06.SpringBoot核心技术
一、配置文件
SpringBoot除了可以在全局编写一个properties配置文件外,还可以使用yaml作为配置文件
新建一个类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Component
@Data
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Integer age;
private String[] interests;
private List<String> animal;
private Map<String, Object> score;
private Set<Double> salarys;
}
编写yaml配置文件
person:
username: ss
boss: true
Date: 2019/7/8
age: 20
interests: [ylc,ww]
animal:
- 篮球
- 足球
- 羽毛球
score: {English: 99,math: 66,chinese: 100}
salarys:
- 99.9
- 12.3
- 45.0
发起请求
@Autowired
Person person;
@RequestMapping("/GetPerson")
public Person getPerson()
{
return person;
}

单引号会将/n作为字符串输出,双引号会将字符串作为换行输出,双引号会转义
properties配置文件优先级大于yaml
让自定义的类和配置文件绑定一般有提示可以引入下包,可以更方便的开发
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
二、Web开发
先新建一个自动配置的SpringBoot项目
静态资源访问
只要静态资源放在类路径(main)下: /static(or/publicor/resourcesor/META-INF/resources`
访问 : 当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名
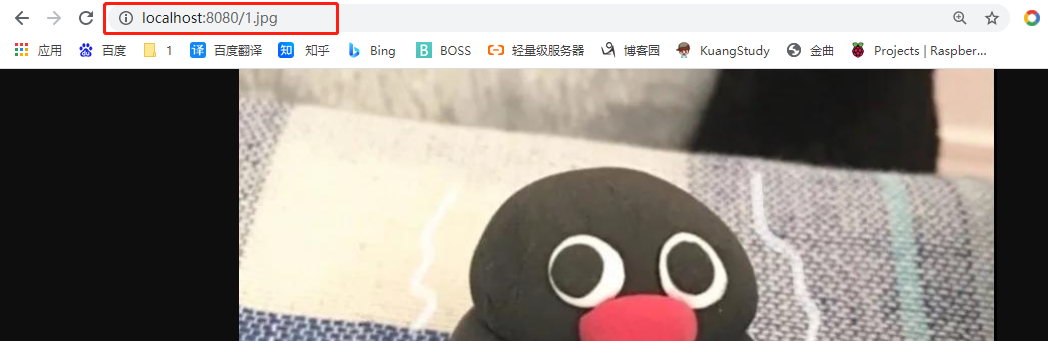
原理:当有控制器的情况下,请求会先找Controller处理,没有找到就找静态资源处理器,如果静态资源也找不到返回404
一般项目相会指定静态资源访问路径前缀:
application.yaml
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**
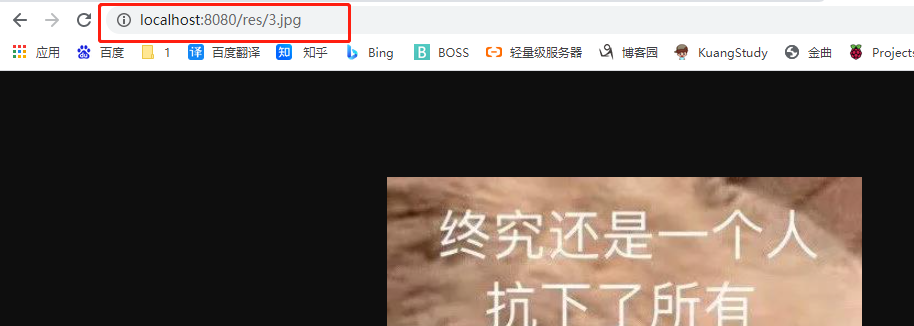
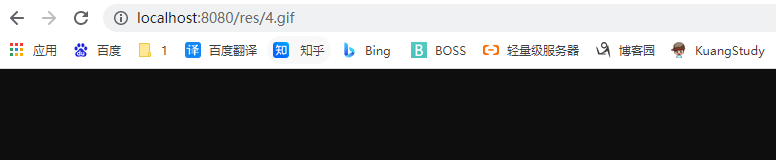
还可以指定静态资源的目录:
web:
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/Picture/]
欢迎页支持
在静态资源路径下 index.html,如果配置静态资源能访问前缀就会导致index.html页面不能被访问
自定义 Favicon
欢迎页图标:默认在static下引入favicon.ico图标就可以实现
普通参数和基本注解
1.1 @PathVariable
用于接收RestFul风格的参数,路径变量
@RestController
public class HelloController {
//restFul风格
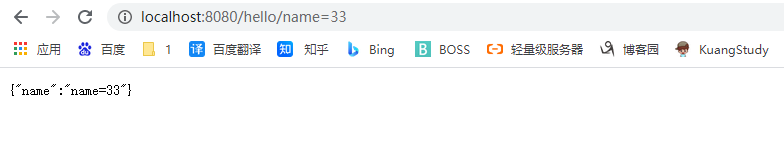
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
public Map<String,String> Hello(@PathVariable("name") String name)
{
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name",name);
return map;
}
}
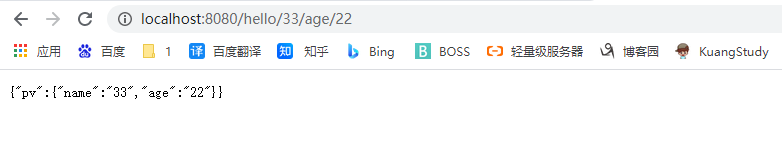
还可以用一个Map集合全部接收出来
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}/age/{age}")
