【C# 数据结构】线性表

线性表的实现方式
线性表的实现方式有下面几种
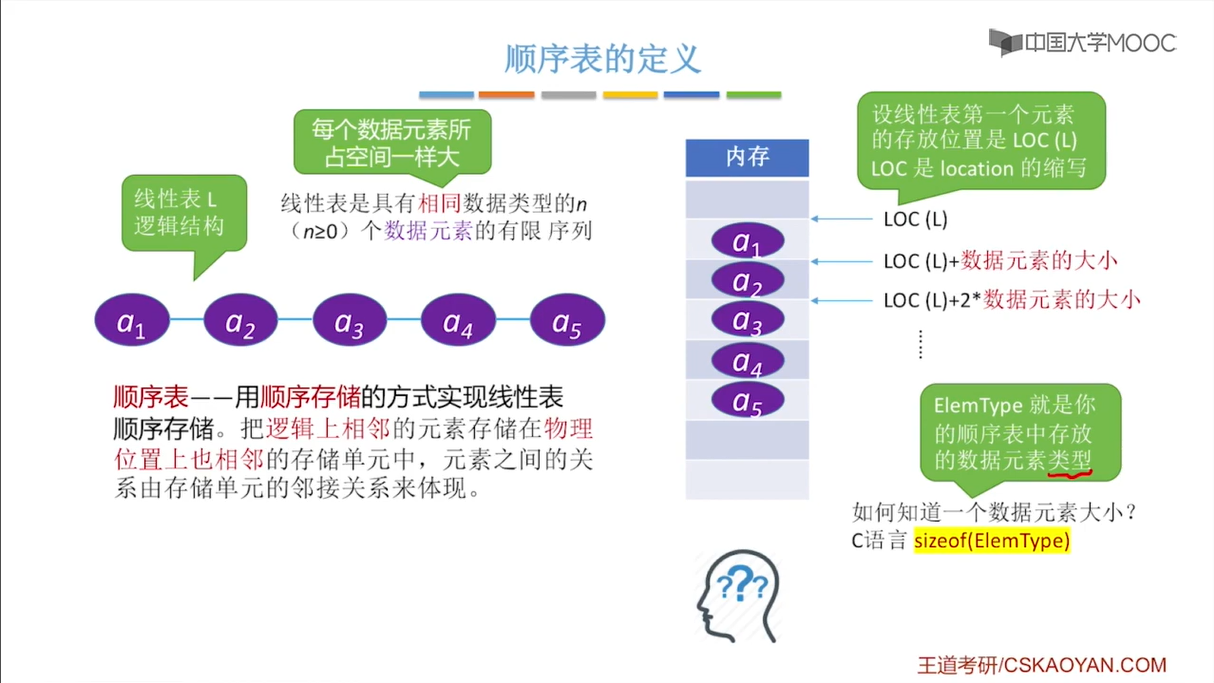
- 顺序表 :数组
- 单链表:list<>
- 单向循环链表
- 双向链表:linkedlist<>
- 循环链表:
自定义顺序表

public class SequenceList<T> { private T[] items; private int count; private bool empty; private bool full; int capacity; //列表的元素个数 public int Count { get => count; set => count = value; } //判断列表是否为空 public bool Empty { get => count == 0; } public bool Full { get => count == items.Length; } public int Capacity { get => capacity; set => capacity = value; } //构造函数 public SequenceList(int count) {items = new T[count] ;this.count=0;Capacity = count; } public SequenceList() : this(16) { } public SequenceList(T[] items) { count = items.Length ; int capacity = count + 16; this.items =new T[capacity]; for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) { this.items[i++] = items[i]; } } /// <summary> /// 扩容数组 /// </summary> private void AutoExtensionCacpacity() { capacity = this.items.Length * 2; T[] newitems = new T[capacity]; this.items.CopyTo(newitems, 0); this.items = newitems; } /// <summary> /// 索引 /// </summary> /// <param name="i"></param> /// <returns></returns> /// <exception cref="IndexOutOfRangeException"></exception> public T this[int i] { get { if (i >= 0 && i<items.Length) return items[i]; else throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } set { if (i > 0 && i < items.Length) items[i]=value; else throw new IndexOutOfRangeException($"index out of range in {this.GetType()}"); } } /// <summary> /// 查找list是否包含改值 /// </summary> /// <param name="K"></param> /// <returns></returns> public bool Contains(T K) { return IndexOf(K) != -1 ? true : false; } public int IndexOf(T itme) { int j = 0; while (j < count && !itme.Equals(items[j])) j++; return j>=0 && j <count? j: -1; } /// <summary> /// 在指定的索引位置插入元素 /// </summary> /// <param name="j">索引位置</param> /// <param name="k">item</param> public void Insert(int j ,T k) { if (j > items.Length) { AutoExtensionCacpacity(); } if (j > count) { j = count; }else if(j < 0) { j=0; } else { for(int i=count-1;i>=j && i<= count; i--) { items[i+1] = items[i]; } items[j] = k; } count++; } /// <summary> /// 在尾部添加 /// </summary> /// <param name="k">要添加item</param> public void Append(T k) { if (count >= items.Length) { AutoExtensionCacpacity(); } items[count] = k; count++; } /// <summary> /// 删除指定索引的元素 /// </summary> /// <param name="i">元素的索引</param> /// <exception cref="IndexOutOfRangeException"></exception> public void RemoveAt(int i) { if (i >= 0 && i < count) { for (int j=i+1;j<=count;j++) { items[j-1] = items[j]; } count--; } else { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException( ); } } public void Remove(T k) { int j= IndexOf(k); if (j >= 0) { RemoveAt(j); } } /// <summary> /// 打印列表 /// </summary> public void Show() { for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Console.Write (items[i] +" "); } } }
