延迟任务
前些天同事有延迟任务的处理任务,因为业务涉及量不是很大,而且时间以天为单位,之前的方案就是每天定时任务查询一下,然后进行触发,没有深思。
今天又刚好看到了相关的处理方案文章,记录一下
在开发中遇到一些任务, 需要在 某个触发条件后 多长时间时 执行任务, 比如订单30分钟后未支付则取消,客户操作某些业务后多长时间需要提示发送短信等
目前看到的各种方案有:
(1)、 数据库轮循
(2)、JDK 延迟队列 DelayQueue
(3)、Timer 处理延迟订单
(4)、时间轮循算法
(5)、redis 之 zset
(6)、 消息队列 rabbitMQ
各种方案的选用根据实际情况,进行选择,也不必非得选用复杂方案杀鸡用牛刀
一、 数据库轮循
此种方案设定定时任务,定时去触发扫描符合条件数据,然后执行对应的操作
优点: 简单易行,支持集群操作
缺点: 对服务器内存消耗大;
存在延时,最坏的情况延时就是定时任务的间隔长度
数据量大的情况每次扫描 数据库损耗大
二、 JDK延迟队列 DelayQueue
该方案是用JDK自带的 DelayQueue实现,延迟队列DelayQueue是一个无界阻塞队列,它的队列元素只能在该元素的延迟已经结束或者说过期才能被出队,即是该队列只有在延迟期满的时候才能从中获取元素, 放入DelayQueue队列的对象,必须是实现了Delayed 接口。
所以需要明确两个问题, 如何判定一个元素的延迟是否结束; 如何保证按照延迟短优先出列;
a、 如何判定一个元素的延迟是否结束 - Delayed接口有一个getDelay() 方法需要实现,延迟队列就是通过实时的调用元素的该方法来判断当前元素是否延迟已经结束
public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E> { private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>();
/** * A mix-in style interface for marking objects that should be * acted upon after a given delay. * * <p>An implementation of this interface must define a * {@code compareTo} method that provides an ordering consistent with * its {@code getDelay} method. * * @since 1.5 * @author Doug Lea */ public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed> { /** * Returns the remaining delay associated with this object, in the * given time unit. * * @param unit the time unit * @return the remaining delay; zero or negative values indicate * that the delay has already elapsed */ long getDelay(TimeUnit unit); }
b、按照延迟时间短优先出列 - DelayedQueue 是基于PriorityQueue实现的,DelayQueue队列实际上就是将队列元素保存到内部的一个PriorityQueue实例中的
优先级队列的原理
PriorityQueue采用基于数组的平衡二叉堆实现,不论入队的顺序怎么样,take、poll出队的节点都是按优先级排序的。
PriorityQueue队列中的所有元素并不是在入队之后就已经全部按优先级排好序了,而是只保证head节点即队列的首个元素是当前最小或者说最高优先级的,其它节点的顺序并不保证是按优先级排序的。
PriorityQueue队列只会在通过take、poll取走head之后才会再次决出新的最小或者说最高优先级的节点作为新的head,其它节点的顺序依然不保证。所以通过peek拿到的head节点就是当前队列中最高优先级的节点!
既然DelayQueue是基于优先级队列来实现的,那么队列元素也要实现Comparable接口,这是因为Delayed接口继承了Comparable接口(可以看上图),所以实现Delayed的队列元素也必须要实现Comparable的compareTo方法。
延迟队列就是以时间作为比较基准的优先级队列,基于延迟时间运用优先级队列并配合getDelay方法达到延迟队列中的元素在延迟结束时精准出队。
示例:
@Slf4j public class OrderDelay implements Delayed { private String orderId; private long start = 0; public OrderDelay(String orderId, long delayInMillSeconds) { this.orderId = orderId; this.start = System.currentTimeMillis() + delayInMillSeconds; } /** * getDelay 用于返回任务是否到期,如果返回-1, 则表示任务已经到期 * @param unit * @return */ @Override public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) { long diff = this.start - System.currentTimeMillis(); // 返回距离你自定义的超时时间还有多少,延迟剩余时间,单位unit指定 return unit.convert(diff, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } @Override public int compareTo(Delayed o) { return (int)(this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); } /*模拟处理状态为已提交未支付的订单*/ public void orderHandle(){ log.info("系统在" + LocalDateTime.now() +"---处理延时任务---订单超时未付款---" + orderId); } }