public Map<String,Object> Hello2(@PathVariable Map<String,String> pv)
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("pv",pv);
return map;
}
1.2 @RequestHeader
用于获取指定请求头
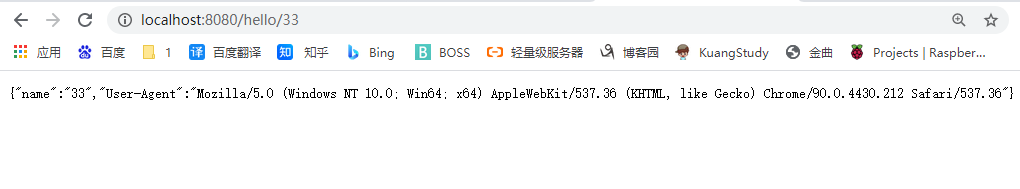
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
public Map<String,String> Hello3(@PathVariable("name") String name,@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String length )
{
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name",name);
map.put("User-Agent",length);
return map;
}
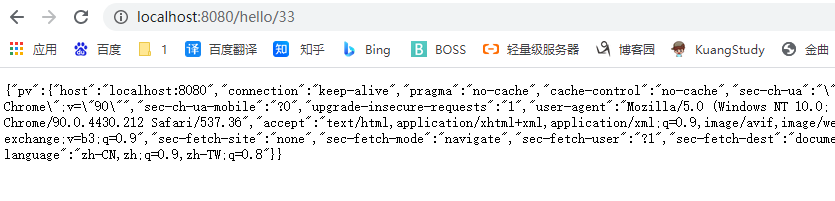
获取全部请求头,把头部参数用一个Map接收
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
public Map<String,Object> Hello3(@PathVariable("name") String name,@RequestHeader Map<String,String> pv )
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("pv",pv);
return map;
}
1.3 @RequestParam
获取指定请求参数
@GetMapping("/hello")
public Map<String,Object> Hello3(@RequestParam("name") String name,@RequestParam("age") Integer age )
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name",name);
map.put("age",age);
return map;
}
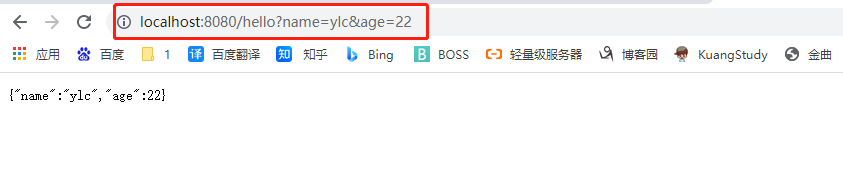
获取全部参数
@GetMapping("/hello2")
public Map<String,Object> Hello4(@RequestParam Map<String,String> params )
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("params",params);
return map;
}
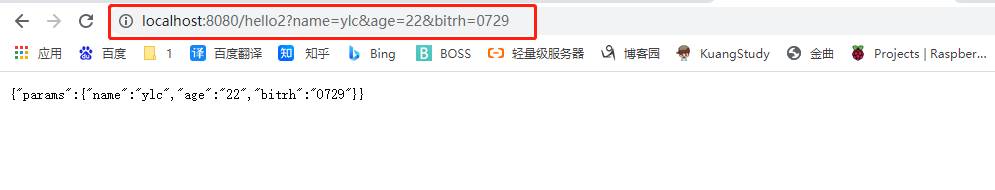
1.4 @CookieValue
获取指定的Cookie值
@GetMapping("/GetCookie")
public Map<String,Object> Hello5(@CookieValue("_ga") String _ga )
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("_ga",_ga);
return map;
}
获取Cookie
@GetMapping("/GetCookie")
public Map<String,Object> Hello5(@CookieValue("_ga") Cookie cookie )
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("cookie",cookie);
System.out.println(cookie.getName());
System.out.println(cookie.getValue());
return map;
}
1.5 @RequestBody
获取请求体,只有Post请求才有请求体,表单提交
<form action="/save" method="post">
