【多线程】利用例子理解静态代理模式以及Thread代理模式
假设我们现在作为学生要去吃饭,服务员来服务我们。
我们来看一下静态代理例子。
在下图中 我们新建一个student传参到waiter里面
而waiter类里的那个student实例赋值传进来的值
然后调用waiter的eat。在waiter的eat里面有waiter自己的服务,还有student的eat
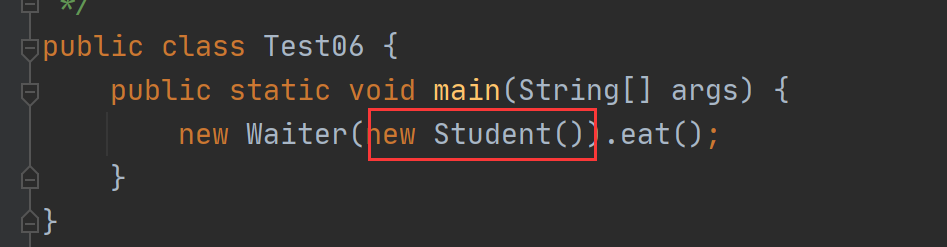
/** * @Description: 用来了解静态代理模式 以及实现runnable接口创建线程 * @Author: cckong * @Date: 2021/2/3 */ public class Test06 { public static void main(String[] args) { new Waiter(new Student()).eat(); } } interface people{ public void eat(); } class Student implements people{ @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("学生吃东西"); } } class Waiter implements people{ private Student stu; Waiter(Student student){ this.stu=student; } @Override public void eat() { serviceBefore(); this.stu.eat(); serviceAfter(); } public void serviceBefore(){ System.out.println("端上饭菜"); } public void serviceAfter(){ System.out.println("收拾桌子"); }
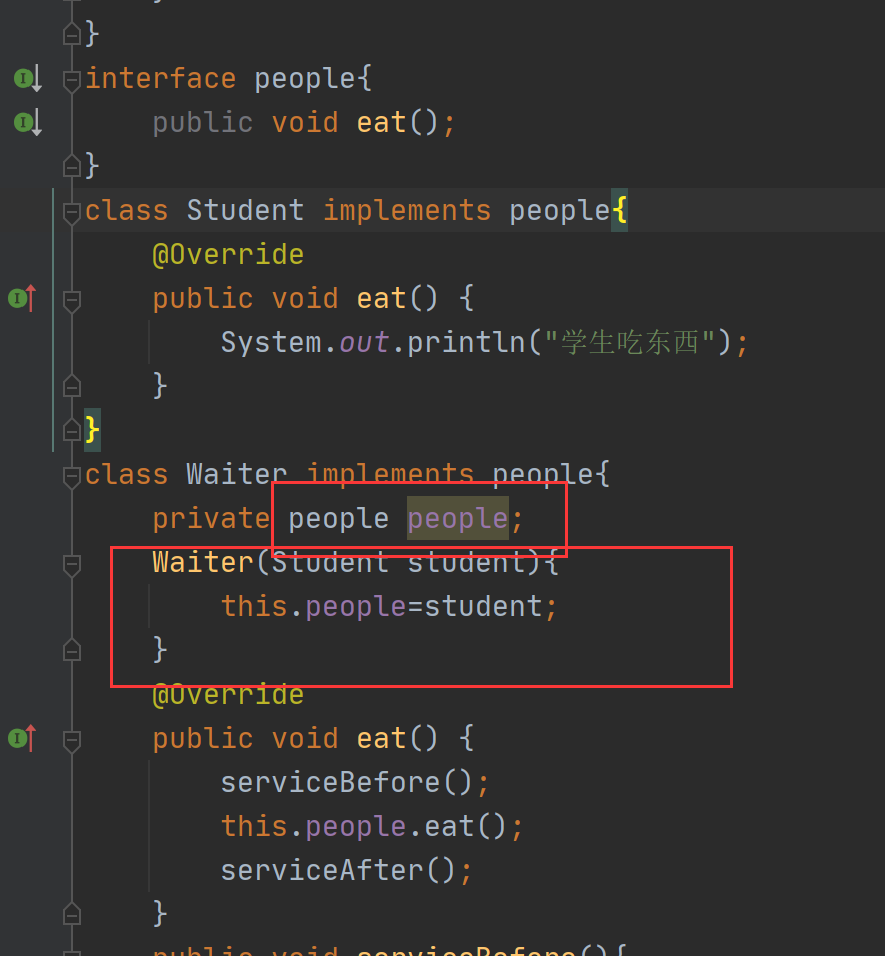
我们也可以使用多态来进行调用 这样就对于任何只要是实现了people接口的对象 waiter都可以服务了
这就是我们实现Runnable接口然后新建线程的时候需要传进去参
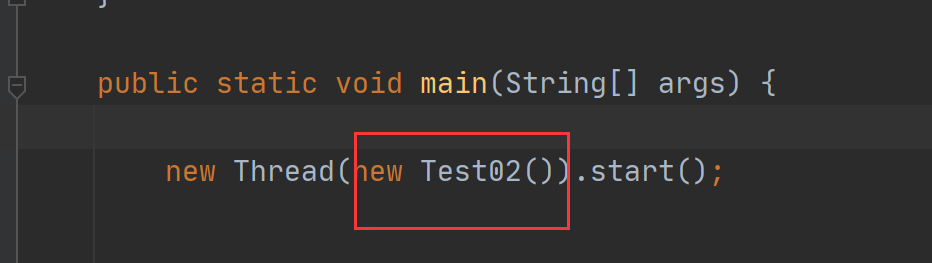
我们开看一下Thread源码的构造函数
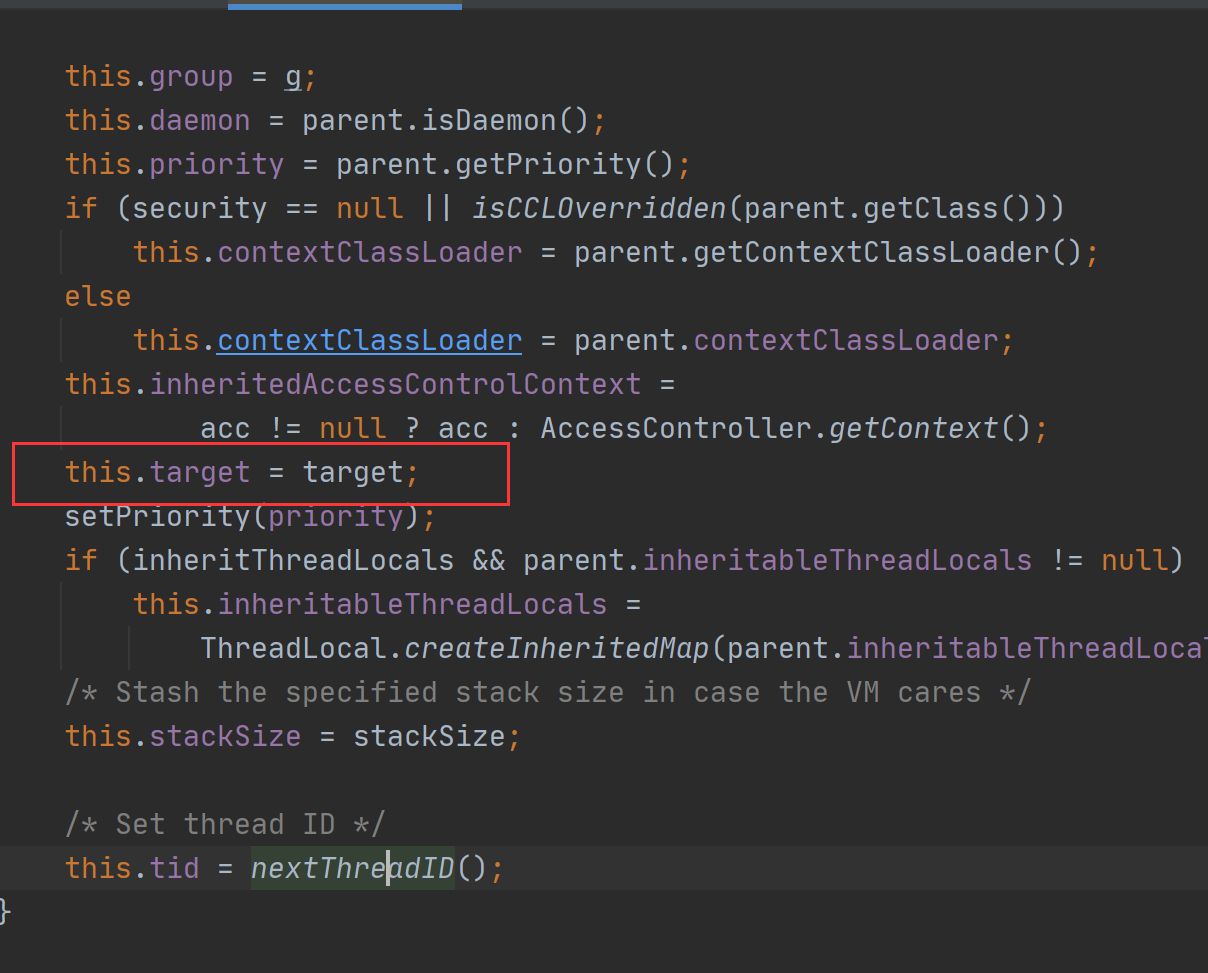
