一些简单二分题,简单的hash,H(i),字符串题
说在前面: 题是乱七八糟的.
几个二分的题. (但是我的做法不一定是二分,有些裸暴力.
1. Equations HDU - 1496
输入a,b,c,d问你这个方程有多少解.
a*x1^2+b*x2^2+c*x3^2+d*x4^2=0
a,b,c,d属于[-50, 50]
x1,x2,x3,x4属于[-100,100]且Xi不等于零
解法很简单, 把式子拆两边,拆成a*x1^2 + b*x2^2 = -(c*x3^2 + d*x4^2)的形式,然后暴力枚举就行了.
// 注意 如果只枚举正数开始枚举的 答案注意乘以16.

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> const int maxn = 1000010; int z[maxn], f[maxn]; int main() { int x1, x2, x3, x4, tmp; int a, b, c, d, res; while (~scanf("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d)) { res = 0; if ((a>0 && b>0 && c>0 && d>0) || (a<0 && b<0 && c<0 && d<0)) goto A; // 加上无解的判断 会快很多. memset(z, 0, sizeof(z)); memset(f, 0, sizeof(f)); for (x1=1; x1<=100; ++x1) for (x2=1; x2<=100; ++x2) { tmp = a * x1 * x1 + b * x2 * x2; if (tmp < 0) f[-tmp]++; else z[tmp]++; } for (x3=1; x3<=100; ++x3) for (x4=1; x4<=100; ++x4) { tmp = c * x3 * x3 + d * x4 * x4; if (tmp <= 0) res += z[-tmp]; else res += f[tmp]; } res *= 16; // 注意 答案要乘以16 A: printf("%d\n", res); } return 0; }
2. B - Eqs POJ - 1840
a1x1^3+a2x2^3+a3x3^3+a4x4^3+a5x5^3=0
和上一个题一样的问方程有多少解,我们拆开.
然后注意到 a1x1^3+a2x2^3 = -(a3x3^3+a4x4^3+a5x5^3) 左边只有2500种值,
所以我们不妨把值存起来,然后二分就可以简单过了.
二分思路很好想,但是我....做的时候SB了,没有用二分写.
还是直接暴力,但是爆内存了.然后我就类似前向星一样建了个hash表来存值.然后继续暴力...

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <map> using namespace std; int qsz; int head[13500000]; int hash_table[1000000]; int hash_val[1000000]; void add(int val) { hash_val[qsz] = val; hash_table[qsz] = head[abs(val)]; head[abs(val)] = qsz++; } int find(int val) { int res = 0; for (int i=head[abs(val)]; i; i=hash_table[i]) { if (val + hash_val[i] == 0) res++; // printf("%d ", i); } return res; } int main() { int a, b, c, d, e; while (scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d, &e)!=-1) { memset(head, 0, sizeof(head)); qsz = 1; int x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, tmp; for (x1=-50; x1<=50; ++x1) { if (!x1) continue; for (x2=-50; x2<=50; ++x2) { if (!x2) continue; tmp = x1 * x1 * x1 * a + x2 * x2 * x2 * b; add(tmp); } } long long res = 0; for (x3=-50; x3<=50; ++x3) { if (!x3) continue; for (x4=-50; x4<=50; ++x4) { if (!x4) continue; for (x5=-50; x5<=50; ++x5) { if (!x5) continue; tmp = x3 *x3 * x3 * c + x4 * x4 * x4 * d + x5 * x5 * x5 * e; if (tmp>12500000 || tmp<-12500000) continue; res += find(tmp); } } } printf("%lld\n", res); } return 0; }
当然,这道题还有一些有趣的事情, 如果你直接用map[value]来暴力的话,会T, 但是如果你先用map.find(value)来判断一下子的话..可以水过去.
我发现STL用lower_bound 之类的 用类的方法 会比 函数快得多!!