用户名:<input name="username"/>
密码:<input name="pwd"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
@PostMapping("/save")
public Map<String,Object> PostMethod(@RequestBody String content)
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("content",content);
return map;
}
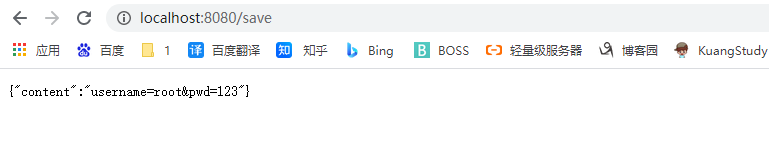
1.6 @RequestAttribute
获取request的属性
@Controller
public class TextController {
@GetMapping("/goto")
public String goToPage(HttpServletRequest request)
{
request.setAttribute("msg","成功");
return "forward:/success";
}
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/success")
public Map<String,Object> Success(HttpServletRequest request)
{
Object msg = request.getAttribute("msg");
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("msg",msg);
return map;
}
}
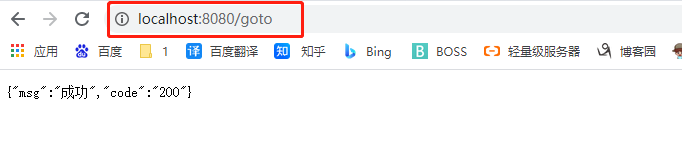
发送请求响应成功,利用转发把信息发送到成功页面
视图解析和模板引擎
Web原生组件注入
1.1 使用Selvlet API
Servlet
在主方法指定Servlet放置的位置
//servlet扫描的位置
@ServletComponentScan(basePackages = "com.ylc")
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootWebApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootWebApplication.class, args);
}
}
编写Servlet
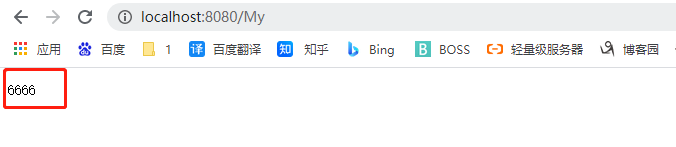
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/My")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("6666");
}
}
Filter
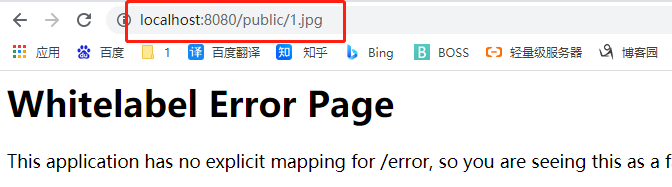
@Slf4j
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = {"/public/*"})
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
//filter初始化
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
log.info("Filter初始化");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("Filter销毁");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("Filter过滤");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
}
访问public下的都会被拦截

Listener
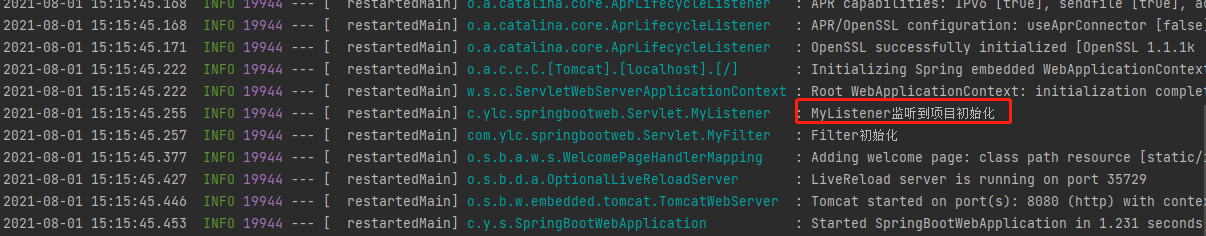
@Slf4j
@WebListener
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
