二分专题
Points in Segments
Given n points (1 dimensional) and q segments, you have to find the number of points that lie in each of the segments. A point pi will lie in a segment A B if A ≤ pi ≤ B.
For example if the points are 1, 4, 6, 8, 10. And the segment is 0 to 5. Then there are 2 points that lie in the segment.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 5), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case starts with a line containing two integers n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) and q (1 ≤ q ≤ 50000). The next line contains n space separated integers denoting the points in ascending order. All the integers are distinct and each of them range in [0, 108].
Each of the next q lines contains two integers Ak Bk (0 ≤ Ak ≤ Bk ≤ 108) denoting a segment.
OutputFor each case, print the case number in a single line. Then for each segment, print the number of points that lie in that segment.
Sample Input1
5 3
1 4 6 8 10
0 5
6 10
7 100000
Sample OutputCase 1:
2
3
2
题目分析 :
对于刚学C++ 的我 , 这题真的好坑我 , 程序写的没问题 , 就是因为输入输出的时候用的 cin , cout ,导致超时 , 找BUG找了好长时间 。
好了 , 下面正式分析题目 , 最开始看这个题就感觉是要用线段树 , 我哪会什么线段树 , 这题直接过 , 后来也是听了题解才知道 , 原来并不用线段树 , 就是用到一个 二分找数组下标 , 用后一个数组下标 - 前一个元素的数组下标 + 1 。
////*****/////
在二分区间找数组下标时 , 若此元素存在 , 直接返回数组下标 。 若此元素不存在 ,一直执行二分 , 二分退出的条件为 Left > Right , 此时被二分的元素一定是夹在 Left 与 Right 中的 , 所以若此元素作为待查询数据的左端临界值 , 则返回Left , 相反则返回 Right 。
附图介绍下 :
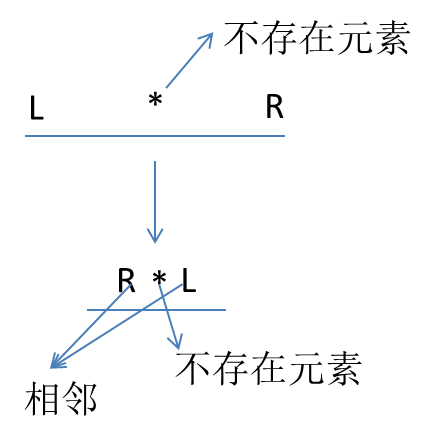
////*********/////
代码示例 :
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std ;
int pre[100000] ;
int search_1 ( int key , int l , int r ) {
int mid ;
while ( l <= r ) {
mid = ( l + r ) / 2 ;
if ( pre[mid] == key ) return mid ;
if ( pre[mid] < key ) l = mid + 1 ;
else r = mid - 1 ;
}
return l ;
}
int search_2 ( int key , int l , int r ) {
int mid ;
while ( l <= r ) {
mid = ( l + r ) / 2 ;
if ( pre[mid] == key ) return mid ;
if ( pre[mid] < key ) l = mid + 1 ;
else r = mid - 1 ;
}
return r ;
}
int main ( ) {
int t , n , q ;
int x , y , k = 1 ;
cin >> t ;
while ( t-- ) {
scanf ( "%d%d" , &n , &q ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++ ) {
scanf ( "%d" , &pre[i] ) ;
}
cout << "Case " << k++ << ':' << endl ;
while ( q-- ) {
scanf ( "%d%d" , &x , &y ) ;
int a = search_1 ( x , 0 , n-1 ) , b = search_2 ( y , 0 , n - 1 ) ;
printf ( "%d\n" , b -a + 1 ) ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
经过 一番讨论 ,这个题的测试样例还是有水的 , 有一种情况没想到但是是A 了 , 比如 在 3 3 3 中 , 要查找的区间是 [ 0 , 2 ] , 若按照我的方法 , 则返回 L = 0 , R = -1 ; 此时就会出错 , 所以这个题可以再最后在特判两种情况 ,带查找的两数位于 最左边 或 是待查找的两个数 位于最最右边 , 此时特判都应该输出 0 。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
补充 一种 二分查找数组下标的方法
在一个包含 N 个元素 , 从小到大排序的 int 数组中查找比给定整数 P 小的 , 下标最大的元素 , 找到则返回其下标 , 找不到则返回 - 1 。
代码示例 :
int searh_low ( int p ) {
int l = 0 , r = n - 1 , mid ;
int pt = -1 ; // 在初始时刻默认给定的最优解
while ( low <= high ) {
mid = l + ( r - l ) / 2 ;
if ( a[mid] >= p ) r = mid - 1 ;
else {
pt = mid ;
l = mid + 1 ;
}
}
return pt ;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号