The linux command 之存储媒介
一、常用的命令
- mount:挂载文件系统
- unmount:卸载文件系统
- fdisk:硬盘分区命令
- fdformat:格式化软盘
- fsck:检查和修复文件系统
- mkfs:创建文件系统
- dd:转换和拷贝一个文件
- genisoimage(mkisofs):创建一个ISO 9660映象文件
- wodim(cdrecord):向光存储介质中写入数据
- md5sum:计算MD5校验码
二、挂载、卸载存储设备
挂载:将该设备添加到文件树中,从而允许操作系统可以操作该设备,这个过程称为挂载。
/etc/fstab 文件列出了系统启动时挂载的设备。

使用mount命令,查看已经挂载的文件系统列表。

列表的格式是:device on mount_point type filesystem_type(options)
1 /dev/sda2 on / type ext4 (rw)
以上表示dev/sda2设备挂载在根目录下,可读写.
首先切换到超级用户,再使用(umount)命令卸载设备。
[me@linuxbox ~]$ su -
Password:
[root@linuxbox ~]# umount /dev/sdc
然后为设备创建一个新的挂载节点,挂载节点仅仅是文件系统上的某个目录。
1 [root@linuxbox ~]# mkdir /mnt/cdrom
使用 -t 选项指定文件系统类型:
1 [root@linuxbox ~]# mount -t iso9660 /dev/sdc /mnt/cdrom
通过新建的挂载节点访问CD光盘的内容:
1 [root@linuxbox ~]# cd /mnt/cdrom 2 [root@linuxbox cdrom]# ls
然后将目录切换到挂载节点以外的地方,卸载光盘:
1 [root@linuxbox cdrom]# cd 2 [root@linuxbox ~]# umount /dev/sdc
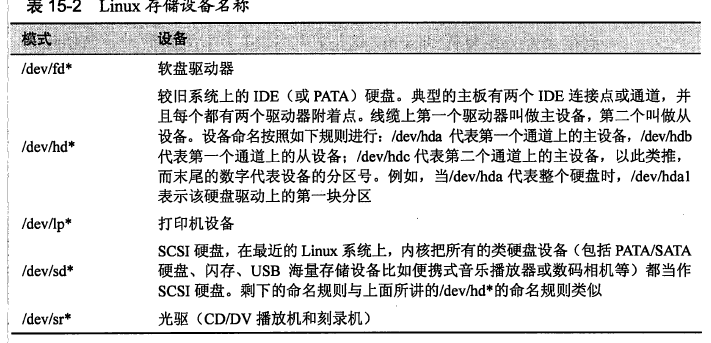
经过上述操作,我们还需要确定设备的名称:
二、创建新的文件系统
使用fdisk命令进行磁盘分区,fdisk命令实现用户与磁盘设备进行较低层次的直接交互,该工具可以用来编辑、删除、创建设备分区。
1 [me@linuxbox ~]$ sudo umount /dev/sdb1 2 [me@linuxbox ~]$ sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
然后输入m:
1 Command action 2 a toggle a bootable flag 3 b edit bsd disklabel 4 c toggle the dos compatibility flag 5 d delete a partition 6 l list known partition types 7 m print this menu 8 n add a new partition 9 o create a new empty DOS partition table 10 p print the partition table 11 q quit without saving changes 12 s create a new empty Sun disklabel 13 t change a partition's system id 14 u change display/entry units 15 v verify the partition table 16 w write table to disk and exit 17 x extra functionality (experts only) 18 Command (m for help):
使用p可以显示设备的分区表:
1 Command (m for help): p 2 Disk /dev/sdb: 16 MB, 16006656 bytes 3 1 heads, 31 sectors/track, 1008 cylinders 4 Units = cylinders of 31 * 512 = 15872 bytes 5 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System 6 /dev/sdb1 2 1008 15608+ b W95 FAT32
未完待续....
陈小洁的三只猫


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号