单向链表
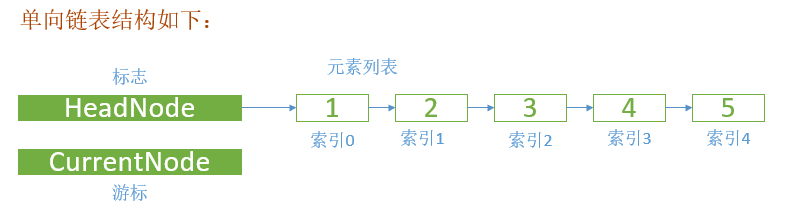
对应的C# 代码如下:
编写了如下功能:insert、reverse、Remove、RemoveAt、add
1、读取线程安全
2、未实现序列化功能

using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis; using System.Drawing.Drawing2D; using System.IO; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Xml; using System.Xml.XPath; namespace LinearList; public class Sample { public static void Main() { int[] vs = new int[10]; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { vs[i] = i; } CircularList<int> list = new(vs ); Console.WriteLine(list.Length); } public class Node<T> { private T? item; private Node<T>? next; public T? Item { get => item; set => item = value; } public Node<T>? Next { get => next; set => next = value; } public Node(T value) { item = value; } public Node() { } public override string ToString() { return item.ToString(); } } //读取时线程安全 public class NodeList<T> where T : notnull { public Node<T> Head; private int length; [ThreadStatic] private static Node<T> currntNode; public Node<T> CurrntNode { get { if (Head.Next == null) currntNode= Head; return currntNode; } set { currntNode = value; } } /// <summary> /// 构造头节点,他是开始的标志 /// </summary> public NodeList() { Head=new Node<T>(); currntNode = new(); CurrntNode = Head; } public NodeList(Node<T> firstnode) :this() { Head.Next = firstnode; } public NodeList( T [] array) : this() { for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { Node<T> node = new (array[i]); CurrntNode.Next = node; if (i == 0)Head.Next = node; CurrntNode = CurrntNode.Next; } } /// <summary> /// 列表长度 ,为了方便循环单向链表 继承后修改改方法,所以改方法设置成virtual /// </summary> public virtual int Length { get { Node<T>? node = Head; length = 0; while (node != null) { node = node.Next; length++; } return length; } set => length = value; } /// <summary> /// 添加数据项 ,为了方便循环单向链表 继承后修改改方法,所以改方法设置成virtual /// </summary> /// <param name="item"></param> public virtual void Add(T item) { Node<T> newNOde = new(item); if (CurrntNode == null) { CurrntNode = new(); CurrntNode = newNOde; Head = newNOde; } else { CurrntNode.Next = newNOde; CurrntNode = CurrntNode.Next; } } /// <summary> /// 输出完整的列表 /// </summary> public void Print() { if (Head.Next != null) CurrntNode = Head.Next; while (CurrntNode != null) { Console.WriteLine(CurrntNode.Item); CurrntNode = CurrntNode .Next; } } /// <summary> /// 是否是空列表 /// </summary> public virtual bool IsEmpty{get{ return Head.Next == null; } } /// <summary> /// suo'y /// </summary> /// <param name="item"></param> /// <returns></returns> /// <exception cref="IndexOutOfRangeException"></exception> public virtual T this[int item] { get { if(item < 0)throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); if(Head.Next==null) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); CurrntNode = Head.Next; int n = 0; while( n!