rabbitmq五种模式详解(含实现代码)
一、五种模式详解
1.简单模式(Queue模式)
当生产端发送消息到交换机,交换机根据消息属性发送到队列,消费者监听绑定队列实现消息的接收和消费逻辑编写.简单模式下,强调的一个队列queue只被一个消费者监听消费.
1.1 结构

- 生产者:生成消息,发送到交换机
- 交换机:根据消息属性,将消息发送给队列
- 消费者:监听这个队列,发现消息后,获取消息执行消费逻辑
1.2应用场景
常见的应用场景就是一发,一接的结构
例如:
- 手机短信
- 邮件单发
2.争抢模式(Work模式)
强调的也是后端队列与消费者绑定的结构
2.1结构

- 生产者:发送消息到交换机
- 交换机:根据消息属性将消息发送给队列
- 消费者:多个消费者,同时绑定监听一个队列,之间形成了争抢消息的效果
2.2应用场景
- 抢红包
- 资源分配系统
3.路由模式(Route模式 Direct定向)
从路由模式开始,关心的就是消息如何到达的队列,路由模式需要使用的交换机类型就是路由交换机(direct)
3.1 结构

- 生产端:发送消息,在消息中处理消息内容,携带一个routingkey
- 交换机:接收消息,根据消息的routingkey去计算匹配后端队列的routingkey
- 队列:存储交换机发送的消息
- 消费端:简单模式 工作争抢
3.2应用场景
- 短信
- 聊天工具
- 邮箱。。
手机号/邮箱地址,都可以是路由key
4.发布订阅模式(Pulish/Subscribe模式 Fanout广播)
不计算路由的一种特殊交换机
4.1结构

4.2应用场景
- 消息推送
- 广告
5.主题模式(Topics模式 Tpoic通配符)
路由key值是一种多级路径。中国.四川.成都.武侯区
5.1结构

-
生产端:携带路由key,发送消息到交换机
-
队列:绑定交换机和路由不一样,不是一个具体的路由key,而可以使用*和#代替一个范围
| * | 字符串,只能表示一级 |
| --- | --- |
| # | 多级字符串 | -
交换机:根据匹配规则,将路由key对应发送到队列
-
消息路由key:
- 北京市.朝阳区.酒仙桥
- 北京市.#: 匹配true
- 上海市.浦东区.*: 没匹配false
- 新疆.乌鲁木齐.#
5.2 应用场景
- 做物流分拣的多级传递.
6.完整结构

二、代码实现
1.创建SpringBoot工程
1.1 工程基本信息

1.2 依赖信息

1.3 配置文件applicasion.properties
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=springboot-demo
# Actuator Web 访问端口
management.server.port=8801
management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.include=*
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口
server.port=8801
######################### RabbitMQ配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ主机
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
# RabbitMQ虚拟主机
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=demo
# RabbitMQ服务端口
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
# RabbitMQ服务用户名
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
# RabbitMQ服务密码
spring.rabbitmq.password=admin
# RabbitMQ服务发布确认属性配置
## NONE值是禁用发布确认模式,是默认值
## CORRELATED值是发布消息成功到交换器后会触发回调方法
## SIMPLE值经测试有两种效果,其一效果和CORRELATED值一样会触发回调方法,其二在发布消息成功后使用rabbitTemplate调用waitForConfirms或waitForConfirmsOrDie方法等待broker节点返回发送结果,根据返回结果来判定下一步的逻辑,要注意的点是waitForConfirmsOrDie方法如果返回false则会关闭channel,则接下来无法发送消息到broker;
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirm-type=simple
# RabbitMQ服务开启消息发送确认
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true
######################### simple模式配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ服务 消息接收确认模式
## NONE:不确认
## AUTO:自动确认
## MANUAL:手动确认
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
# 指定最小的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.concurrency=1
# 指定最大的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.max-concurrency=1
# 开启支持重试
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.enabled=true
2.简单模式
2.1 创建SimpleQueueConfig 简单队列配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class SimpleQueueConfig {
/**
* 定义简单队列名.
*/
private final String simpleQueue = "queue_simple";
@Bean
public Queue simpleQueue() {
return new Queue(simpleQueue);
}
}
2.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SimpleProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "简单消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend( "queue_simple", message);
}
}
}
2.3 编写消费者
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SimpleConsumers {
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_simple")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
2.4 编写访问类
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/rabbitMq")
public class SimpleRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private SimpleProducer simpleProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "/simpleQueueTest")
public String simpleQueueTest() {
simpleProducer.sendMessage();
return "success";
}
}
2.5 测试启动项目访问 simpleQueueTest

