spring BeanPostProcessor 生命周期
转载: https://bugpool.blog.csdn.net/article/details/104833590
BeanPostProcessor:后置处理器
spring使用模板模式,在bean的创建过程中安插了许多锚点,用户寻找对应的锚点,通过重写方法介入到bean的创建过程当中。本节通过重写这些锚点,学习如何使用BeanPostProcessor、获取各类BeanAware并且理清bean的生命周期
1、创建类LifeCycleBean
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.*; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class LifeCycleBean implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { private BeanFactory beanfactory; private ApplicationContext applicationContext; private String name; public LifeCycleBean() { System.out.println("无参构造方法"); } public LifeCycleBean(String name){ System.out.println("2. 构造方法被调用, name" + name); this.name = name; } @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { this.beanfactory = beanFactory; System.out.println("6. BeanFactoryAware 被调用, 获取到的BeanFactory: " + beanFactory); } @Override public void setBeanName(String s) { System.out.println("5. BeanNameAware 被调用, 获取到的beanName:" + name); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("13. DisposableBean 被调用"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("9. afterPropertiesSet 被调用"); } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; System.out.println("7. ApplicationContextAware 被调用, 获取到 ApplicationContextAware: " + applicationContext); } public void myInit() { System.out.println("10. myInit 自定义初始化方法被调用, name:" + getName()); } public void myDestroy(){ System.out.println("14. destroy-method 自定义销毁方法被调用"); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public BeanFactory getBeanfactory() { return beanfactory; } public ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { return applicationContext; } }
2、创建BeanPostProcessor后置处理器(postProcessProperties过时了,这里就不演示了)
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor; public class LifeCycleBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { if( beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")) { System.out.println("1. postProcessBeforeInstantiation 被调用"); } return null; } @Override public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")) { System.out.println("3. postProcessAfterInstantiation 被调用"); } return true; } @Override public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")) { System.out.println("4. postProcessProperties 被调用"); } return null; } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")) { ((LifeCycleBean)bean).setName("中中"); System.out.println("8. postProcessBeforeInitialization 被调用, 把 name 改成 中中"); } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")) { ((LifeCycleBean) bean).setName("大大"); System.out.println(" 11. postProcessAfterInitialization 被调用, 把 name 改成 大大"); } return null; } }
3、 配置文件, 此处使用 注解配置, 原文为 xml 配置方式
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class BeanCfg { @Bean(name = "lifeCycleBean", destroyMethod = "myDestroy", initMethod = "myInit") public LifeCycleBean lifeCycleBean() { return new LifeCycleBean("小小"); } @Bean public LifeCycleBeanPostProcessor lifeCycleBeanPostProcessor() { return new LifeCycleBeanPostProcessor(); } }