log.info("MyListener监听到项目初始化");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
log.info("MyListener监听到项目完成");
}
}
1.2 RegistrationBean Springboot中注入组件
ServletRegistrationBean、FilterRegistrationBean、 ServletListenerRegistrationBean
//保证组件始终是单实例
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)
public class MyRegistConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet()
{
MyServlet myServlet=new MyServlet();
return new ServletRegistrationBean(myServlet,"/My");
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter()
{
MyFilter myFilter=new MyFilter();
//第一种
//这里只有通过myServlet的请求下才会显示666 才会被过滤器找到
//return new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter,myServlet());
//第二种 自己定义过滤url
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean=new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter);
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/public/*"));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myLister()
{
MyListener myListener=new MyListener();
return new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(myListener);
}
}
此方法同理
定制化
Web应用 编写一个配置类实现WebMvcConfigurer 即可定制化web功能,里面加@Bean给容器中再扩展一些组件
@EnableWebMvc + 实现WebMvcConfigurer接口 —— @Bean 可以全面接管SpringMVC,所有规则全部自己重新配置; 实现定制和扩展功能
三、数据访问
数据源配置
导入JDBC场景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
场景里面已经导入了数据源、JDBC、事务,还需要导入数据库的驱动,因为官方不知道我们接下要操作什么数据库
默认版本:<mysql.version>8.0.22</mysql.version>
数据库版本要和驱动版本对应
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.22</version>
</dependency>
//重新声明版本(maven的属性的就近优先原则)
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.49</mysql.version>
</properties>
分析自动配置
-
DataSourceAutoConfiguration : 数据源的自动配置
-
修改数据源相关的配置:spring.datasource
-
数据库连接池的配置,是自己容器中没有DataSource才自动配置的
-
底层配置好的连接池是:HikariDataSource
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(PooledDataSourceCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ DataSource.class, XADataSource.class })