=item) { CurrntNode = CurrntNode.Next; n++; } return CurrntNode.Item; } set { CurrntNode = Head.Next; int n = 0; while (n != item) { CurrntNode = CurrntNode.Next; n++; } CurrntNode.Item= value; } } public override string ToString() { if(Head == null) return string.Empty; CurrntNode = Head; StringBuilder str = new(); while (CurrntNode != null) { str.Append(CurrntNode.Item+" ") ; CurrntNode = CurrntNode.Next; } return str.ToString(); } /// <summary> /// 在指定的索引位置之后插入元素 ,为了方便循环单向链表 继承后修改改方法,所以改方法设置成virtual /// </summary> /// <param name="index">索引位置</param> /// <param name="item"></param> /// <exception cref="IndexOutOfRangeException"></exception> public virtual void Insert(int index ,T item) { Node<T> node=new(item); if(index<0||index>Length)throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); CurrntNode =Head; Node<T> nextnode = CurrntNode.Next; int i = 0; while (CurrntNode!=null) { if (i == index) { break; } CurrntNode = nextnode; nextnode = nextnode.Next; i++; } node.Next = CurrntNode!.Next; CurrntNode.Next= node; } /// <summary> /// 在队列的末尾添加 数据元素 /// </summary> /// <param name="item"></param> public virtual void Append(T item) { Node<T> node =new(item); if (Head == null) { Head = node;return; } CurrntNode = Head; Node<T> nextnode = CurrntNode.Next; while (nextnode != null) { CurrntNode = nextnode; } CurrntNode.Next = node; } /// <summary> /// 删除出现item的数据元素 /// </summary> /// <param name="item"></param> public void Remove(T item) { if (Head == null) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(item)) ; } CurrntNode = Head; Node<T> nextnode = CurrntNode.Next; if (CurrntNode.Item.Equals(item)) { Head = nextnode; } while (nextnode != null) { if (nextnode.Item.Equals(item)) { CurrntNode.Next=nextnode.Next; return; } CurrntNode = nextnode; nextnode = nextnode.Next; } Console.WriteLine( "未找到删除的元素"); } /// <summary> /// 删除指定索引的元素 /// </summary> /// <param name="i"></param> /// <exception cref="IndexOutOfRangeException"></exception> public void RemoveAt(int i) { if (Head == null || i < 0|| i >Length ) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } if (i == 0){ Head = null; return; } CurrntNode = Head; Node<T> nextnode = CurrntNode.Next; int n = 0; while (nextnode != null) { if (i-1==n) { CurrntNode.Next = nextnode.Next; return; } CurrntNode = nextnode; nextnode = nextnode.Next; n++; } if (Length == i) { CurrntNode = null;return; } Console.WriteLine("未找到删除的元素"); } public void Reverse() { if (Head.Next == null) return; CurrntNode = Head.Next; Node<T> nextnode = CurrntNode.Next; Node<T> prenode; int n = 0; while (nextnode != null) { prenode = CurrntNode; if (n == 0) prenode.Next = null; CurrntNode = nextnode; nextnode = nextnode.Next; CurrntNode.Next = prenode; n++; } Head.Next = CurrntNode; } } }