@Service @Slf4j public class TaskService { private TaskService taskService; //创建延时任务队列 private DelayQueue<OrderDelay> orderDelayQueue = new DelayQueue<>(); //服务启动的时候就开始监听这个延时队列有没有任务 @PostConstruct public void init() { taskService = this; Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ try { orderDelayQueue.take().orderHandle(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }); } public void addTask(OrderDelay task) { if(orderDelayQueue.contains(task)){ return; } orderDelayQueue.add(task); } public void removeTask(OrderDelay task){ orderDelayQueue.remove(task); } }
@RequestMapping @RestController @Slf4j public class OrderController { @Autowired private TaskService taskService; @GetMapping("/delayTaskSubmit") public void submit() { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("订单10001"); list.add("订单10002"); list.add("订单10003"); list.add("订单10004"); list.add("订单10005"); for (int i=0 ; i < list.size(); i++){ taskService.addTask(new OrderDelay(list.get(i),5*1000)); log.info(list.get(i)+"在"+ LocalDateTime.now() +"加入了延时任务,5s后开始执行"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
运行结果:
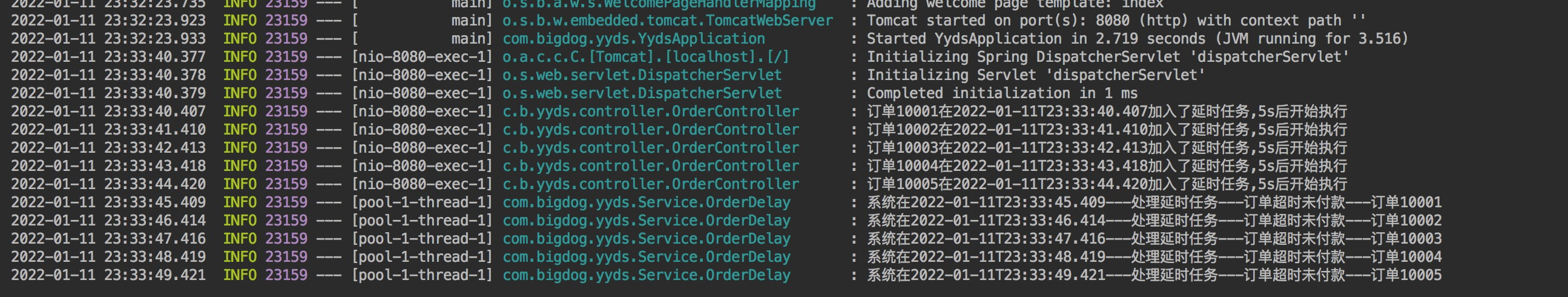
优点: 效率高,触发任务延时低
缺点:队列在内存中,服务重启后任务丢失, 解决方案: 在启动服务后执行查询,把目前尚未处理的订单重新加入到延时队列中
集群扩展比较麻烦
如果任务过多,容易出现OOM
三、 Timer 处理延时任务
当设置的延时时间到了,就执行 orderHandle 方法, 示例如下:
@Slf4j public class OrderTimer { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("订单10001"); list.add("订单10002"); list.add("订单10003"); list.add("订单10004"); list.add("订单10005"); for (int i=0; i < list.size();i++){ String orderId = list.get(i); log.info(orderId+"在"+ LocalDateTime.now() +"加入了延时任务"); Timer timer = new Timer(); timer.schedule(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { // 处理延时订单 orderHandle(orderId); } }, (3* 1000)); } } /*模拟处理状态为已提交未支付的订单*/ public static void orderHandle(String orderId){ log.info("系统在" + LocalDateTime.now() +"---处理延时任务---订单超时未付款---" + orderId); }
运行结果:
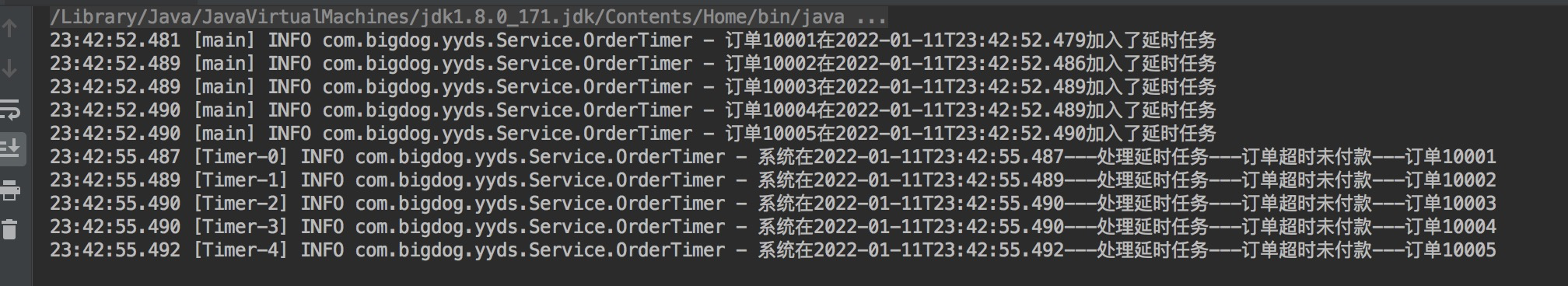
缺点:
1、Timer在执行所有定时任务时只会创建一个线程。如果某个任务的执行时间长度大于其周期时间长度,那么就会导致这一次的任务还在执行,而下一个周期的任务已经需要开始执行了,当然在一个线程内这两个任务只能顺序执行,有两种情况:对于之前需要执行但还没有执行的任务,一是当前任务执行完马上执行那些任务(按顺序来),二是干脆把那些任务丢掉,不去执行它们。