3.Work队列
3.1 编写工作配置
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class WorkQueueConfig {
/**
* 队列名.
*/
private final String work = "work_queue";
@Bean
public Queue workQueue() {
return new Queue(work);
}
}
3.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String message = "工作消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("work_queue", message);
}
}
}
3.3 编写消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "work_queue")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
3.4 编写消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "work_queue")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
3.5 编写测试方法
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class WorkRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private WorkProducer workProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "workQueueTest")
public String workQueueTest() {
workProducer.sendMessage();
return "success";
}
}
3.6 测试启动项目访问 workQueueTest

控制台打印,发现10条消息 偶数条消费者1获取,奇数条消费者2获取,并且平均分配。
当然通过代码实现按需分配,即谁的性能强,谁优先原则,实现负载均衡。
配置可控分配数
4. 发布订阅模式(Publish/Subscibe模式)
订阅模式–多个消费者监听不同的队列,但队列都绑定同一个交换机
4.1 编写订阅配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class FanoutQueueConfig {
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String fanout1 = "fanout_queue_1";
private final String fanout2 = "fanout_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String fanoutExchange = "fanoutExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1() {
return new Queue(fanout1);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2() {
return new Queue(fanout2);
}
/**
* 声明交换机.
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange exchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(fanoutExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingFanoutQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(exchange);
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingFanoutQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(exchange);
}
}
4.2 编写订阅生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "订阅模式消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange", "", message);
}
}
}
4.3 编写订阅消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout_queue_1")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
4.4 编写订阅消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout_queue_2")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
4.5 编写测试方法
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class FanoutRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private FanoutProducer fanoutProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "fanoutQueueTest")
public String fanoutQueueTest() {
fanoutProducer.sendMessage();
return "success";
}
}
3.6 测试启动项目访问 fanoutQueueTest

控制台打印 ,发现两个绑定了不同队列的消费者都接受到了同一条消息查看RabbitMq 服务器:



5. 路由模式(Route模式 Direct定向)
5.1 编写路由配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class DirectQueueConfig {
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String direct1 = "direct_queue_1";
private final String direct2 = "direct_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String directExchange = "directExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue directQueue1() {
return new Queue(direct1);
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueue2() {
return new Queue(direct2);
}
/**
* 声明路由交换机.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(directExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectExchange1(Queue directQueue1, DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(exchange).with("update");
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectExchange2(Queue directQueue2, DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(exchange).with("add");
}
}
5.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessageA() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "路由模式--routingKey=update消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange", "update", message);
}
}
public void sendMessageB() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "路由模式--routingKey=add消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange", "add", message);
}
}
}
5.3 编写消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue_1")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
5.4 编写消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue_2")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
5.5 编写访问类
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class DirectRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private DirectProducer directProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "directQueueTest1")
public String directQueueTest1() {
directProducer.sendMessageA();
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "directQueueTest2")
public String directQueueTest2() {
directProducer.sendMessageB();
return "success";
}
}
5.6 测试启动项目访问directQueueTest1 , directQueueTest2
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/directQueueTest1
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/directQueueTest2
- 结果:
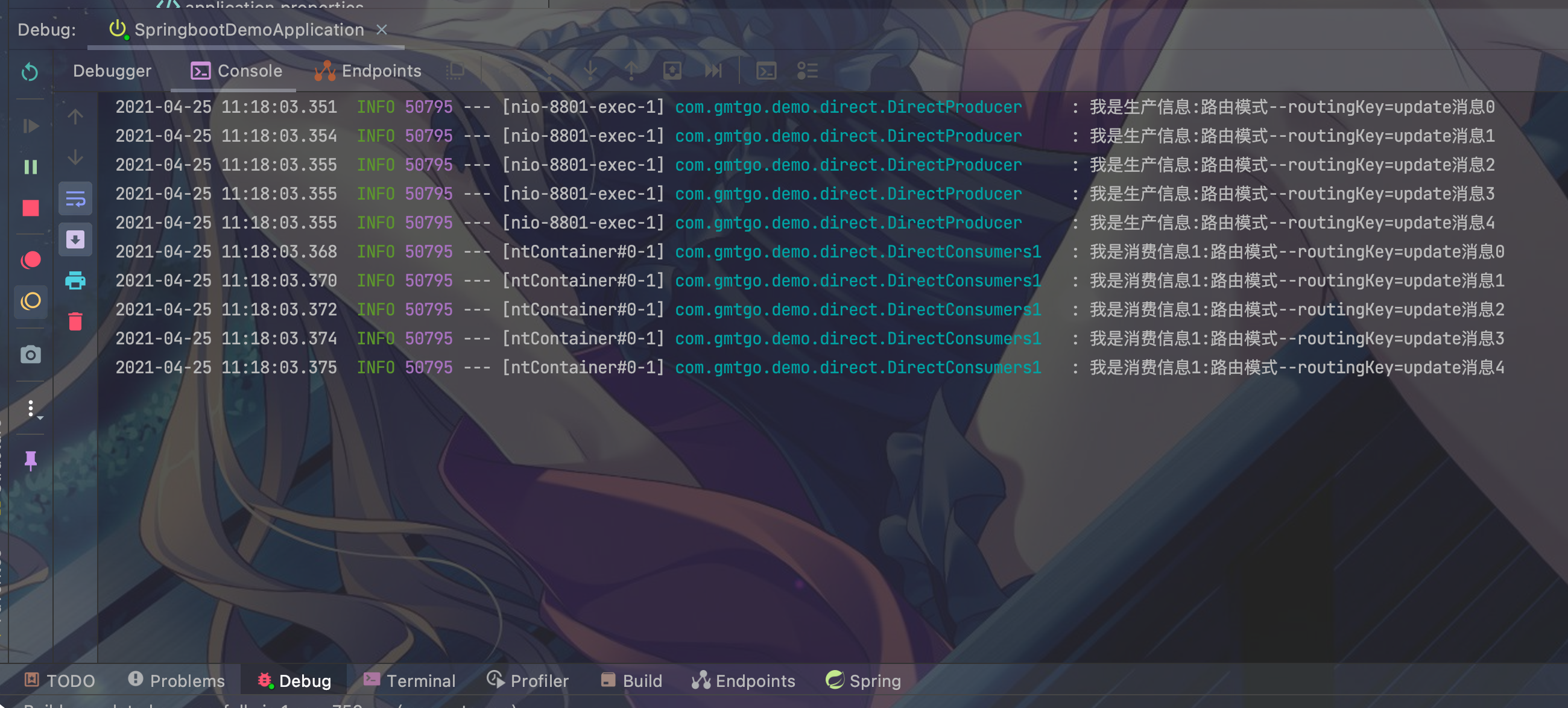
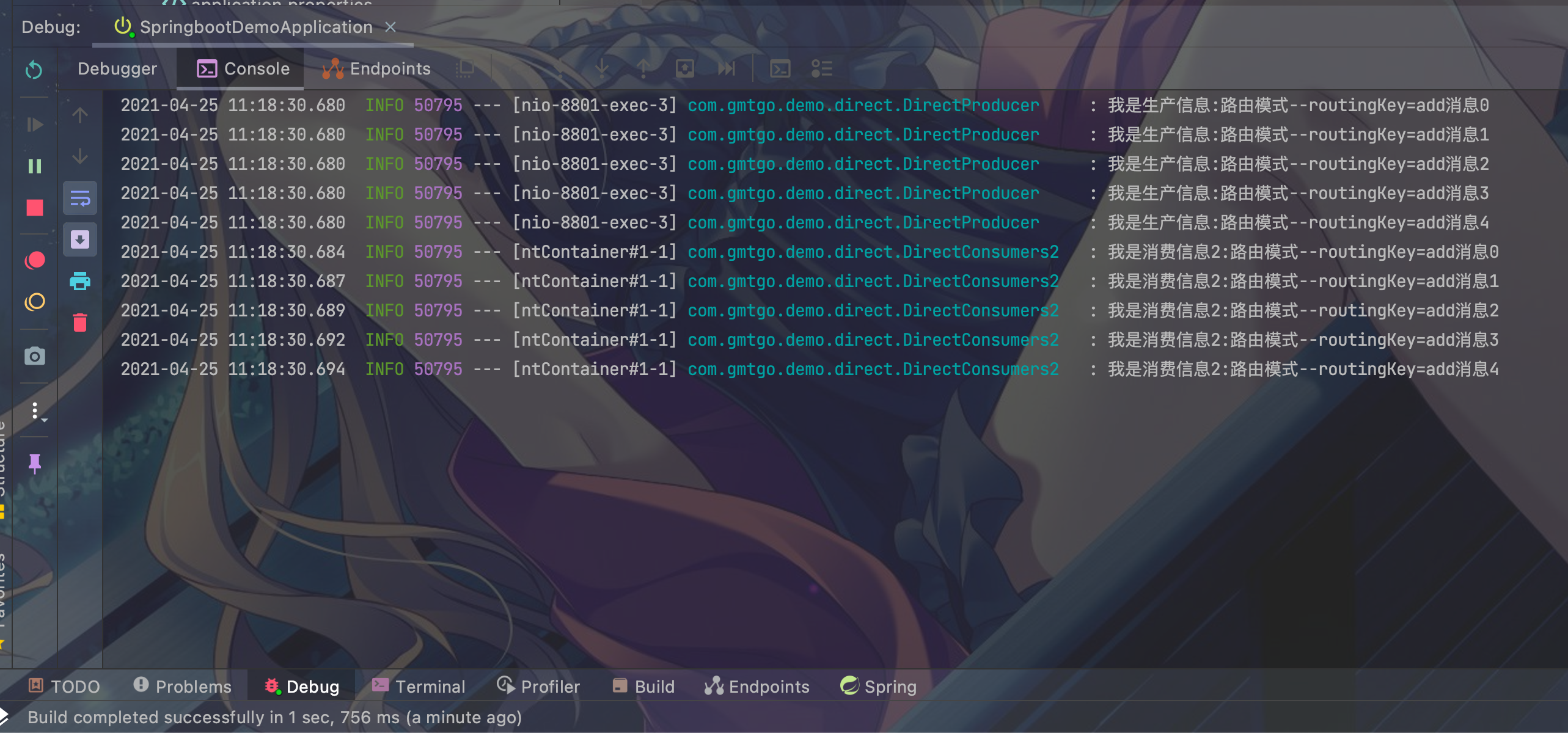
- directQueueTest1:
- directQueueTest2:
- directQueueTest1:
6. 主题模式(Topics模式 Tpoic通配符)
