SpringBoot与Redis多线程入门——多线程redis存取数据
1. SpringBoot Redis yml 配置
此处省略密码
spring:
redis:
database: 0
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
timeout: 3000
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-wait: -1
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
2. RedisCofig.java 配置类代码
@EnableCaching
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.database}")
private Integer database;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private Integer port;
@Primary
@Bean(name = "jedisPoolConfig")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis.pool")
public JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig() {
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(10000);
return jedisPoolConfig;
}
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory(JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig) {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setHostName(host);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setDatabase(database);
// redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPassword(pwd);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPort(port);
JedisClientConfiguration.JedisPoolingClientConfigurationBuilder jpcb = (JedisClientConfiguration.JedisPoolingClientConfigurationBuilder) JedisClientConfiguration.builder();
jpcb.poolConfig(jedisPoolConfig);
JedisClientConfiguration jedisClientConfiguration = jpcb.build();
return new JedisConnectionFactory(redisStandaloneConfiguration, jedisClientConfiguration);
}
/**
* 配置redisTemplate针对不同key和value场景下不同序列化的方式
* 此处针对key为String,value为CustomerVo对象的序列化方式
* @param factory Redis连接工厂
* @return
*/
@Primary
@Bean(name = "customerRedisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<String, CustomerVo> customerRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, CustomerVo> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
// 这里是关键,注意替换为自己的类
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<CustomerVo> redisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(CustomerVo.class);
template.setValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
@Bean(name = "doctorRedisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<String, DoctorVo> doctorRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, DoctorVo> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<DoctorVo> redisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(DoctorVo.class);
template.setValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(RedisConnectionFactory.class)
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
3. Vo类和Service类代码
CustomerVo.java
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CustomerVo {
private Integer customerId;
private String queueSeq;
private String customerName;
private String customerSex;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CustomerVo{" +
"queueSeq='" + queueSeq + '\'' +
", customerName='" + customerName + '\'' +
", customerSex='" + customerSex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Service
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RedisLookupService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, CustomerVo> redisTemplate;
@Async("taskExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<Long> enqueueCustomer(CustomerVo customer) {
Long result = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("queue", customer);
log.info("{} 入队..", customer);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(result);
}
@Async("taskExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<CustomerVo> dequeueCustomer() {