4、测试类
import com.yyds.springlifecycle.lifecycle.BeanCfg; import com.yyds.springlifecycle.lifecycle.LifeCycleBean; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; class SpringlifecycleApplicationTests { @Test public void test() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanCfg.class); LifeCycleBean myLifeCycleBean = applicationContext.getBean("lifeCycleBean", LifeCycleBean.class); System.out.println("12. bean 创建完成, name : " + myLifeCycleBean.getName()); ((AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)applicationContext).close(); } }
结果:
1. postProcessBeforeInstantiation 被调用 2. 构造方法被调用, name小小 3. postProcessAfterInstantiation 被调用 4. postProcessProperties 被调用 5. BeanNameAware 被调用, 获取到的beanName:小小 6. BeanFactoryAware 被调用, 获取到的BeanFactory: org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@445b295b: defining beans [org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory,beanCfg,lifeCycleBean,lifeCycleBeanPostProcessor]; root of factory hierarchy 7. ApplicationContextAware 被调用, 获取到 ApplicationContextAware: org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@3745e5c6, started on Thu Jul 28 18:31:16 CST 2022 8. postProcessBeforeInitialization 被调用, 把 name 改成 中中 9. afterPropertiesSet 被调用 10. myInit 自定义初始化方法被调用, name:中中 11. postProcessAfterInitialization 被调用, 把 name 改成 大大 12. bean 创建完成, name : 大大 18:31:17.042 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext - Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@3745e5c6, started on Thu Jul 28 18:31:16 CST 2022 13. DisposableBean 被调用 14. destroy-method 自定义销毁方法被调用
分析总结:
1、 BeanPostProcess
实例化相关: postProcessBeforeInstantiation、 postProcessAfterInstantiation
填充属性相关: postProcessProperties、 postProcessPropertyValues(已经过时,没有演示)
初始化相关: postProcessBeforeInitialization、postProcessAfterInitialization
通过重写 BeanPostProcess 的方法,可以介入 bean 创建的不同环节。 同时通过postProcessBeforeInitialization将bean的name属性值从小小改成了中中,又通过postProcessAfterInitialization将中中改成了大大,成功介入了bean的创建,并且依据我们的意愿修改了bean。
2、 BeanNameAware、 BeanFactoryAware、 ApplicationContextAware
这3类不属于后置处理器的范畴, 学名叫 感知器, 让 bean 嫩个感知到整个容器上下文信息的接口。 spring 在创建过程中, 通过回调子类的 setBeanName 、 setBeanFactory 、 setApplicationContext 实现了 beanName, beanFactory,ApplicationContext 的注入,
让bean能够感知获取到spring上下文的相关信息。虽然实现的东西很牛逼,但是实现的原理一点不复杂。通过检测当前的bean是否实现相关Aware,如果实现则调用子类set方法,将当前的BeanFactory等作为参数传入,直接上源码,看不懂可以参考这篇源码:(https://blog.csdn.net/chaitoudaren/article/details/104833613)
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); } if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader(); if (bcl != null) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl); } } if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this); } } }
3、 最后贴出总结后的流程图
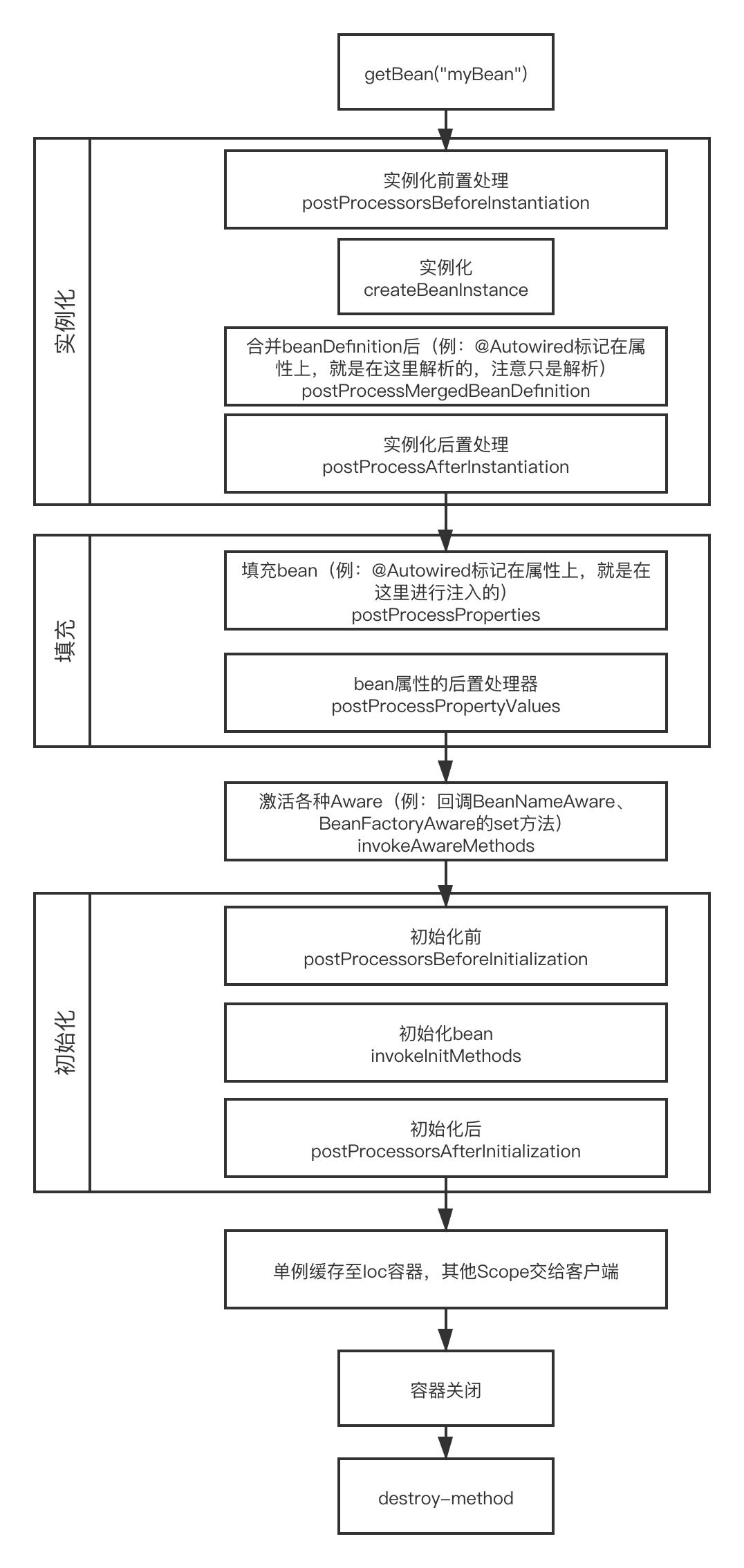





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)