@Import({ DataSourceConfiguration.Hikari.class, DataSourceConfiguration.Tomcat.class,
DataSourceConfiguration.Dbcp2.class, DataSourceConfiguration.OracleUcp.class,
DataSourceConfiguration.Generic.class, DataSourceJmxConfiguration.class })
protected static class PooledDataSourceConfiguration
-
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration: 事务管理器的自动配置
-
JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration: JdbcTemplate的自动配置,可以来对数据库进行crud
-
JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration: jndi的自动配置
-
XADataSourceAutoConfiguration: 分布式事务相关的
修改配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://waiwanga.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com:3306/student
username: root
password: XXXX
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class SpringBootWebApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Long aLong = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from student", Long.class);
log.info("记录总数:{}",aLong);
}
}

使用Druid数据源
官方文档:https://github.com/alibaba/druid
引入jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>
编写一个数据源配置类和配置文件关联起来
@Configuration
public class MyDataSourseConfig {
//把DruidDataSource属性跟配置文件绑定起来
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource()
{
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://waiwanga.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com:3306/student
username: root
password: xxxx
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
测试类
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class SpringBootWebApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Long aLong = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from student", Long.class);
log.info("记录总数:{}",aLong);
log.info("数据源"+dataSource.getClass());
}
}
查看监控页
访问http://localhost:8080/druid/
@Configuration