if (Objects.requireNonNull(redisTemplate.opsForList().size("queue")) < 1) {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(null);
}
CustomerVo vo = redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop("queue");
log.info("{} 出队...", vo);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(vo);
}
}
AsyncConfig.java 配置类
因为用到了SpringBoot的多线程,所以要加一下这个配置类
@Configuration
@EnableAsync // 启用异步任务
public class AsyncConfig {
// 声明一个线程池(并指定线程池的名字)
@Bean("taskExecutor")
public Executor asyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//核心线程数5:线程池创建时候初始化的线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(5);
//最大线程数5:线程池最大的线程数,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
executor.setMaxPoolSize(5);
//缓冲队列500:用来缓冲执行任务的队列
executor.setQueueCapacity(500);
//允许线程的空闲时间60秒:当超过了核心线程出之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
//线程池名的前缀:设置好了之后可以方便我们定位处理任务所在的线程池
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("RaviAsync-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
4. Controller 测试代码
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private RedisLookupService service;
@GetMapping("/en")
public String enqueueTry() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
CustomerVo c1 = new CustomerVo(1, "A031", "马哲", "男");
CustomerVo c2 = new CustomerVo(2, "A039", "马王", "男");
CustomerVo c3 = new CustomerVo(3, "A040", "马丽", "女");
CompletableFuture<Long> future1 = service.enqueueCustomer(c1);
CompletableFuture<Long> future2 = service.enqueueCustomer(c3);
CompletableFuture<Long> future3 = service.enqueueCustomer(c2);
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3).join();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("complete test: {}s",(float)(end - start) / 1000);
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping("/qn")
public String dequeueTry() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<CustomerVo> customer1 = service.dequeueCustomer();
CompletableFuture<CustomerVo> customer2 = service.dequeueCustomer();
CompletableFuture<CustomerVo> customer3 = service.dequeueCustomer();
CompletableFuture.allOf(customer1, customer2, customer3).join();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("complete test: {}s",(float)(end - start) / 1000);
return "ok";
}
}
/en的测试结果:
图1
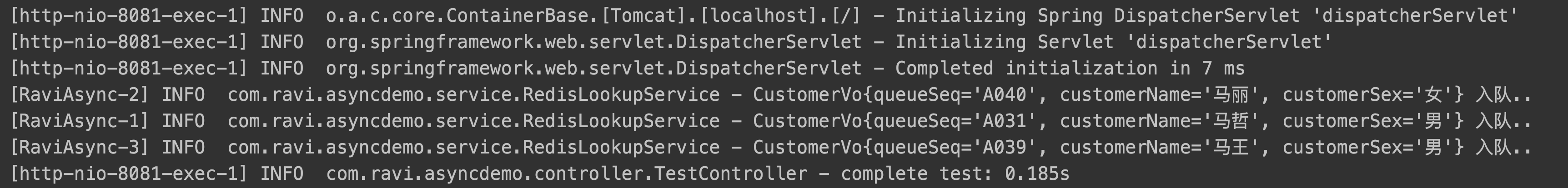
图2
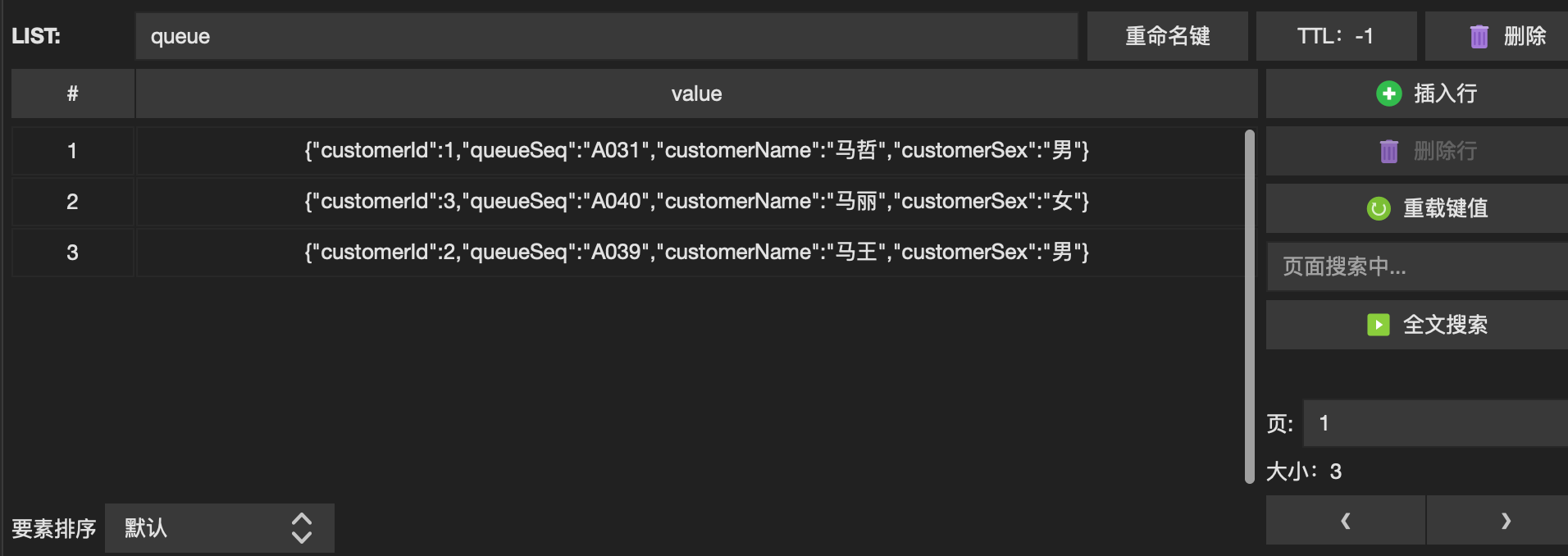
/qn的测试结果:

由此可以发现,多线程已经启动。
5. 日志设置
yml配置
logging:
config: classpath:logback.xml
level:
com.ravi.mapper: trace
xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="false">
<!--定义日志文件的存储地址 勿在 LogBack 的配置中使用相对路径-->
<property name="LOG_HOME" value="/Users/ravi/codes/myproject/log"/>
<!-- 定义日志格式 -->
<property name="LOG_PATTERN" value="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%-5level] [%thread] [%-30.30logger{30}] %msg%n"/>
<!-- 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 按照每天生成日志文件 -->
<appender name="FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名-->
<FileNamePattern>${LOG_HOME}/Slf4j_%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数-->
<MaxHistory>30</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
<!--日志文件最大的大小-->
<triggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy">
<MaxFileSize>10MB</MaxFileSize>
</triggeringPolicy>
</appender>
<!-- 日志输出级别 -->
<logger name="org.springframework" level="INFO"/>
<logger name="com.ravi.mapper" level="INFO"/>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE"/>
</root>
</configuration>
参考文章大数据从业者


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号