Python学习—数据库篇之SQL语句
一、数据库级别
1.显示数据库
show databases;
默认数据库:
mysql - 用户权限相关数据
test - 用于用户测试数据
information_schema - MySQL本身架构相关数据
2.创建数据库
# utf-8 (推荐使用) CREATE DATABASE 数据库名称 DEFAULT CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; # gbk CREATE DATABASE 数据库名称 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET gbk COLLATE gbk_chinese_ci;
3.删除数据库
drop database 数据库名称;
4.使用数据库
use 数据库名称;
二、表级别
1.显示表
show tables; ---显示表 desc 表名; ---显示表字段
2.创建表
create table 表名( 列名 类型 是否可以为空, 列名 类型 是否可以为空 )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 -- InnoDB为数据库引擎的一种,支持事务操作

是否可空,null表示空,非字符串 not null - 不可空 null - 可空

创建列时可以指定默认值,当插入数据时如果未主动设置值,则自动添加默认值 create table tb1( nid int not null defalut 2, num int not null )

自增,如果为某列设置自增列,插入数据时无需设置此列,默认将自增(表中只能有一个自增列) create table tb1( nid int not null auto_increment primary key, num int null ) 或 create table tb1( nid int not null auto_increment, num int null, index(nid) ) 注意:1、对于自增列,必须是索引(含主键)。 2、对于自增可以设置步长和起始值 show session variables like 'auto_inc%'; set session auto_increment_increment=2; set session auto_increment_offset=10; shwo global variables like 'auto_inc%'; set global auto_increment_increment=2; set global auto_increment_offset=10;

主键,一种特殊的唯一索引,不允许有空值,如果主键使用单个列,则它的值必须唯一,如果是多列,则其组合必须唯一。 主键的好处:约束,加速查找 create table tb1( nid int not null auto_increment primary key, num int null ) 或 create table tb1( nid int not null, num int not null, primary key(nid,num) )

外键,一个特殊的索引,只能是指定内容 creat table color( nid int not null primary key, name char(16) not null ) create table fruit( nid int not null primary key, smt char(32) null , color_id int not null, constraint fk_cc foreign key (color_id) references color(nid) )
外键示例:创建一张学生信息表和一张班级信息表,将学生表中的class_no和班级表中的nid相关联
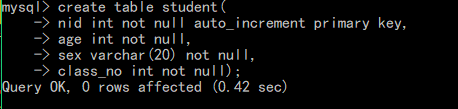
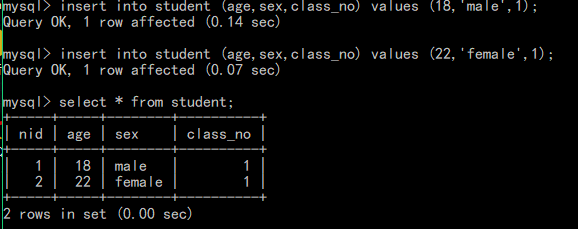


建立外键约束

相当于将学生表中的class_no和班级表中的nid约束起来

当再向student表中插入数据时,如果class_no不在class表的nid的值域内,则报错

3.删除表
drop table 表名; ---直接删除表 delete from 表名; ---清空表内容 truncate table 表名; ---清空表内容,速度快,有自增时清空表后插入数据会重新开始编号
4.查询表
select * from 表名; ----查询表内容
5.修改表
添加列:alter table 表名 add 列名 类型 删除列:alter table 表名 drop column 列名 修改列: alter table 表名 modify column 列名 类型; -- 类型 alter table 表名 change 原列名 新列名 类型; -- 列名,类型 添加主键: alter table 表名 add primary key(列名); 删除主键: alter table 表名 drop primary key; alter table 表名 modify 列名 int, drop primary key; 添加外键:alter table 从表 add constraint 外键名称(形如:FK_从表_主表) foreign key 从表(外键字段) references 主表(主键字段); 删除外键:alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称 修改默认值:ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i SET DEFAULT 1000; 删除默认值:ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i DROP DEFAULT;
三、表内容级别
1.增
--向表中插入一条数据 insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...)

