性能测试工具 nGrinder 项目剖析及二次开发
转:https://testerhome.com/topics/4225
0.背景
组内需要一款轻量级的性能测试工具,之前考虑过LR(太笨重,单实例,当然它的地位是不容置疑的),阿里云的PTS(https://pts.aliyun.com/lite/index.htm, 仅支持阿里云内网和公网机器),Gatling(http://gatling.io/#/)没有TPS数据等等,不太适合我们。
nGrinderr是NAVER(韩国最大互联网公司NHN旗下搜索引擎网站)开源的性能测试工具,直接部署成web服务,支持多用户使用,可扩展性好,可自定义plugin(http://www.cubrid.org/wiki_ngrinder/entry/how-to-develop-plugin),wiki文档较丰富(http://www.cubrid.org/wiki_ngrinder/entry/ngrinder-devzone),数据及图形化展示满足需求;但是展示的统计数据较简单,二次开发整合数据:TPS标准差,TPS波动率,最小/大RT,RT 25/50/75/80/85/90/95/99百分位数字段,并将这些数据展示在详细测试报告页中。
1.项目剖析
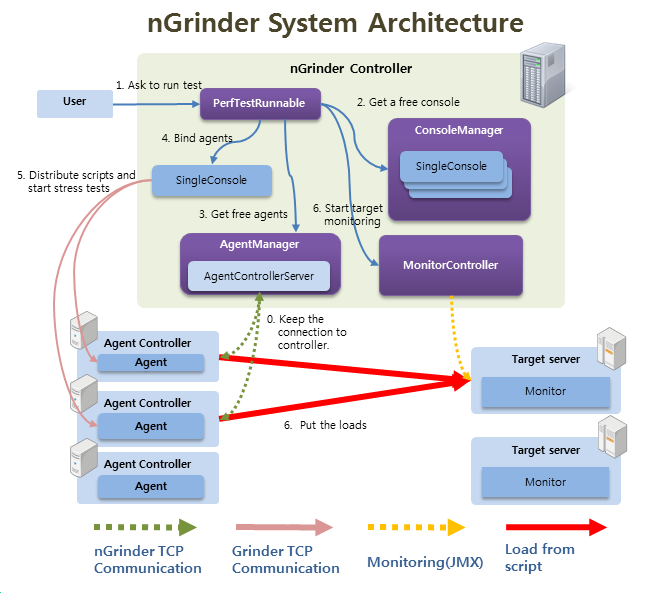
1-1. nGrinder架构
nGrinder是一款在一系列机器上执行Groovy或JPython测试脚本的应用,内部引擎是基于Grinder。
架构图:
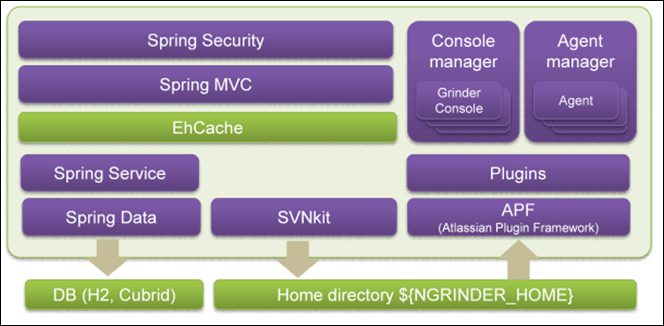
层级图:
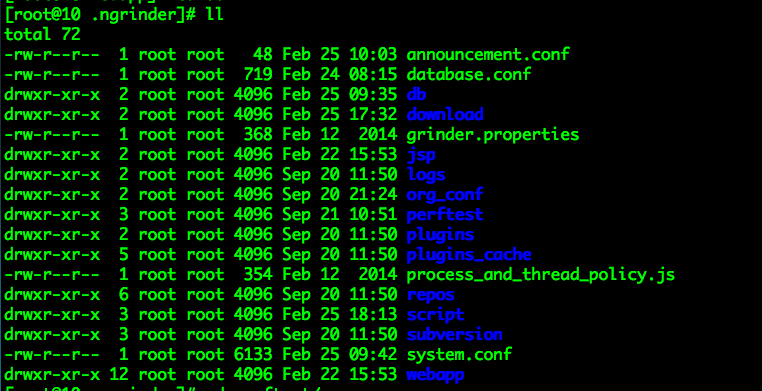
默认的NGRINDER_HOME为/root/.ngrinder, 大多是配置文件和数据文件。
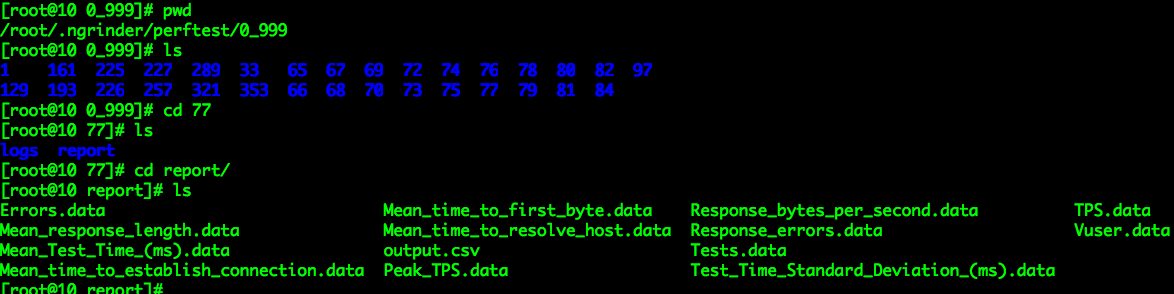
目录/root/.ngrinder/perftest/0_999下,以每个test_id为名的文件夹对应的存储了执行性能测试时的采样数据:
*.data文件就是执行性能测试时对应的各种性能采样数据,性能测试详细报告页就是根据这些data文件,进行图形化展示(ajax)。
nGrinder包含2大组件:
1)Controller
为性能测试提供web interface
协同测试进程
收集和显示测试数据
新建和修改脚本
2)Agent
agent mode: 运行进程和线程,压测目标服务
monitor mode: 监控目标系统性能(cpu/memory), 可以自定义收集的数据(比如 jvm数据)
http://www.cubrid.org/wiki_ngrinder/entry/general-architecture
1-2. 技术栈
1)Controller 层
FreeMarker: 基于Java的模板引擎
Spring Security
Spring Mvc:Spring MVC provides rich functionality for building robust web applications.
GSon
SVNKit Dav
2)Service 层
Grinder
Spring
EhCache: Ehcache has excellent Spring integration.
3)Data层
Spring Data
Hibernate:Hibernate is a powerful technology for persisting data,and it is Spring Data back-end within nGrinder.
H2: (nGrinder默认使用该DB)
Cubrid:(nGrinder同一家公司的DB)
Liquidase: Liquibase is an open source that automates database schema updates.
SVNKit
http://www.cubrid.org/wiki_ngrinder/entry/technology-stack
2.源码实现
需求:在详细测试报告页中展示TPS标准差,TPS波动率,最小/大RT,RT 25/50/75/80/85/90/95/99百分位数这些数据。