单向循环单链表
定义:将链表的最后一个节点的指针域指向链表的头节点。
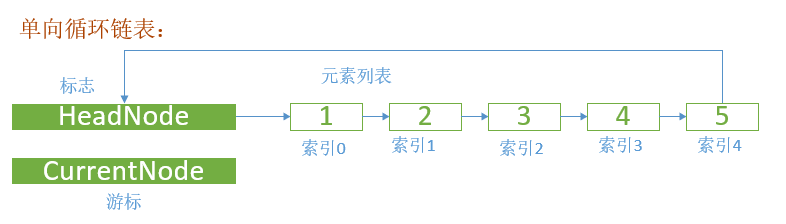
对应的C# 代码如下:
继承单向链表,并且重写其中方法

public class CircularList<T> : NodeList<T> where T:notnull { public CircularList():base() { } public CircularList(T[] array ):base() { Node<T> node; CurrntNode = Head; for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { node = new(array[i]); CurrntNode.Next = node; CurrntNode = node; } CurrntNode.Next = Head; } public override int Length { get { if(Head.Next==null)return 0; CurrntNode = Head.Next; int n = 0; while (CurrntNode != Head ) { n++; CurrntNode = CurrntNode.Next; } return n; } } public override bool IsEmpty =>Head.Next==null; }
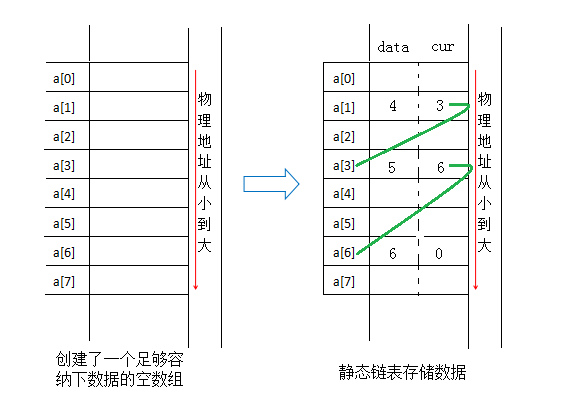
静态链表
静态链表:线性存储结构的一种,兼顾顺序表和链表的优点,是顺序表和链表的升级;静态链表的数据全部存储在数组中(顺序表),但存储的位置是随机的,数据直接的一对一关系是通过一个整型变量(称为“游标”,类似指针的功能)维持。
1. 静态链表中的节点
数据域:用于存储数据元素的值
游标:即数组下标,表示直接后继元素所在数组中的位置
public struct StaticLinear { int data; //静态链表节点中的数据 int cur; //静态链表节点中的游标 }
例:使用静态链表存储数据元素4、5、6,过程如下:
双向链表
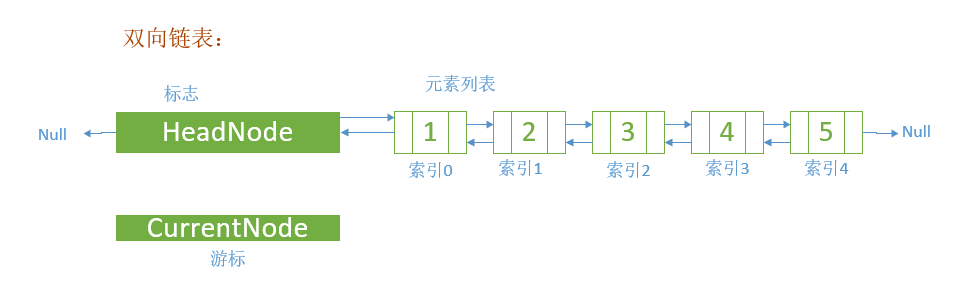
自定义双向链表:功能 add、 remove、 insert、 print

using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis; using System.Drawing.Drawing2D; using System.IO; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Xml; using System.Xml.XPath; namespace LinearList; public class Sample { static void Main() { DoubleDirectionList<int> doubleDirectionList = new DoubleDirectionList<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { doubleDirectionList.Add(i); } doubleDirectionList.Print(); doubleDirectionList.Insert(2, 100); doubleDirectionList.Print(); doubleDirectionList.RemoveAt(10); doubleDirectionList.Print(); } public class DNode<T> where T : notnull { private T item; private DNode<T>? next; private DNode<T>? prior; public T Item { get => item; set => item = value; } public DNode<T>? Next { get => next; set => next = value; } public DNode<T>? Prior { get => prior; set => prior = value; } public DNode(T item) { this.item = item; next=prior=null; } public DNode() { next=prior = null; item=default; } } public class DoubleDirectionList<T> where T:notnull { private DNode<T> head; [ThreadStatic] private static DNode<T> currentNode; private int lenght; public DoubleDirectionList () { head = new DNode<T>(); currentNode = head; } public virtual bool IsEmpty => head.Next == null; public DNode<T> Head { get => head; set => head = value; } public DNode<T> CurrentNode { get => currentNode; set => currentNode = value; } public int Lenght { get { currentNode = head.Next; int n = 0; while(currentNode != null) { currentNode=currentNode.Next; n++; } return n; } set => lenght = value; } /// <summary> /// 添加节点 /// </summary> /// <param name="item"></param> public virtual void Add(T item ) { DNode<T> dNode = new(item); if (head.Next==null) { currentNode = head; currentNode.Next = dNode; dNode.Prior= currentNode; currentNode = currentNode.Next; } else { while (currentNode.Next!= null) { currentNode = currentNode.Next; } currentNode.Next = dNode; dNode.Prior = currentNode ; } } public virtual void Print() { currentNode = head.Next; while (currentNode != null) { Console.WriteLine(currentNode.Item); currentNode = currentNode.Next; } } /// <summary> /// 在当前节点之前插入 /// </summary> /// <param name="index"></param> /// <param name="item"></param> public virtual void Insert(int index ,T item) { currentNode = head.Next; DNode<T> dNode = new(item); if (head.Next == null) { currentNode = head; currentNode.Next = dNode; dNode.Prior = currentNode; currentNode = currentNode.Next; } else { int n = 0; while (n != index) { currentNode = currentNode.Next; ++n; } if (n == index) { DNode<T> prior = currentNode.Prior; prior.Next = dNode; dNode.Prior = prior; currentNode.Prior = dNode; dNode.Next = currentNode; } } } public virtual void RemoveAt(int index) { lenght = Lenght; if (index < 0|| index>lenght) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); if(head.Next == null) throw new OverflowException("list is null"); currentNode=head.Next; int n = 0; while(currentNode!=null) { if (n == index) { if (n == 0 && currentNode.Next == null) { head.Next.Prior = null; head.Next = null; return; } DNode<T> priro = currentNode.Prior; DNode<T> next = currentNode.Next; if (next == null) {priro.Next = null; return; } priro.Next = next; next.Prior = priro ; } currentNode =currentNode.Next; n++; } } } }
循环双向链表
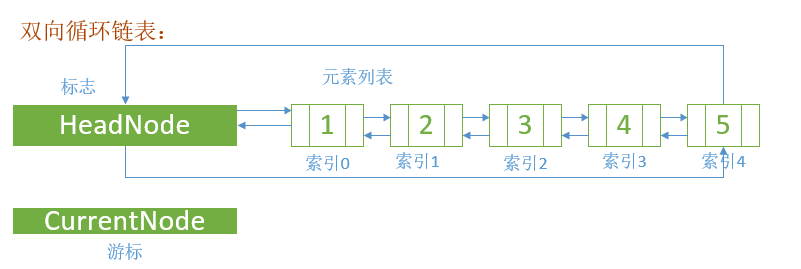
功能类似 就不写了。
空表:头指的next针指向自己
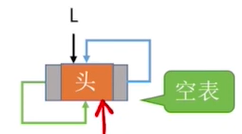
表示
C# 线性表
List<T>:顺序存储 内部是数组,查找O(1),插入最坏O(N)
LinkedList<T>:链式存储的双向链表。插入是O(1),查找最坏是O(n)
List<T>基本上是一个数组支持,通常大于当前的项目数.这些元素放在一个数组中,当旧的数组空间不足时,会创建一个新数组.这对于索引访问来说很快,但在删除或插入列表中或开头的元素时速度很慢.添加/删除列表末尾的条目相当便宜.
LinkedList<T>是一个双向链表 - 每个节点都知道它的前一个条目和下一个条目.这对于在特定节点(或头部/尾部)之后/之前插入是快速的,但是在索引访问时速度慢.
LinkedList<T>将通常采取更多的内存比List<T>,因为它需要对所有这些下一个/前一个的参考空间-和数据将可能有的参考局部性较少,因为每个节点是一个单独的对象.另一方面,a List<T> 可以具有比其当前需要大得多的后备阵列.
A List<T>实际上是一个数组,意味着它的Add操作在结尾是O(1)而在前面是O(n),但是你可以在O(1)中索引它.LinkedList<T>正如它所说,A 是一个链表.由于它是双重链接的,你可以在O(1)中向前面或后面添加项目,但索引到它是O(n).




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号