2、Timer线程是不会捕获异常的,如果TimerTask抛出了未检查异常则会导致Timer线程终止,同时Timer也不会重新恢复线程的执行,他会错误的认为整个Timer线程都会取消。同时,已经被安排单尚未执行的TimerTask也不会再执行了,新的任务也不能被调度。故如果TimerTask抛出未检查的异常,Timer将会产生无法预料的行为。
3、 可以用ScheduledExecutorService替代。但是由于ScheduledExecutorService是多线程处理,即不同任务会被分放到其线程池中的不同线程,因此当订单数据量稍微增长,随着线程的消耗,就容易出现无可用线程池甚至内存溢出等异常。
四、时间轮循算法
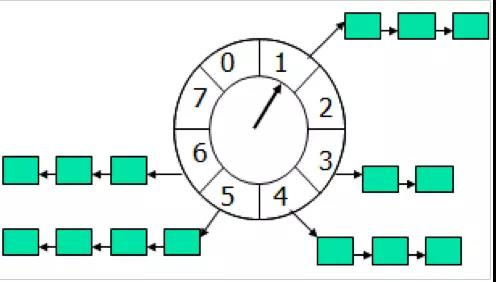
时间轮算法可以类比于时钟,如上图箭头(指针)按某一个方向按固定频率轮动,每一次跳动称为一个 tick。这样可以看出定时轮由个3个重要的属性参数,ticksPerWheel(一轮的tick数),tickDuration(一个tick的持续时间)以及 timeUnit(时间单位),例如当ticksPerWheel=60,tickDuration=1,timeUnit=秒,这就和现实中的始终的秒针走动完全类似了。
如果当前指针指在1上面,我有一个任务需要4秒以后执行,那么这个执行的线程回调或者消息将会被放在5上。那如果需要在20秒之后执行怎么办,由于这个环形结构槽数只到8,如果要20秒,指针需要多转2圈。位置是在2圈之后的5上面(20 % 8 + 1)
我们用Netty的HashedWheelTimer来实现, 需要添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>io.netty</groupId> <artifactId>netty-all</artifactId> <version>4.1.36.Final</version> </dependency>
import io.netty.util.HashedWheelTimer; import io.netty.util.Timeout; import io.netty.util.Timer; import io.netty.util.TimerTask; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class HashedWheelTimerTest { static class MyTimerTask implements TimerTask { boolean flag; private String orderId; public MyTimerTask(boolean flag, String orderId){ this.flag = flag; this.orderId = orderId; } public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception { System.out.println("要去数据库删除订单 " + orderId + " 了。。。。"); this.flag =false; } } public static void main(String[] argv) { MyTimerTask timerTask1 = new MyTimerTask(true,"订单0001"); MyTimerTask timerTask2 = new MyTimerTask(true,"订单0002"); MyTimerTask timerTask3 = new MyTimerTask(true,"订单0003"); Timer timer = new HashedWheelTimer(); timer.newTimeout(timerTask1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); timer.newTimeout(timerTask2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); timer.newTimeout(timerTask3, 4, TimeUnit.SECONDS); int i = 1; while(i < 5){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(i+"秒过去了"); i++; } } }
运行结果:
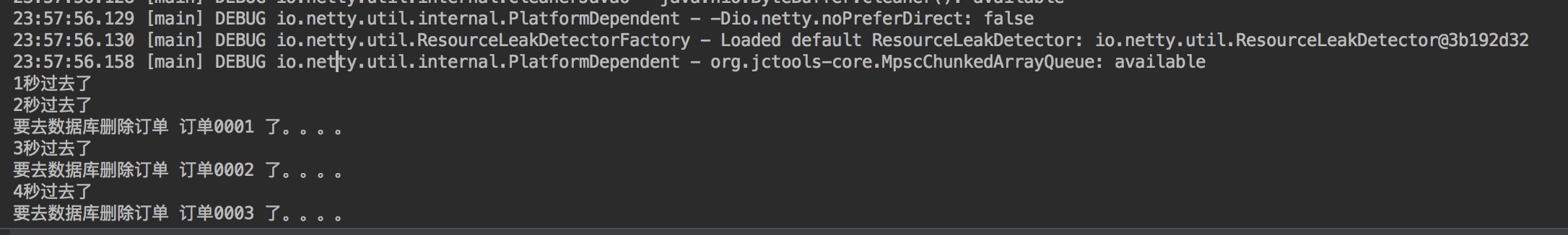
优点:效率高,任务触发时间延迟时间比delayQueue低,代码复杂度比delayQueue低
缺点:服务器重启后任务丢失 - 解决方案,启动服务时,查询需处理订单,然后添加任务
集群扩展复杂
任务过多容易 OOM
五、 Redis缓存
思路一:利用redis的zset,zset是一个有序集合,每一个元素(member)都关联了一个score,通过score排序来取集合中的值
添加元素:ZADD key score member [[score member] [score member] …]
按顺序查询元素:ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
查询元素score:ZSCORE key member
移除元素:ZREM key member [member …]