修改Controller层,增加数据处理业务逻辑(计算TPS标准差,TPS波动率,最小/大RT,RT 25/50/75/80/85/90/95/99百分位数)
在获取采样数据
ngrinder-core/src/main/java/net/grinder/SingleConsole.java中新增处理业务逻辑,核心修改代码片段:
// tps list
List<Double> tps = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<Double>();
// rt list
List<Double> meanTestTime = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<Double>();
/**
*
* 每次请求调用一次 Build up statistics for current sampling.
*
* @param accumulatedStatistics
* intervalStatistics
* @param intervalStatistics
* accumulatedStatistics
*/
protected void updateStatistics(StatisticsSet intervalStatistics,
StatisticsSet accumulatedStatistics) {
Map<String, Object> result = newHashMap();
result.put("testTime", getCurrentRunningTime() / 1000);
List<Map<String, Object>> cumulativeStatistics = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
List<Map<String, Object>> lastSampleStatistics = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
for (Test test : accumulatedStatisticMapPerTest.keySet()) {
Map<String, Object> accumulatedStatisticMap = newHashMap();
Map<String, Object> intervalStatisticsMap = newHashMap();
StatisticsSet accumulatedSet = this.accumulatedStatisticMapPerTest
.get(test);
StatisticsSet intervalSet = this.intervalStatisticMapPerTest
.get(test);
accumulatedStatisticMap.put("testNumber", test.getNumber());
accumulatedStatisticMap.put("testDescription",
test.getDescription());
intervalStatisticsMap.put("testNumber", test.getNumber());
intervalStatisticsMap.put("testDescription", test.getDescription());
// When only 1 test is running, it's better to use the parametrized
// snapshot.
for (Entry<String, StatisticExpression> each : getExpressionEntrySet()) {
if (INTERESTING_STATISTICS.contains(each.getKey())) {
accumulatedStatisticMap.put(
each.getKey(),
getRealDoubleValue(each.getValue().getDoubleValue(
accumulatedSet)));
intervalStatisticsMap.put(
each.getKey(),
getRealDoubleValue(each.