P2934 [USACO09JAN] Safe Travel G 题解
一个用平衡树,不用脑子的写法。(目前没有用平衡树的诶。)
题意
不经过最短路的最后一条边的最短路,保证最短路唯一。
思路
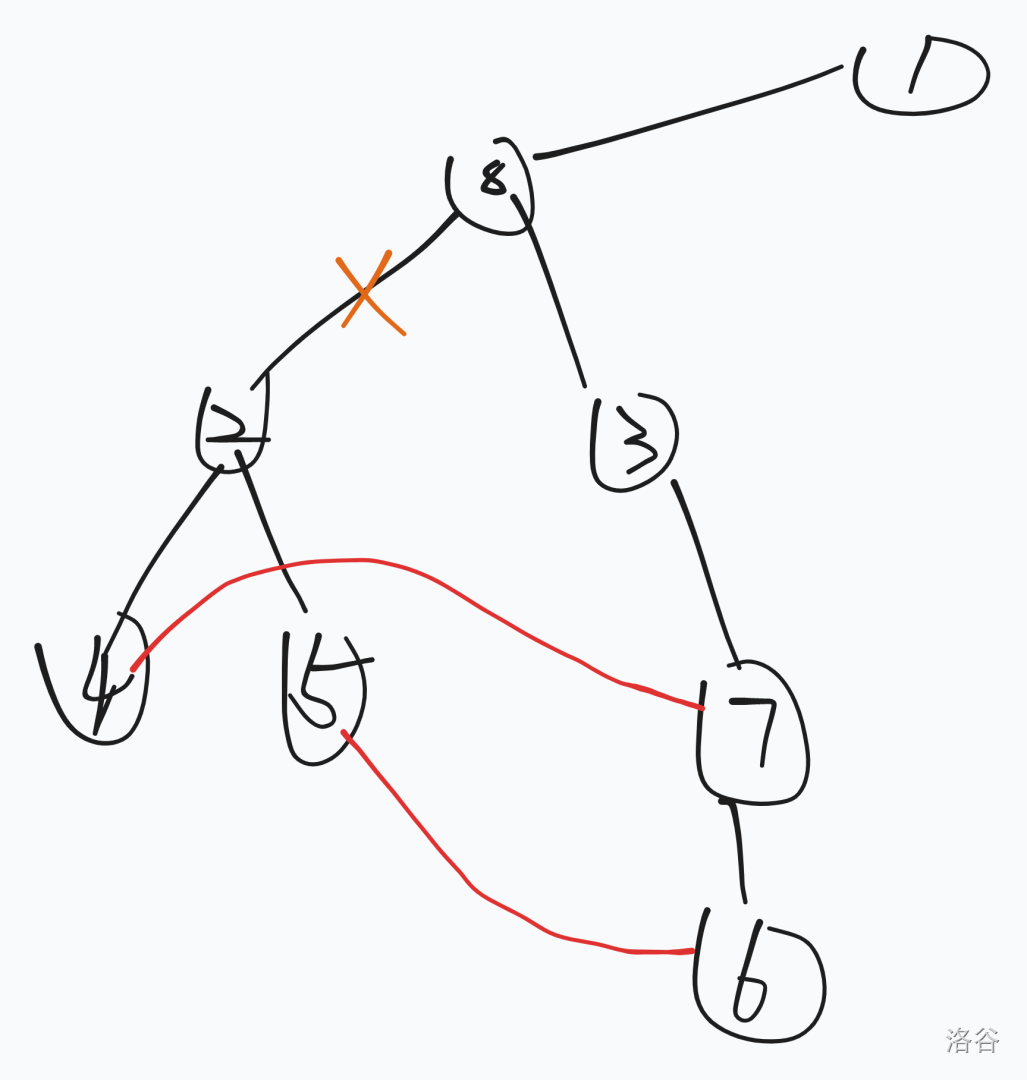
看到最短路唯一容易想到建出的最短路 DAG 其实是最短路树(以
那题意转化为求每个节点不经过与父亲的连边,所能到根节点的最短路。
容易发现每个点的答案都是被子树内的点与子树外的点的连边贡献的,称这些边为关键边。
记节点
节点
在最短路树中 dfs 求解。
用平衡树来维护关键边的信息。
具体的,维护经过这条边的到当前节点的路径长度,以及这条边连接的子树外的节点的 dfn 序。
平衡树内的点按记录的 dfn 序有序排列。
子节点的信息合并到当前节点,暴力合并即可,具体可以看这个,这个。
但要注意多了一条边,需要给这颗子树内所有路径的长度加上这条边的权值。
还需要解决一个问题,当我们计算节点
这时刚才记录的这些边连接的点的 dfn 序就有用了。
这些边的终点都是当前子树内的点(起点不用说,所有边的起点都在子树内),根据这个直接删除即可。
平衡树实现了全局最小值,全局加,带交合并。
复杂度的瓶颈在于平衡树的带交合并。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int read() {
int s = 0, w = 1;
char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) {
w = c == '-' ? -w : w;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
s = s * 10 + c - 48;
c = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
const int inf = 1e9;
const int maxN = 1e5 + 7;
int n, m;
int head[maxN], tot;
struct edge {
int to, ls, w;
} e[maxN * 4];
void add(int u, int v, int w) {
e[++tot] = {v, head[u], w};
head[u] = tot;
}
int dis[maxN], pre[maxN], prw[maxN];
bool vis[maxN];
using pii = pair<int, int>;
void dij() {
fill(dis + 1, dis + n + 1, inf);
dis[1] = 0;
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii>> Q;
Q.emplace(0, 1);
while (!Q.empty()) {
int f = Q.top().second;
Q.pop();
if (vis[f]) continue;
vis[f] = true;
for (int i = head[f]; i; i = e[i].ls) {
int to = e[i].to, w = e[i].w;
if (dis[to] > dis[f] + w) {
pre[to] = f, prw[to] = w;
dis[to] = dis[f] + w;
Q.emplace(dis[to], to);
}
}
}
}
struct wei {
int to, w;
wei(int to, int w) : to(to), w(w) {}
friend bool operator < (wei A, wei B) {
return A.to < B.to;
}
};
vector<wei> E[maxN];
int dfn[maxN], cnt, siz[maxN];
void initdfs(int x) {
dfn[x] = ++cnt;
siz[x] = 1;
for (auto [to, w] : E[x])
initdfs(to), siz[x] += siz[to];
}
mt19937 rd(5222568);
int nwn, root[maxN];
struct tree {
int l, r;
int to, w;
int key;
int siz;
int mn;
int tg;
} t[maxN * 4];
int New(int to, int v) {
int p = ++nwn;
t[p].l = t[p].r = t[p].tg = 0;
t[p].siz = 1;
t[p].to = to;
t[p].mn = t[p].w = v;
t[p].key = rd();
return p;
}
void upd(int p) {