public class MyDataSourseConfig {
//把DruidDataSource属性跟配置文件绑定起来
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource()
{
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//配置监控功能
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean()
{
StatViewServlet statViewServlet=new StatViewServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> registrationBean=new ServletRegistrationBean<>(statViewServlet,"/druid/*");
return registrationBean;
}
}
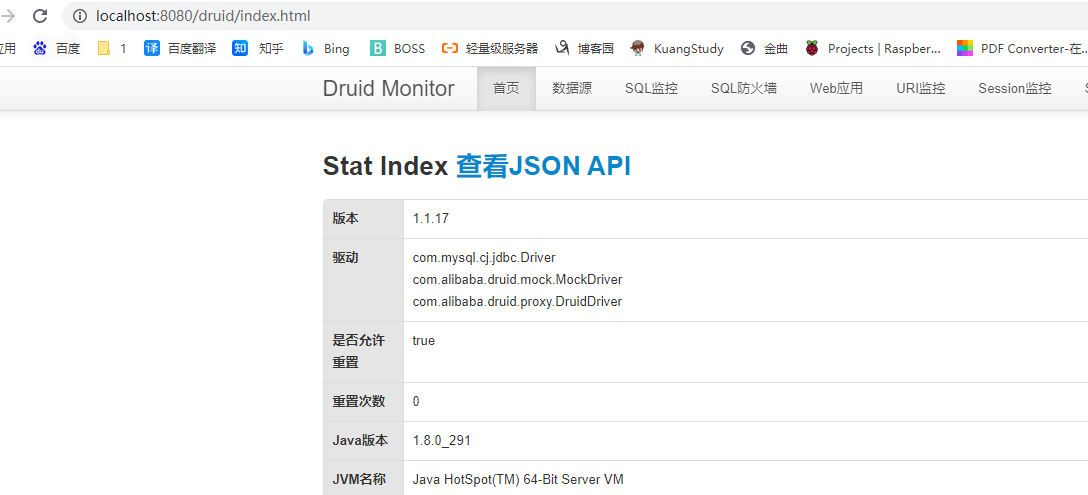
开启监控功能
需要在DataSourse中Filter参数配置stat
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource dataSource=new DruidDataSource();
//加入监控功能
dataSource.setFilters("stat");
return dataSource;
}
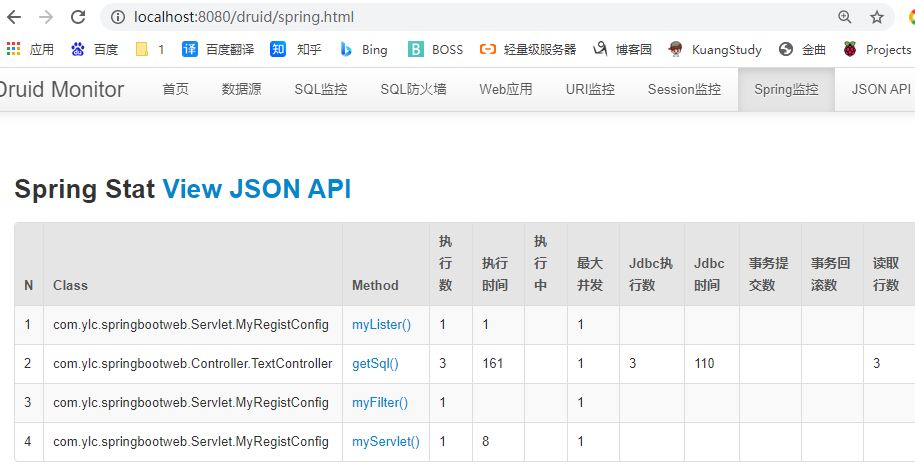
执行sql
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/sql")
public String getSql()
{
Long aLong = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from student", Long.class);
return aLong.toString();
}
查看监控信息
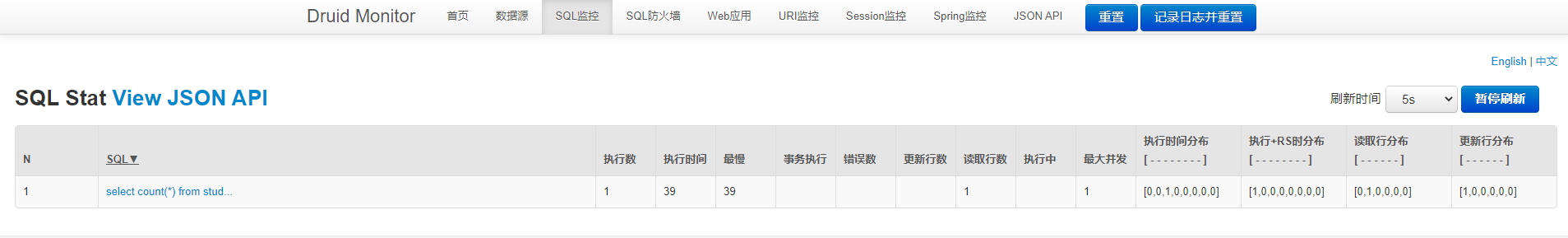
开启URl监控
WebStatFilter用于采集web-jdbc关联监控的数据
exclusions配置经常需要排除一些不必要的url,比如.js,/jslib/等等。配置在init-param中。比如:
<init-param>
<param-name>exclusions</param-name>
<param-value>*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*</param-value>
</init-param>
根据官方xml,写成注解的方式
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webstatFilter()
{
WebStatFilter webStatFilter=new WebStatFilter();
FilterRegistrationBean<WebStatFilter> filterRegistrationBean=new FilterRegistrationBean<>(webStatFilter);
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
filterRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("exclusions","*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*");
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
可以查看每次请求的信息
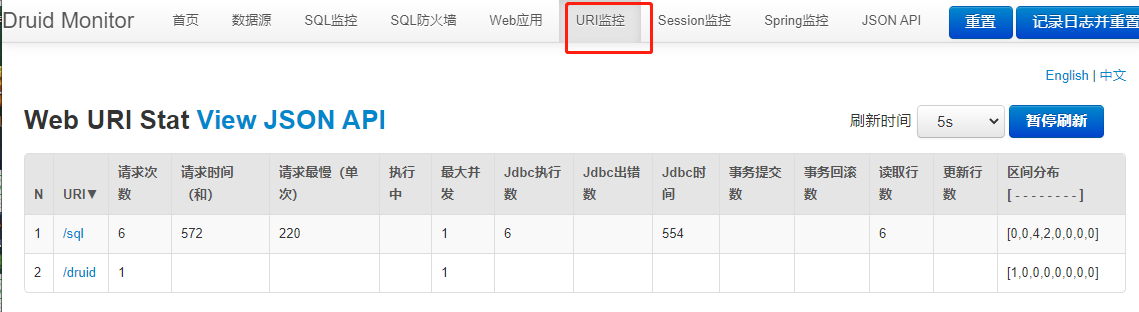
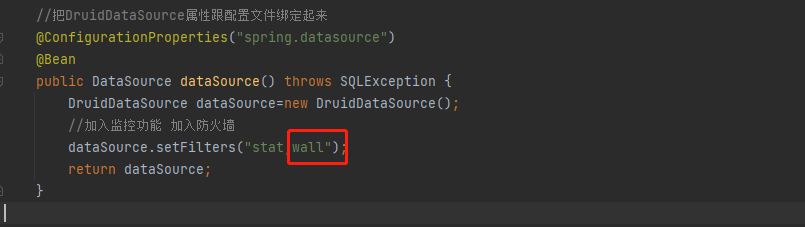
开启防火墙
使用缺省配置的WallFilter
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
...