#include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; map<int, int> z; int main() { int a, b, c, d, e; while (scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d, &e)!=-1) { z.clear(); int x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, tmp; for (x1=-50; x1<=50; ++x1) { if (!x1) continue; for (x2=-50; x2<=50; ++x2) { if (!x2) continue; tmp = x1 * x1 * x1 * a + x2 * x2 * x2 * b; z[tmp]++; } } long long res = 0; for (x3=-50; x3<=50; ++x3) { if (!x3) continue; for (x4=-50; x4<=50; ++x4) { if (!x4) continue; for (x5=-50; x5<=50; ++x5) { if (!x5) continue; tmp = x3 *x3 * x3 * c + x4 * x4 * x4 * d + x5 * x5 * x5 * e; if (z.find(tmp) != z.end()) res += z[tmp]; } } } printf("%lld\n", res); } return 0; }
3. Sumsets POJ - 2549
题意很简单,给你一些数,然后要求出满足a+b+c=d式子,d的最大指. 同时a,b,c,d都不相同.
范围是1~1000个数, 我们还是不难想到拆两边,然后就有 a+b = d - c 然后我们把左边值保存起来,
同时记录下标,然后我们再枚举右边,在左边的值中二分查找,同时核对小标. 不难发现,这是可行的..

#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; struct nobe { int a, b; ll val; bool operator < (const nobe &a) const { return val < a.val; } nobe () {} nobe (int ja, int jb, ll jval) : a(ja), b(jb), val(jval) {}; }; ll dt[1000500]; nobe date[1000500]; int main() { int n, i, j; // freopen("E:\\input.txt", "r", stdin); while (scanf("%d", &n) && n) { for (i=1; i<=n; ++i) scanf("%lld", dt+i); sort(dt+1, dt+1+n); int cnt = 1; for (i=1; i<=n; ++i) for (j=i+1; j<=n; ++j) { date[cnt].a = i; date[cnt].b = j; date[cnt++].val = dt[i] + dt[j]; // printf("-- %I64d \n", date[cnt-1].val); } sort(date+1, date+1+cnt); // for (i=1; i<cnt; ++i) int ans = 0; for (i=n; i>=1; --i) { // printf("%I64d \n", dt[i]); for (j=1; j<=n; ++j) { if (i == j) continue; ll val = dt[i] - dt[j]; // printf("%I64d \n", val); int left = 1, right = cnt; while (left <= right) { int m = (left + right) / 2; if (date[m].val >= val) right = m - 1; else left = m + 1; } if (date[left].val == val) { // printf("%I64d %I64d \n", ); if (date[left].a != i && date[left].b != i && date[left].a != j && date[left].b != j) { ans = i; goto A; } } } } A: if (!ans) printf("no solution\n"); else printf("%lld\n", dt[ans]); } return 0; }
4. Stammering Aliens UVALive - 4513
一个简单字符串的题目,题意是这样的.
给你两个数n,m和一个字符串s, 其中m表示字符的种类
输出长度为n的子串有多少种
范围: 子串所形成的字符集不会超过一千六百万
例如: n= 3 m=4 字符串为: daababac
输出: 5
解释: 长度为3的子串有五种:
“daa”; “aab”; “aba”; “bab”; “bac“
题目说了 子串所形成的字符集的种类不超过一千六百万,也就是说长度为n的子串最多只有一千六百万种,所以我们不妨把长度为n的子串都转化成十进制数 ,然后判种类. (这种转化成对应进制数的方法有一种对应的算法叫做: Rabin-Karp算法. 可以自己看看,不过感觉也没啥用..至少我用不到= =.)