--向表中插入多条数据 insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...),(值,值,值...)

--将另一个表中的数据插到其他表中,对应列的数据类型要一样或者可以转换 insert into 表1 (列名,列名...) select 列名,列名... from 表2
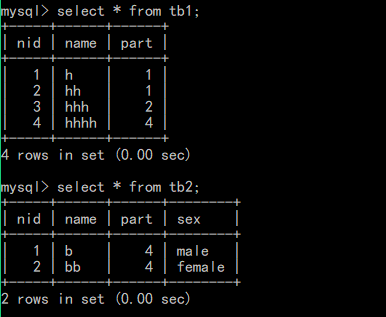
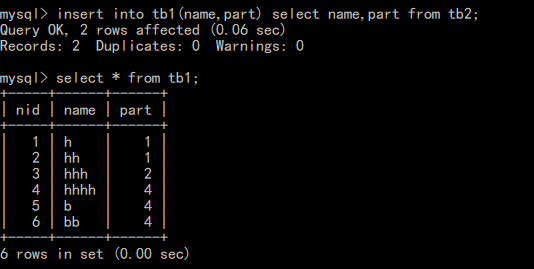
2.删
--删除整张表 delete from 表 --条件删除,where后面可以跟判断条件 delete from 表 where nid=1 and name='h'

3.改
update 表 set name = 'alex' where nid>1

4.查
select * from 表 select * from 表 where id > 1 --as的作用是可以将原来的表头以定义的字段命名 select nid,name,sex as gender from 表 where id > 1

5.其他
a.条件
select * from 表 where id > 1 and name != 'alex' and num = 12; select * from 表 where id between 5 and 16; select * from 表 where id in (11,22,33) select * from 表 where id not in (11,22,33) select * from 表 where id in (select nid from 表)
b.通配符
select * from 表 where name like 'ale%' -- ale开头的所有(多个字符串) select * from 表 where name like 'ale_' -- ale开头的所有(一个字符) select * from 表 where name like '%le%' -- 包含le的所有(多个字符串) select * from 表 where name like '_le_' -- le前只有一个字符的所有(一个字符)
c.分页(限制)
select * from 表 limit 5; - 前5行 select * from 表 limit 4,5; - 从第4行开始的5行 select * from 表 limit 5 offset 4 - 从第4行开始的5行(推荐写法)
d.排序
select * from 表 order by 列 asc - 根据 “列” 从小到大排列 select * from 表 order by 列 desc - 根据 “列” 从大到小排列 select * from 表 order by 列1 desc,列2 asc - 根据 “列1” 从大到小排列,如果相同则按列2从小到大排序
e.分组
假设一个公司有多个部门,每个部门有若干员工,要统计每个部门分别有多少人时,则可用分组的方法轻松解决。
分组之后,数据会按照分part_no属性进行值的去重,将相同的值归类在一起

但当一个part_no值有多个name值对应时,直接分组,数据库将无法确定究竟取哪一个name的值,因而报错

此时,可以根据数据库内置函数方法来避免这类问题

其余方法示例:
select num from 表 group by num select num,nid from 表 group by num,nid select num,nid from 表 where nid > 10 group by num,nid order nid desc select num,nid,count(*),sum(score),max(score),min(score) from 表 group by num,nid --分组里面条件判断时用having select num from 表 group by num having max(id) > 10 特别的:group by 必须在where之后,order by之前
f.组合(上下连接表)
--组合,自动处理重合 select part_no from A union select id from B


--组合,不处理重合 select part_no from A union all select id from B


g.连表(左右连接表)
--无对应关系则不显示 select A.num, A.name, B.name from A,B Where A.nid = B.nid --左连接,A表所有显示,如果B中无对应关系,则值为null,此时A为主表 select A.num, A.name, B.name from A left join B on A.nid = B.nid --右连接,B表所有显示,如果B中无对应关系,则值为null,此时B为主表 select A.num, A.name, B.name from A right join B on A.nid = B.nid --相互迁就,会将两张表连接后为空的部分去掉,AB左右连接结果一样 select A.num, A.name, B.name from A inner join B on A.nid = B.nid