6.1 编写路由配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicQueueConfig {
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String topic1 = "topic_queue_1";
private final String topic2 = "topic_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String topicExchange = "topicExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return new Queue(topic1);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return new Queue(topic2);
}
/**
* 声明路由交换机.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(topicExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange1(Queue topicQueue1, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1).to(exchange).with("topic.keyA");
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
* 绑定的routing key 也可以使用通配符:
* *:匹配不多不少一个词
* #:匹配一个或多个词
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange2(Queue topicQueue2, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
}
6.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessageA() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "通配符模式--routingKey=topic.keyA消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "topic.keyA", message);
}
}
public void sendMessageB() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "通配符模式--routingKey=topic.#消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "topic.keyD.keyE", message);
}
}
}
6.3 编写消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue_1")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}",new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
6.4 编写消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue_2")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}",new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
6.5 编写访问类
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class TopicRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private TopicProducer topicProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "topicQueueTest1")
public String topicQueueTest1() {
topicProducer.sendMessageA();
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "topicQueueTest2")
public String topicQueueTest2() {
topicProducer.sendMessageB();
return "success";
}
}
6.6 测试启动项目访问topicQueueTest1 , topicQueueTest2
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/topicQueueTest1
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/topicQueueTest2
- 结果:
- topicQueueTest1,两个消费者都能消费
- topicQueueTest2,只有消费者2 可以消费