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; char str[1000010]; int xhash[256]; bool _hash[16000010]; int main() { int n, m, i, len, cnt, pwr; while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)) { scanf("%s", str + 1); len = strlen(str + 1); cnt = 0; memset(xhash, -1, sizeof(xhash)); memset(_hash, 0, sizeof(_hash)); for (i=1; i<=len; ++i) if(xhash[str[i]] == -1) xhash[str[i]] = cnt++; pwr = 1; for (i=1; i<n; ++i) pwr *= m; int res = 0; for (i=1; i<n; ++i) res = res * m + xhash[str[i]]; for (i=n; i<=len; ++i) { res = res * m + xhash[str[i]]; _hash[res] = true; res = res - xhash[str[i-n+1]] * pwr; } int ans = 0; for (i=0; i<16000010; ++i) if (_hash[i]) ans++; printf("%d\n", ans); } return 0; }
这道题还有一个类似的做法,就是求出长度为n的子串的hash,然后用set保存,最好set的大小就是答案了.
根据白书上的P224页给的hash方法,我们可以知道,预处理出H(i)以后,我们就可以O(1)的求出一段区间的hash值了.. (具体的方法介绍下面,因为懒,我直接放公式,没有好的解说,只适合自己看.所以不要看...不懂去看别的博客,公式只是加字数罢了.或者以后复习过一下大概而已.)

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <set> using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long ull; const int maxn = 1e6+500; const ull SmallPrime = 31; char s[maxn]; set<ull> se; ull pre[maxn]; ull _hash[maxn]; int main() { pre[0] = 1; for (int i=1; i<maxn; ++i) pre[i] = pre[i-1] * SmallPrime; int t, n, i, m; while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)) { scanf("%s", s + 1); int len = strlen(s+1); se.clear(); _hash[len+1] = 0; for (i=len; i>=1; --i) _hash[i] = _hash[i+1] * SmallPrime + s[i]; for (i=n; i<=len; ++i) se.insert(_hash[i-n+1] - _hash[i+1] * pre[n]); printf("%d\n", se.size()); } return 0; }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
二,白书224给出了一个基于哈希值的LCP算法:
为每个后缀计算一个哈希值 H(i) = H(i+1)*x + s[i]
// 注意,这儿s[]下标是从1开始的.白书是从0开始的.
所以对于
H(i) = s[i]*x + s[i+1]*x^2 + … + s[n]*x^(n-i+1)
所以我们对应一段子串s[l...r]它两端对应的hash值是:
H(l) = s[l]*x + s[l+1]*x^2 + … + s[r]*x^(r-l+1) +
+ s[r+1]^(r-l+2) + … + s[n]*x^(n-l+1)
H(r) = s[r]*x + s[r+1]*x^2 + … + s[r]*x^(n-r+1)
所以可以定义H(l, r) = H(l) – H(r+1) * x ^ (r – l + 1)
所以 H(l, r) = s[l]*x + x[l]*x^2 + … + x[r]*x^(r-l+1)
// 说白了…就是类似前缀和的思想.
也可以看图:
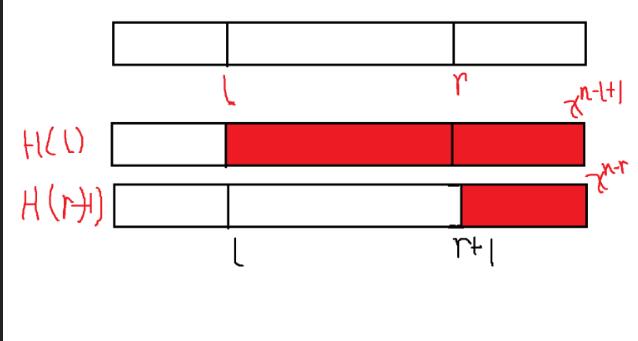
当我们预处理好H(i)后,我们就可以通过减法来O(1)的求出H(l, r) 这一段的hash值了. x是一个质数. 相差x^(r-l+1)次方
然后预处理H(i)可以正着,也可以倒着,怎么顺手怎么写呗.一般没有什么大问题.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OK 讲到白书的哈希方法,那就把白书的题放上来.
5.Stammering Aliens UVALive - 4513
给一个字符串,找出至少出现m次的最长字符串.存在则输出长度及其起始位置.
