file_operations read_gpio_ops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = read_gpio_open, .release = read_gpio_release, .unlocked_ioctl = read_gpio_ioctl, }; static struct miscdevice read_gpio_dev = { .minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, .name = DEVICE_NAME, .fops = &read_gpio_ops, }; static int read_gpio_probe(struct platform_device *pdv) { int ret; printk(KERN_EMERG "\tinitialized\n"); ret = gpio_request(EXYNOS4_GPC0(3),"Switch3"); if(ret < 0){ printk(KERN_EMERG "gpio_request EXYNOS4_GPL2(0) failed!\n"); return ret; } else { s3c_gpio_cfgpin(EXYNOS4_GPC0(3), S3C_GPIO_INPUT); s3c_gpio_setpull(EXYNOS4_GPC0(3), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE); } ret = gpio_request(EXYNOS4_GPX0(6),"Switch4"); if(ret < 0){ printk(KERN_EMERG "gpio_request EXYNOS4_GPL2(0) failed!\n"); return ret; } else { s3c_gpio_cfgpin(EXYNOS4_GPX0(6), S3C_GPIO_INPUT); s3c_gpio_setpull(EXYNOS4_GPX0(6), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE); } misc_register(&read_gpio_dev); return 0; } static int read_gpio_remove(struct platform_device *pdv) { printk(KERN_EMERG "\tremove\n"); gpio_free(EXYNOS4_GPC0(3)); gpio_free(EXYNOS4_GPX0(6)); misc_deregister(&read_gpio_dev); return 0; } static void read_gpio_shutdown(struct platform_device *pdv) { ; } static int read_gpio_suspend(struct platform_device *pdv,pm_message_t pmt) { return 0; } static int read_gpio_resume(struct platform_device *pdv) { return 0; } struct platform_driver read_gpio_driver = { .probe = read_gpio_probe, .remove = read_gpio_remove, .shutdown = read_gpio_shutdown, .suspend = read_gpio_suspend, .resume = read_gpio_resume, .driver = { .name = DRIVER_NAME, .owner = THIS_MODULE, } }; static int read_gpio_init(void) { int DriverState; printk(KERN_EMERG "read_gpio enter!\n"); DriverState = platform_driver_register(&read_gpio_driver); printk(KERN_EMERG "\tDriverState is %d\n",DriverState); return 0; } static void read_gpio_exit(void) { printk(KERN_EMERG "read_gpio exit!\n"); platform_driver_unregister(&read_gpio_driver); } module_init(read_gpio_init); module_exit(read_gpio_exit);
应用程序:

#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <string.h> #define GPIOS 32 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int fd, i, cmd = 2; char *read_gpio = "/dev/read_gpio_ctl"; char *cmd0 = "0"; char *cmd1 = "1"; printf("argv[0] is %s;argv[1] is %s;\n", argv[0], argv[1]); if(strcmp(argv[1], cmd0) == 0) { cmd = 0; } if(strcmp(argv[1], cmd1) == 0) { cmd = 1; } if((fd = open(read_gpio, O_RDWR|O_NDELAY)) < 0) { printf("APP open %s failed\n", read_gpio); } else { printf("APP open %s success!\n", read_gpio); printf("%d io value is %d\n", cmd, ioctl(fd, cmd, 0)); } close(fd); }
测试结果:

[root@iTOP-4412]# ./app_read_gpio 1 argv[0] is ./app_[ 312.514145] read_gpio open [ 312.516876] cmd is 1,arg is 0 [ 312.519870] read_gpio release read_gpio;argv[1] is 1; APP open /dev/read_gpio_ctl success! 1 io value is 0 [root@iTOP-4412]# ./app_read_gpio 0 argv[0] is ./app_[ 314.786489] read_gpio open [ 314.789131] cmd is 0,arg is 0 [ 314.792307] read_gpio release read_gpio;argv[1] is 0; APP open /dev/read_gpio_ctl success! 0 io value is 0 [root@iTOP-4412]# ./app_read_gpio 1 argv[0] is ./app_[ 321.786146] read_gpio open [ 321.788790] cmd is 1,arg is 0 [ 321.791899] read_gpio release read_gpio;argv[1] is 1; APP open /dev/read_gpio_ctl success! 1 io value is 1 [root@iTOP-4412]# ./app_read_gpio 0 argv[0] is ./app_[ 323.449833] read_gpio open [ 323.452526] cmd is 0,arg is 0 [ 323.455489] read_gpio release read_gpio;argv[1] is 0; APP open /dev/read_gpio_ctl success! 0 io value is 1
二、ioremap控制GPIO寄存器
上面使用的是直接通过软件转换好了的,其实内核也是可以自己做转化的。
自己实现物理地址到虚拟地址的转化,iounmap和ioremap函数可以实现物理地址到虚拟地址的转化
1.硬件
- 原理图部分

- datasheet物理地址
- GPL2CON = 0x1100 0000 + 0x0100 = 0x1100 0100
- GPL2DAT = 0x1100 0000 + 0x0104 = 0x1100 0104
- GPL2PUD = 0x1100 0000 + 0x0108 = 0x1100 0108
- 寄存器不一定是32位的,也有16位或8位的
2.软件

#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <asm/io.h> MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("Topeet"); //用于存放虚拟地址和物理地址 volatile unsigned long virt_addr, phys_addr; //用户存放三个寄存器的地址 volatile unsigned long *GPL2CON, *GPL2DAT, *GPL2PUD; static void gpl2_device_init(void) { //物理地址起始地址0x1100 0100 phys_addr = 0x11000100; //0x11000100是GPL2CON的物理地址 virt_addr = (unsigned long)ioremap(phys_addr, 0x10); //指定需要操作的寄存器地址 GPL2CON = (unsigned long *)(virt_addr + 0x00); GPL2DAT = (unsigned long *)(virt_addr + 0x04); GPL2PUD = (unsigned long *)(virt_addr + 0x08); } //配置开发板的GPIO寄存器 static void gpl2_configure(void) { //配置为输出模式 *GPL2CON &= 0xFFFFFFF0; *GPL2CON |= 0x00000001; //GPL2PUD &= 0xfff0; //GPL2PUD寄存器,bit[0:1]设为0x03,上拉模式 *GPL2PUD |= 0x0003; } //点灯 static void gpl2_on(void) { *GPL2DAT |= 0x01; } //灭灯 static void gpl2_off(void) { *GPL2DAT &= 0xfe; } static int led_gpl2_init(void) { printk(KERN_EMERG "led enter!\n"); gpl2_device_init(); //实现IO内存映射 gpl2_configure(); //配置GPL2为输出模式 gpl2_on(); printk("led dgp2 open\n"); return 0; } static void led_gpl2_exit(void) { gpl2_off(); printk(KERN_EMERG "led exit!\n"); } module_init(led_gpl2_init); module_exit(led_gpl2_exit);
makefile文件:

TARGET_NAME = ioremap_leds obj-m += $(TARGET_NAME).o KDIR := /home/topeet/chen/kernel-3.0/iTop4412_Kernel_3.0 PWD ?= $(shell pwd) all: make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean: rm -rf *.o *.ko *.mod.c *.symvers *.order \ .$(TARGET_NAME)*
3.编译测试

[root@iTOP-4412]# insmod ioremap_leds.ko [ 6116.064904] led enter! [ 6116.065940] led dgp2 open [root@iTOP-4412]# rmmod ioremap_leds [ 6122.913415] led exit! [root@iTOP-4412]# insmod ioremap_leds.ko [ 6133.090595] led enter! [ 6133.091567] led dgp2 open [root@iTOP-4412]# rmmod ioremap_leds [ 6137.830391] led exit
加载驱动,小灯亮
卸载驱动,小灯灭
无欲速,无见小利。欲速,则不达;见小利,则大事不成。




