异常处理 Exception 相关梳理
异常处理 涉及 到的基础语法
一、try {} catch(Exception e) {} finally {} throw throws
1、 普通场景
public void exec01() {
System.out.println("方法开始");
try{
System.out.println("try 内方法");
int a = 1/0;
System.out.println("错误后面的方法");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("catch 内错误");
}
System.out.println("catch 后的方法");
}
打印结果: 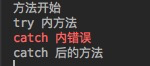 当程序执行到错误位置,跳转到 catch 内, 然后执行完 catch 后 程序继续执行。
当程序执行到错误位置,跳转到 catch 内, 然后执行完 catch 后 程序继续执行。
2、 finally 的使用 , 保证在finally 代码块内的内容一定会执行(JVM 退出情况例外), 常用于释放资源等;
public String exec01() {
System.out.println("方法开始");
try{
System.out.println("try 内方法");
int a = 1/0;
System.out.println("错误后面的方法");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("catch 内错误");
return "return 方法结束了";
}finally{
System.out.println("finally 执行到方法");
}
System.out.println("catch 后的方法");
return "方法的最后一句话";
}
 , 方法返回值:
, 方法返回值: 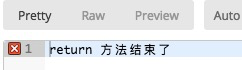
3、 当方法内 throw 抛出异常后,如果执行到 throw 这一句,且外面调用此方法处无 try catch, 则系统报异常,并停止。
public String throw01() {
System.out.println("方法开始");
try{
System.out.println("try 内方法");
int a = 1 / 0;
System.out.println("错误后面的方法");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("catch 方法内错误");
throw e;
}finally {
System.out.println("finally 代码块");
}
System.out.println("finally 后面的方法");
return "方法的最后一句话";
}
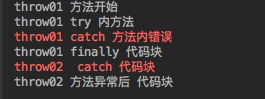
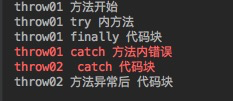
3.1 、 直接调用throw01 方法会报错
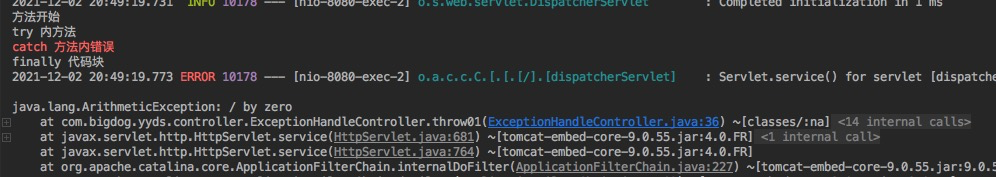
3.2、 调用 throw02 方法则正常, finally 代码块的执行顺序可能在catch之前,之后,或者外部的catch 之前, 总之是保证一定能执行,但时间不定
public void throw02(){
try{
throw01();
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("throw02 catch 代码块");
}
System.out.println("throw02 方法异常后 代码块");
}
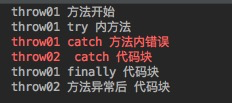
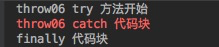
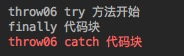
3.3、 当 finally 遇上返回值,执行顺序一样不定, 但执行的return 语句一定是finally 内的。
public String throw06() {
try{
System.out.println("throw06 try 方法开始");
int a = 1/0;
return "正常返回";
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("throw06 catch 代码块");
return "catch 代码块返回";
}finally {
System.out.println("finally 代码块");
return "finally 代码块返回";
}
}
3.4 、 如果直接抛出 new Exception() 则编译器本身会有提示,方法层必须 throws 出异常,以提醒调用此方法的代码去处理异常
public void throw03() throws Exception{
int a = 5;
throw new Exception();
}
二、 自定义异常处理
有时候对于不同的异常我们需要区分,并且做不同的处理,此时就需要我们对异常进行分类,并在异常处理时对不同的异常进行分类处理
自定义异常类继承自 RuntimeException, 如下例:
public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final String code;
private final String msg;
public BusinessException(String code, String msg){
super(msg);
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public BusinessException(String code, String msg, Throwable t){
super(msg,t);
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getCode(){return code;}
public String getMsg(){return msg;}
}
public class SystemException extends RuntimeException{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final String code;
private final String msg;
public SystemException(String code, String msg){
super(msg);
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public SystemException(String code, String msg, Throwable t){
super(msg,t);
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getCode(){return code;}
public String getMsg(){return msg;}
}
异常处理类, @ControllerAdvice 这个注解将这个类标记为全局异常处理类, @ExceptionHandler 注解内是自定义异常类,抛出这个异常时,修饰的方法就会处理对应的异常
///**
// * 全局异常处理
// * 为了方便前端处理,所有异常的 http状态码 返回200
// *
// */
@ControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 业务异常处理,统一返回400状态码,后改为返回200
*
* @param e
* @param response
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ExceptionResponse busExceptionHandler(BusinessException e, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.info("Business Exception catched!", e);
ExceptionResponse resp = new ExceptionResponse();
resp.setCode(e.getCode());
resp.setMsg(StringUtils.isBlank(e.getMessage()) ? "未知异常" : e.getMessage());
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value()); //400的异常统一返回200 状态码
return resp;
}
/**
* 系统异常处理,统一返回500状态码
*
* @param e
* @param response
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(SystemException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ExceptionResponse sysExceptionHandler(SystemException e, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.error("System Exception catched!", e);
ExceptionResponse resp = new ExceptionResponse();
resp.setCode(e.getCode());
resp.setMsg(StringUtils.isBlank(e.getMessage()) ? "未知异常" : e.getMessage());
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value()); //400的异常统一返回200 状态码
return resp;
}
/**
* 所有exception的处理
*
* @param e
* @param response
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public ExceptionResponse exceptionHandler(Exception e, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.error("Exception catched!", e);
ExceptionResponse resp = new ExceptionResponse();
if (e instanceof ServiceUnavailableException) {
resp.setCode(ResponseCode.FAIL.code);
resp.setMsg(ResponseCode.FAIL.msg);
log.info(e.getMessage());
} else if (e instanceof HttpMessageNotReadableException || e instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException
|| e instanceof MissingPathVariableException || e instanceof ServletRequestBindingException
|| e instanceof TypeMismatchException || e instanceof MissingServletRequestPartException
|| e instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) {
resp.setCode(ResponseCode.BAD_REQUEST.getCode());
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value()); //0400的异常统一返回http 200状态码
resp.setMsg(StringUtils.isBlank(e.getMessage()) ? "请求参数有误!" : e.getMessage());
} else {
resp.setCode(ResponseCode.FAIL.getCode());
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value());
resp.setMsg("系统异常!"); //统一返回“系统异常”,不将不可控的异常暴露给前端
}
return resp;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号