# 添加单个元素 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd page_rank 10 google.com (integer) 1 #添加多个元素 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd page_rank 9 baidu.com 8 bing.com (integer) 2 #按score查询所有元素 127.0.0.1:6379> zrange page_rank 0 -1 WITHSCORES 1) "bing.com" 2) "8" 3) "baidu.com" 4) "9" 5) "google.com" 6) "10" #按 score查询前2个元素 127.0.0.1:6379> zrange page_rank 0 1 WITHSCORES 1) "bing.com" 2) "8" 3) "baidu.com" 4) "9" #查询 元素的 score值 127.0.0.1:6379> zscore page_rank google.com "10" #删除元素,返回操作的元素数值 127.0.0.1:6379> zrem page_rank baidu.com (integer) 1 #删除多个元素,返回操作的元素个数 127.0.0.1:6379> zrem page_rank bing.com google.com (integer) 2
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Set; @Service @Slf4j public class RedisDelayTask { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; // 生产消息 public void productDelayMessage() { for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); cal.add(Calendar.SECOND, 3); int second3Later = (int)(cal.getTimeInMillis() / 1000); //add(K key, V value, double score) redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("OrderId","OID000001" + i,second3Later); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + "ms: redis 生成了一个订单任务: 订单号为:" + "OID000001" + i); } } // 消费消息 public void consumerDelayMessage() { while(true) { Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple> items = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeWithScores("OrderId", 0, 1); if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(items)) { System.out.println("当前没有等待的任务"); try{ Thread.sleep(500); }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } continue; } Double score = items.iterator().next().getScore(); Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); int nowSecond = (int) (cal.getTimeInMillis() / 1000); if(nowSecond > score) { String orderId = items.iterator().next().getValue().toString(); long resCnt = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove("OrderId", orderId); if(resCnt > 0) { System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + "ms: redis 消费了一个任务, 任务订单为:" + orderId); } } } } }
@SpringBootTest public class DelayQueue { @Autowired RedisDelayTask redisDelayTask; @Test public void delayTaskTest() { redisDelayTask.productDelayMessage(); redisDelayTask.consumerDelayMessage(); } }
输出结果:
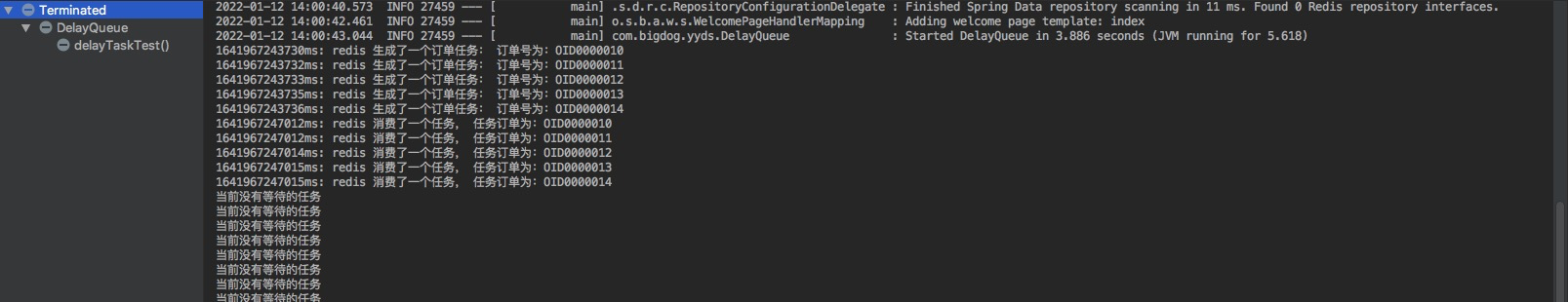
优点: 使用 redis作为消息通道,服务重启不需要额外处理
集群扩展方便
延时低
缺点: 需要额外redis 维护
六、 RabbitMQ 队列
思路1 : 利用 TTL(Time To Live)+DLX(Dead Letter Exchanges)
思路2: rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange插件
目前只是简单了使用 rabbitmq 的解概念思路,待详细了解各种机制后再来补充此种方式...
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/hjm4702192/article/details/80519010
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/188580413