<property name="filters" value="wall"/>
</bean>
根据官方文档,只需要在之前的filters中再添加一个参数wall
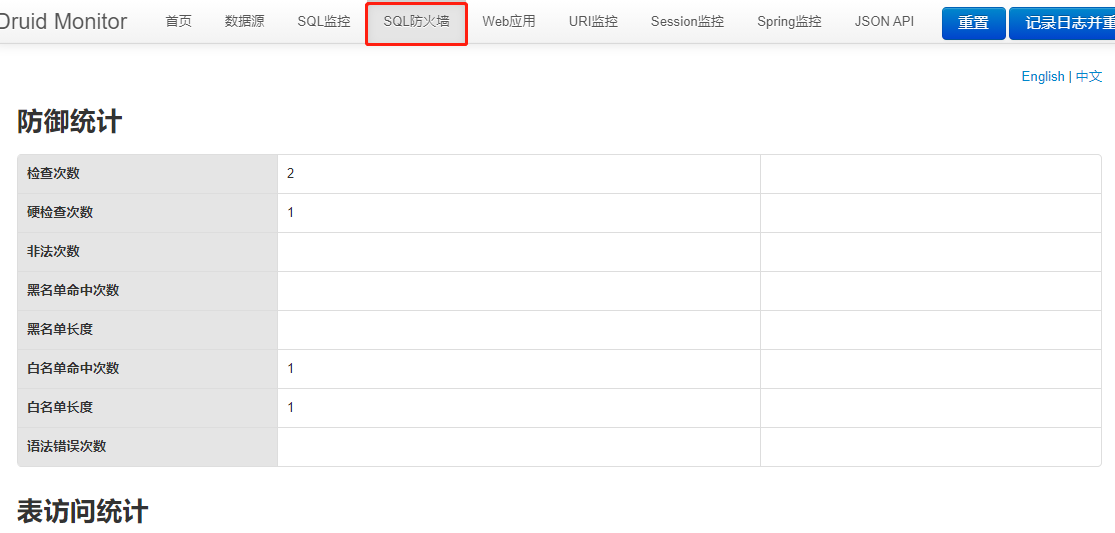
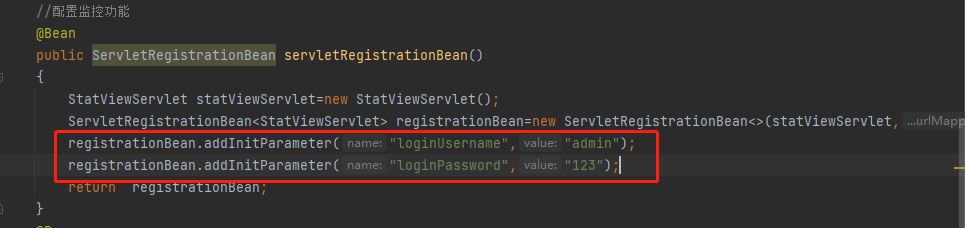
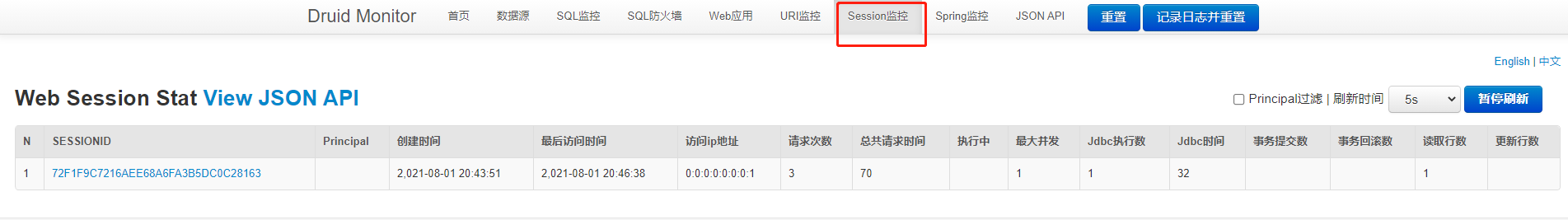
开启Session监控
需要配置Servlet的 loginUsername 和 loginPassword这两个初始参数
再次刷新进入
登陆上就可以看到Session信息
引入官方starter方式
引入druid-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>
分析自动配置
-
扩展配置项 spring.datasource.druid
-
DruidSpringAopConfiguration.class, 监控SpringBean的;配置项:spring.datasource.druid.aop-patterns
-
DruidStatViewServletConfiguration.class, 监控页的配置:spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet;默认开启
-
DruidWebStatFilterConfiguration.class, web监控配置;spring.datasource.druid.web-stat-filter;默认开启
-
DruidFilterConfiguration.class}) 所有Druid自己filter的配置
#spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/**
# web:
# resources:
# static-locations: [classpath:/Picture/]
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://waiwanga.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com:3306/student
username: root
password: xxxxx
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
druid:
aop-patterns: com.ylc.* #监控SpringBean
filters: stat,wall # 底层开启功能,stat(sql监控),wall(防火墙)
stat-view-servlet: # 配置监控页功能
enabled: true
login-password: 123
login-username: admin
reset-enable: true
web-stat-filter: # 监控web
enabled: true
urlPattern: /*
exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*'
filter:
stat: # 对上面filters里面的stat的详细配置
slow-sql-millis: 1000
logSlowSql: true
enabled: true
wall:
enabled: true
config:
drop-table-allow: false
SpringBoot配置示例
https://github.com/alibaba/druid/tree/master/druid-spring-boot-starter
配置项列表
整合Mybatis操作
官方文档:https://github.com/mybatis
引入jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
编写全局配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://waiwanga.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com:3306/student
username: xxx
password: XXX
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
#config-location: classpath:Mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