- topicQueueTest1,两个消费者都能消费
至此,五种队列的实现已结束!
7. 实现生产者消息确认
7.1 配置文件
######################### RabbitMQ配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ主机
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
# RabbitMQ虚拟主机
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=demo
# RabbitMQ服务端口
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
# RabbitMQ服务用户名
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
# RabbitMQ服务密码
spring.rabbitmq.password=admin
# RabbitMQ服务发布确认属性配置
## NONE值是禁用发布确认模式,是默认值
## CORRELATED值是发布消息成功到交换器后会触发回调方法
## SIMPLE值经测试有两种效果,其一效果和CORRELATED值一样会触发回调方法,其二在发布消息成功后使用rabbitTemplate调用waitForConfirms或waitForConfirmsOrDie方法等待broker节点返回发送结果,根据返回结果来判定下一步的逻辑,要注意的点是waitForConfirmsOrDie方法如果返回false则会关闭channel,则接下来无法发送消息到broker;
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirm-type=simple
# 连接超时时间
spring.rabbitmq.connection-timeout=20000
# RabbitMQ服务开启消息发送确认
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true
######################### simple模式配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ服务 消息接收确认模式
## NONE:不确认
## AUTO:自动确认
## MANUAL:手动确认
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
# 指定最小的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.concurrency=1
# 指定最大的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.max-concurrency=1
# 每次只消费一个消息
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.prefetch=1
# 开启支持重试
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.enabled=true
# 启用强制信息,默认为false
spring.rabbitmq.template.mandatory=true
7.2 编写消息发送确认类 RabbitConfirmCallback
package com.gmtgo.demo.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
public class RabbitConfirmCallback implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback {
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
log.info("=======ConfirmCallback=========");
log.info("correlationData {} " , correlationData);
log.info("ack = {}" , ack);
log.info("cause = {}" , cause);
log.info("=======ConfirmCallback=========");
}
}
7.3 编写消息发送交换机返回机制RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack
package com.gmtgo.demo.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
public class RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack implements RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
log.info("--------------ReturnCallback----------------");
log.info("message = " + message);
log.info("replyCode = {}", replyCode);
log.info("replyText = {}", replyText);
log.info("exchange = {}", exchange);
log.info("routingKey = {}", routingKey);
log.info("--------------ReturnCallback----------------");
}
}
7.4 RabbitMQ配置
在我们的rabbit队列配置类里设置RabbitTemplate
举例:
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import com.gmtgo.demo.config.RabbitConfirmCallback;
import com.gmtgo.demo.config.RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicQueueConfig {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@PostConstruct
public void initRabbitTemplate() {
// 设置生产者消息确认
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitConfirmCallback());
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(new RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack());
}
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String topic1 = "topic_queue_1";
private final String topic2 = "topic_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String topicExchange = "topicExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return new Queue(topic1);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return new Queue(topic2);
}
/**
* 声明路由交换机.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(topicExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange1(Queue topicQueue1, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1).to(exchange).with("topic.keyA");
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
* 绑定的routing key 也可以使用通配符:
* *:匹配不多不少一个词
* #:匹配一个或多个词
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange2(Queue topicQueue2, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
}
启动项目发送消息,消息被正常消费,confim回调返回ack=true如果我们将exchange修改,发送到一个不存在的exchange中,会怎么样呢?
会发现confirm回调为false,打印出结果为不存在topicExchange1111的交换机

如果我们在消费端处理逻辑时出错会怎么样呢?修改消费端代码我们在消费时让它报错

confirm回调为true,但是在rabbitmq的web界面会发现存在5条没有消费的消息

如果我们把
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false,false);
中最后一个参数改为false呢,会发现在web管理界面没有未被消费的消息,说明这条消息已经被摒弃。
实际开发中,到底是打回到队列呢还是摒弃,要看自己的需求,但是打回队列应该有次数限制,不然会陷入死循环。
继续测试,将routingKey修改为一个没有的key,
7.5 结论
- 如果消息没有到exchange,则confirm回调,ack=false
- 如果消息到达exchange,则confirm回调,ack=true
- exchange到queue成功,则不回调return
- exchange到queue失败,则回调return



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号