四、数据类型
MySQL的数据类型大致分为:数值、时间和字符串
bit[(M)]
二进制位,m表示二进制位的长度(默认m=1),若m=3,则可表示000,001,010....111,bit取值范围为1~64
tinyint[(m)] [unsigned] [zerofill]
小整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围:
有符号: -128 ~ 127.
无符号:0 ~ 255
(例)创建表时添加无符号属性:create table(num int unsinged);
特别的: MySQL中无布尔值,使用tinyint(1)构造。
smallint 表数介于tinyint和int之间
bigint[(m)][unsigned][zerofill]
大整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围:
有符号:
-9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807
无符号:
0 ~ 18446744073709551615
decimal[(m[,d])] [unsigned] [zerofill]
准确的小数值,m是数字总个数(负号不算),d是小数点后个数。 m最大值为65,d最大值为30。
特别的:对于精确数值计算时需要用此类型
decaimal能够存储精确值的原因在于其内部按照字符串存储。
FLOAT[(M,D)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
单精度浮点数(非准确小数值),m是数字总个数,d是小数点后个数。
无符号:
-3.402823466E+38 to -1.175494351E-38,
0
1.175494351E-38 to 3.402823466E+38
有符号:
0
1.175494351E-38 to 3.402823466E+38
**** 数值越大,越不准确 ****
DOUBLE[(M,D)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
双精度浮点数(非准确小数值),m是数字总个数,d是小数点后个数。
无符号:
-1.7976931348623157E+308 to -2.2250738585072014E-308
0
2.2250738585072014E-308 to 1.7976931348623157E+308
有符号:
0
2.2250738585072014E-308 to 1.7976931348623157E+308
**** 数值越大,越不准确 ****
char (m)
char数据类型用于表示固定长度的字符串,可以包含最多达255个字符。其中m代表字符串的长度。
PS: 即使数据小于m长度,也会占用m长度
varchar(m)
varchars数据类型用于变长的字符串,可以包含最多达255个字符。其中m代表该数据类型所允许保存的字符串的最大长度,只要长度小于该最大值的字符串都可以被保存在该数据类型中。
注:虽然varchar使用起来较为灵活,但是从整个系统的性能角度来说,char数据类型的处理速度更快,有时甚至可以超出varchar处理速度的50%。因此,用户在设计数据库时应当综合考虑各方面的因素,以求达到最佳的平衡
text
text数据类型用于保存变长的大字符串,可以组多到65535 (2**16 − 1)个字符。
mediumtext
A TEXT column with a maximum length of 16,777,215 (2**24 − 1) characters.
longtext
A TEXT column with a maximum length of 4,294,967,295 or 4GB (2**32 − 1) characters.
enum
枚举类型,
An ENUM column can have a maximum of 65,535 distinct elements. (The practical limit is less than 3000.)
示例:
CREATE TABLE shirts (
name VARCHAR(40),
size ENUM('x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large')
);
INSERT INTO shirts (name, size) VALUES ('dress shirt','large'), ('t-shirt','medium'),('polo shirt','small');
set
集合类型
A SET column can have a maximum of 64 distinct members.
示例:
CREATE TABLE myset (col SET('a', 'b', 'c', 'd'));
INSERT INTO myset (col) VALUES ('a,d'), ('d,a'), ('a,d,a'), ('a,d,d'), ('d,a,d');
DATE
YYYY-MM-DD(1000-01-01/9999-12-31)
TIME
HH:MM:SS('-838:59:59'/'838:59:59')
YEAR
YYYY(1901/2155)
DATETIME
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS(1000-01-01 00:00:00/9999-12-31 23:59:59 Y)
TIMESTAMP
YYYYMMDD HHMMSS(1970-01-01 00:00:00/2037 年某时)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号