如果不存在,则输出”none”
M<=4e4
这个题呢,根据白书的说法可以后缀数组,也可以二分答案+hash做.
后缀数组我不会.所以我是二分答案做的. 二分答案很暴力..
怎么二分呢? 没错,我们就直接二分最长的字符串为mid, 然后暴力把长度为mid的所有子串的hash值求出. (这个够暴力把!)
然后暴力判断是否有出现过m次的,如果有那么答案应该向大的方向继续二分,如果没有就往向的方向进行二分.
(注: 为什么可以这样二分呢? 想一想,.
如果我们二分长度为mid的子串出现了至少m次,同时我们也知道这些子串也是某串的子串,所有不难知道,如果最终答案ans一定是>=ans的.
满足我们二分的性质,所以可以二分.)
(再注: 有些二分的写法是需要特判1的情况的, 有些不需要.我的是需要的,白书的是不需要的.)

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long ull; const int maxn = 1e5+10; const int o_o = 31; ull x[maxn]; ull suf[maxn]; ull hx[maxn]; int rk[maxn]; char s[maxn]; int pos; bool cmp(int a, int b) { return hx[a]!=hx[b] ? hx[a]<hx[b] : a<b; } bool isok(int L, int n, int len) { int i; for (i=1; i<=len-L+1; ++i) { hx[i] = suf[i] - suf[i+L] * x[L]; rk[i] = i; // printf("%d %d %llu %llu %llu %llu %llu\n", i, L, hx[i], suf[i] , suf[i+L] , x[len], suf[i+L] * x[len]); } sort(rk+1, rk+len-L+2, cmp); int tpos = 0; int cnt = 1; for (i=2; i<=len-L+1; ++i) { if (hx[rk[i]]!=hx[rk[i-1]]) cnt = 1; else cnt++; if (cnt >= n) { tpos = max(tpos, rk[i]); } // printf("------- %d %d \n", rk[i-1], rk[i]); } if (tpos) pos = tpos; return tpos; } int main() { // freopen("E:\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int n, i, len; int left, right; x[0] = 1; for (i=1; i<maxn; ++i) x[i] = x[i-1] * o_o; while (~scanf("%d", &n) && n) { scanf("%s", s+1); len = strlen(s+1); if (n > len) { printf("none\n"); continue; } else if (n == 1) { printf("%d 0\n", len); continue; } suf[len+1] = 0; for (i=len; i>=1; --i) suf[i] = suf[i+1] * o_o + s[i]; int ans = 1; if (!isok(1, n, len)) { printf("none\n"); continue; } left = 1; right = len + 1; while (left <= right) { int m = (left + right) >> 1; if (!isok(m, n, len)) { right = m - 1; } else{ ans = m; left = m + 1; } } isok(ans, n, len); printf("%d %d\n", ans, pos-1); } return 0; }
OK,然后继续.
刚才的题是不带修改的,那么如果修改的呢?
6. AC's String HDU - 3973
给你一个单词的集合W和一个字符串S.有2个操作,
1,修改, 改变字符串的某个字符.
2,询问, 询问某子串是否属于为单词集合.属于输出Yes, 不属于输出No
范围: 多Case. T<=20 单词数 <= 1e4 单词字符总数 <= 2e6 字符串长度|S| <= 1e5 操作 <= 1e5
如果不带修改,那么很明显的,直接预处理出hash函数然后就可以O(1)的查询了, 但是带了修改. 那我们可不可以通过维护H(i)来支持修改,然后继续快速的查询呢? 怎么维护呢?
答案是线段树. 详细见图片.