t[p].siz = t[t[p].l].siz + t[t[p].r].siz + 1;
t[p].mn = min({t[t[p].l].mn, t[t[p].r].mn, t[p].w});
}
void make(int p, int v) {
if (!p) return;
t[p].mn += v;
t[p].w += v;
t[p].tg += v;
}
void down(int p) {
if (!t[p].tg) return;
make(t[p].l, t[p].tg);
make(t[p].r, t[p].tg);
t[p].tg = 0;
}
int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x | y;
if (t[x].key <= t[y].key) {
down(x);
t[x].r = merge(t[x].r, y);
upd(x);
return x;
} else {
down(y);
t[y].l = merge(x, t[y].l);
upd(y);
return y;
}
}
void split(int p, int k, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) x = y = 0;
else {
down(p);
if (t[p].to <= k)
x = p, split(t[p].r, k, t[x].r, y);
else
y = p, split(t[p].l, k, x, t[y].l);
upd(p);
}
}
int M(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x | y;
if (t[x].key > t[y].key) swap(x, y);
int L, R;
down(x), down(y);
split(y, t[x].to, L, R);
t[x].l = M(t[x].l, L);
t[x].r = M(t[x].r, R);
upd(x);
return x;
}
void insert(int &p, int to, int v) {
int L, R;
split(p, to, L, R);
p = merge(merge(L, New(to, v)), R);
}
void del(int &p, int x) {
int L, M, R;
split(p, dfn[x] + siz[x] - 1, L, R);
split(L, dfn[x] - 1, L, M);
p = merge(L, R);
}
int ans[maxN];
void dfs(int x) {
for (auto [to, w] : E[x]) {
dfs(to);
make(root[to], w);
root[x] = M(root[x], root[to]);
}
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].ls) {
int to = e[i].to, w = e[i].w;
if (dfn[x] <= dfn[to] && dfn[to] <= dfn[x] + siz[x] - 1)
continue;
if (to == pre[x] && w == prw[x]) continue;
insert(root[x], dfn[to], w + dis[to]);
}
del(root[x], x);
ans[x] = root[x] ? t[root[x]].mn : -1;
}
signed main() {
// freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
// ofstream cout("out.out");
t[0].mn = inf;
n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u = read(), v = read(), w = read();
add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w);
}
dij();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (pre[i])
E[pre[i]].emplace_back(i, prw[i]);
initdfs(1);
dfs(1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
cout << ans[i] << '\n';
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具