/** * Initializes a Thread. * * @param g the Thread group * @param target the object whose run() method gets called * @param name the name of the new Thread * @param stackSize the desired stack size for the new thread, or * zero to indicate that this parameter is to be ignored. * @param acc the AccessControlContext to inherit, or * AccessController.getContext() if null * @param inheritThreadLocals if {@code true}, inherit initial values for * inheritable thread-locals from the constructing thread */ private Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc, boolean inheritThreadLocals) { if (name == null) { throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); } this.name = name; Thread parent = currentThread(); SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); if (g == null) { /* Determine if it's an applet or not */ /* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager what to do. */ if (security != null) { g = security.getThreadGroup(); } /* If the security manager doesn't have a strong opinion on the matter, use the parent thread group. */ if (g == null) { g = parent.getThreadGroup(); } } /* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is explicitly passed in. */ g.checkAccess(); /* * Do we have the required permissions? */ if (security != null) { if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) { security.checkPermission( SecurityConstants.SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION); } } g.addUnstarted(); this.group = g; this.daemon = parent.isDaemon(); this.priority = parent.getPriority(); if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass())) this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader(); else this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader; this.inheritedAccessControlContext = acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext(); this.target = target; setPriority(priority); if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals); /* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */ this.stackSize = stackSize; /* Set thread ID */ this.tid = nextThreadID(); }
我们调用的格式是这个构造函数(Thread构造函数很多,但是主要上面那一个完整的 ,根据不同的传参进行不同的构造)
比如说我们调用的是
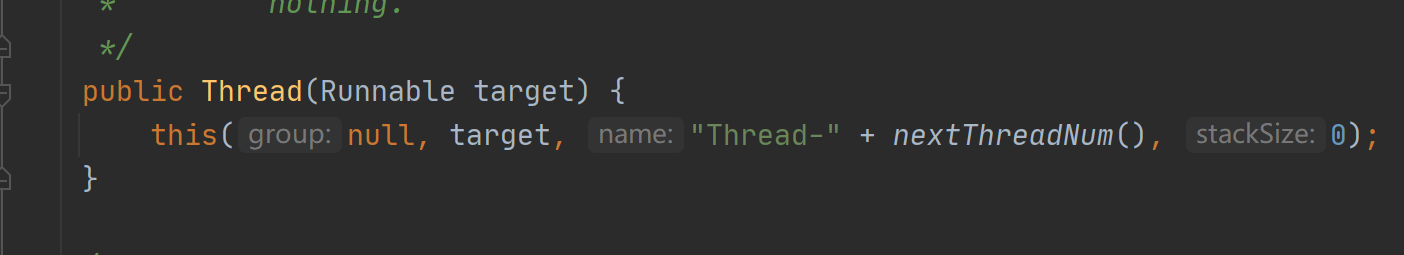
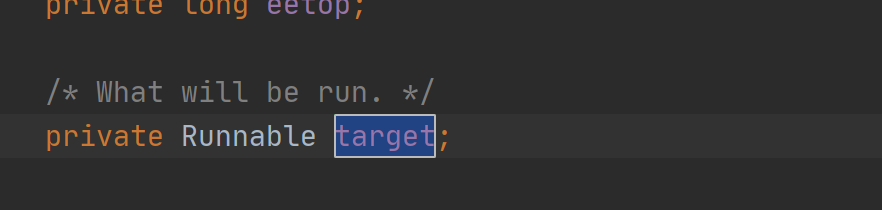
在源码中 利用多态传进去了


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号