这是建树的时候
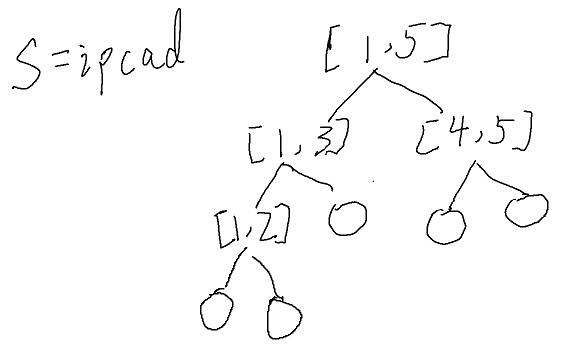
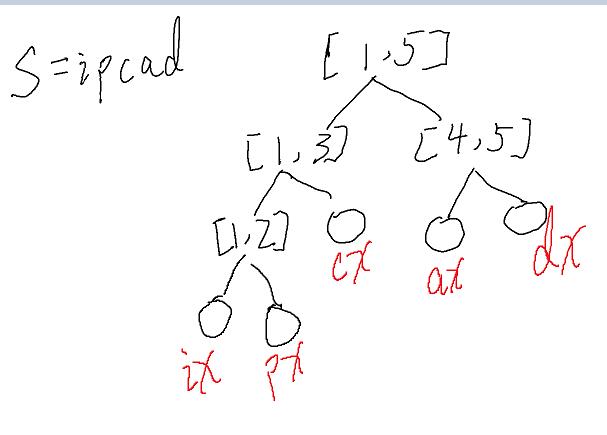
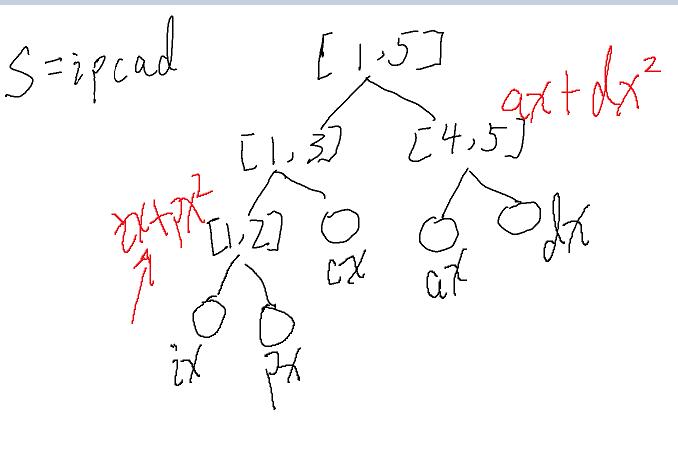
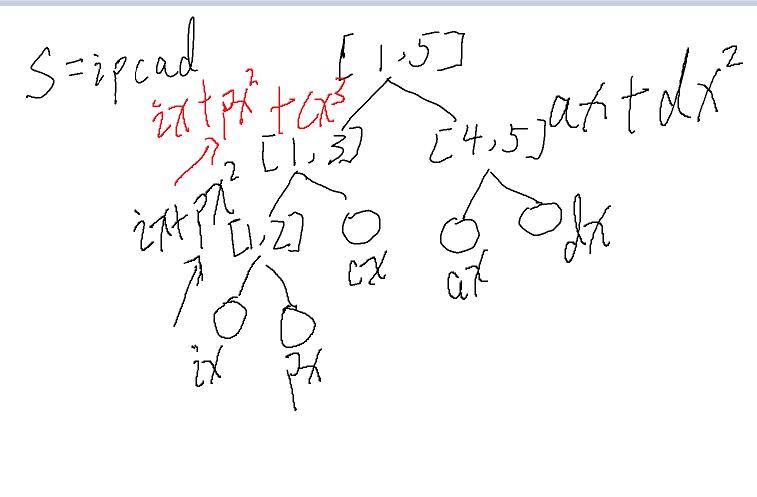
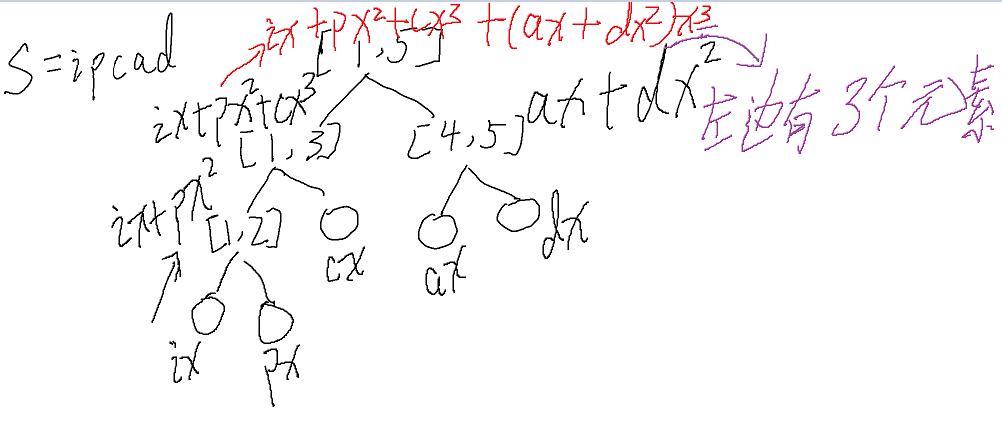
这是我们建好的树
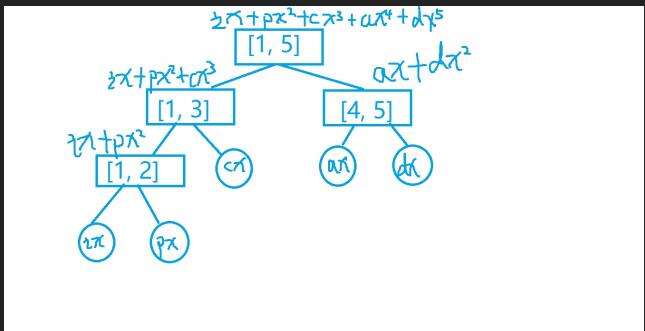
然后这是查询的时候
假设我们查询[3,5]这个子串
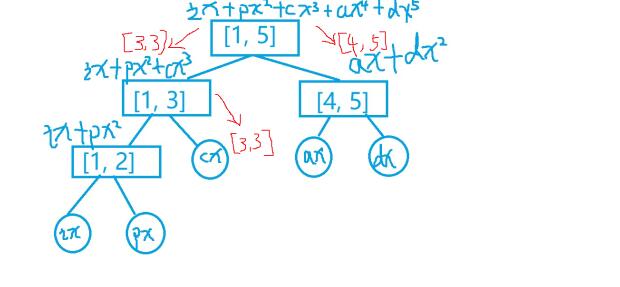
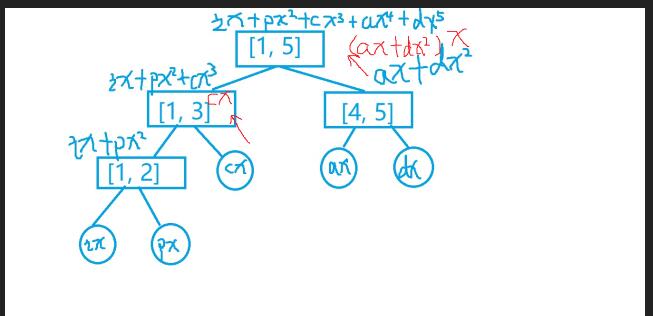
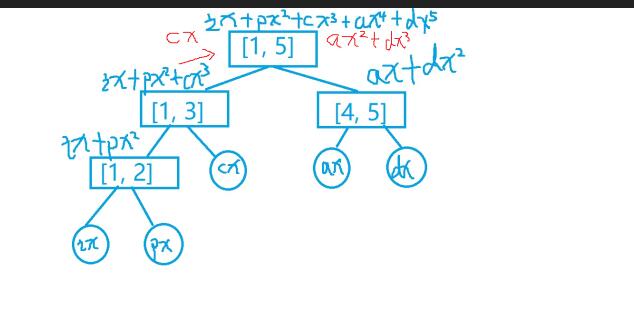
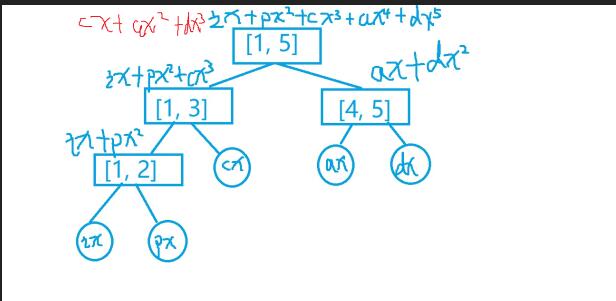
OK 然后这是代码.. (为什么没有解说呢....因为..我觉得你看着图 或者 自己画个图,只有会写线段树和理解哈希的方法H(i),就很简单了....好吧是我说不来.靠图来凑.2333

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <set> using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long ull; #define lson rt<<1 #define rson rt<<1|1 const int maxn = 2e6+500; const ull SmallPrime = 31; char s[maxn]; set<ull> se; ull pre[maxn]; ull _hash() { int i, len = strlen(s + 1); ull res = 0; for (int i=1; i<=len; ++i) res = res + (s[i] - 'a' + 1) * pre[i]; return res; } struct nobe { int l; int r; ull val; }te[maxn<<2]; inline void pshup(int rt) { te[rt].val = te[lson].val + te[rson].val * pre[te[lson].r - te[lson].l + 1]; } void build(int l, int r, int rt) { te[rt].l = l; te[rt].r = r; if (l == r) { // te[rt].val = s[l] * pre[1]; te[rt].val = (s[l] - 'a' + 1) * pre[1]; // te[rt].val = (s[l] - 'a' + 1); return ; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; build(l, m, lson); build(m+1, r, rson); pshup(rt); } void update(int l, int rt) { if (l==te[rt].l && te[rt].r==l) { te[rt].val = (s[l] - 'a' + 1) * pre[1]; // te[rt].val = (s[l] - 'a' + 1) ; return ; } int m = (te[rt].l + te[rt].r) >> 1; if (l <= m) update(l, lson); if (l > m) update(l, rson); pshup(rt); } ull query(int l, int r, int rt) { if (l>te[rt].r || te[rt].l>r) return 0; if (l<=te[rt].l && r>=te[rt].r) return te[rt].val; int m = (te[rt].l + te[rt].r) >> 1; if (r <= m) return query(l, r, lson); else if (l > m) return query(l, r, rson); else return query(l, m, lson) + query(m+1, r, rson) * pre[m - l + 1]; // 注意这里哟. 这也是图为什么一步一步画,我想体现的就是这一步..当然,能不能传达给你们,不管我的事2333 } int main() { pre[0] = 1; for (int i=1; i<maxn; ++i) pre[i] = pre[i-1] * SmallPrime; int t, n, i; scanf("%d", &t); for (int cas=1; cas<=t; cas++) { se.clear(); scanf("%d", &n); for (i=1; i<=n; ++i) { scanf("%s", s+1); se.insert(_hash()); } scanf("%s", s+1); n = strlen(s+1); build(1, n, 1); int q; printf("Case #%d:\n", cas); scanf("%d", &q); char op[16]; int l, r; for (i=1; i<=q; ++i) { scanf("%s", op); if (op[0] == 'C') { scanf("%d%s", &l, op); ++l; s[l] = op[0]; update(l, 1); } else { scanf("%d%d", &l, &r); ++l; ++r; printf("%s\n", (se.find(query(l, r, 1)) != se.end()) ? "Yes" : "No"); } } } return 0; }
emmmmm 不想写了.