configuration: #指定Mybatis全局配置文件中的配置项 有了这个就不需要mybatis-config.xml
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
编写实体类
@Data
public class Student {
public String name;
public int id;
public int getId;
}
编写Mapper接口
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
//获取所有学生
List<Student> getStudent();
}
在resourse文件夹下编写mapper文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.ylc.springbootweb.mapper.StudentMapper">
<select id="getStudent" resultType="com.ylc.springbootweb.bean.Student">
select * from student
</select>
</mapper>
编写StudentService
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
StudentMapper studentMapper;
public List<Student> getStudent()
{
return studentMapper.getStudent();
}
}
编写控制器
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("/getStu")
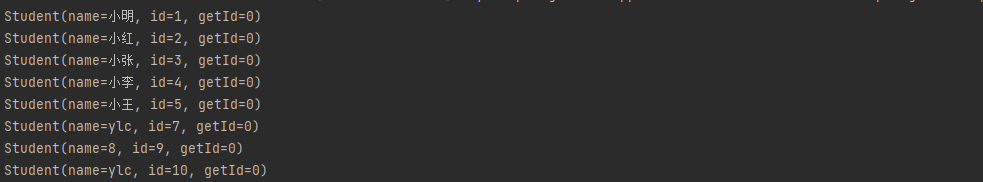
public List<Student> getStudent()
{
List<Student> students=studentService.getStudent();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
return students;
}
}
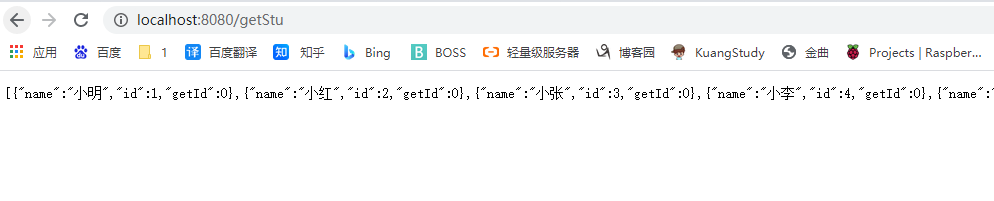
注意mapper.xml文件和Mybatis配置文件不能放在同一层级,不然系统识别不了哪个是配置文件
整合Mybatis-Plus
引入Mybatis-Plus jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
在SpringBootWebApplication中用@MapperScan扫描Mapper接口
继承BaseMapper实现crud
public interface PlusStudentMapper<T> extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
测试
@Autowired
PlusStudentMapper plusStudentMapper;
@Test
void plusText()
{
Student student = (Student) plusStudentMapper.selectById(2);
System.out.println(student);
}
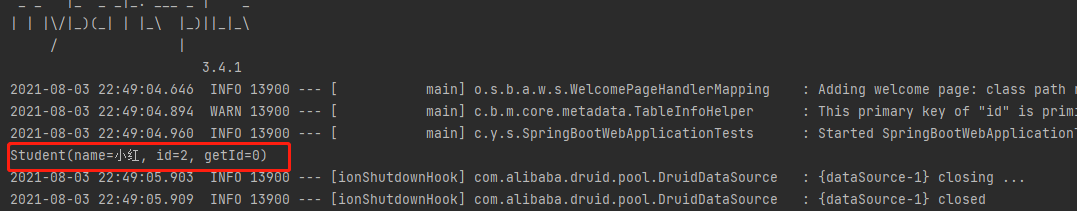
Crud操作
编写Mapper接口
public interface StudentMapper<T> extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
编写service接口
public interface TService extends IService<Student> {
}
编写service实现类
@Service
public class StudentTServiceImp extends ServiceImpl<StudentMapper<Student>,Student> implements TService {
}
测试类
@Autowired
StudentTServiceImp serviceImp;
@Test
void Crud()
{
List<Student> list = serviceImp.list();
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}