# PTA博客作业(三)
PTA博客作业(三)
1.前言
本次电信系列题目集相较于之前的多边形题目集来说,所涉及的东西其实并不多,整体难度反而更简单一些,差不多是以中、高、低的难度层次来划分这三次作业的。不过和之前题目集不同的一点,就是这次老师给出了可参考的类图,由于给出的类和函数、属性等过多,联系起来十分复杂,需要花一大半的时间去理解参悟,否则根本串联不到一起,很难想到这个函数怎么用,这个属性是干嘛的。因此本体的题目和类图理解就显得十分重要,一旦你掌握了理解了,那么这道题就你能够轻松拿下了。
2.设计与分析
①题目集六
7-1 电信计费系列1-座机计费
题目:
实现一个简单的电信计费程序:
假设南昌市电信分公司针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式:
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
南昌市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
输入格式:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码除区号外由是7-8位数字组成。
本题只考虑计费类型0-座机计费,电信系列2、3题会逐步增加计费类型。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
注意:
本题非法输入只做格式非法的判断,不做内容是否合理的判断(时间除外,否则无法计算),比如:
1、输入的所有通讯信息均认为是同一个月的通讯信息,不做日期是否在同一个月还是多个月的判定,直接将通讯费用累加,因此月租只计算一次。
2、记录中如果同一电话号码的多条通话记录时间出现重合,这种情况也不做判断,直接 计算每条记录的费用并累加。
3、用户区号不为南昌市的区号也作为正常用户处理。
输出格式:
根据输入的详细通讯信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月费用(精确到小数点后2位,
单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条通讯信息单独计费后累加,不是将所有时间累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3,可根据理解自行调整:
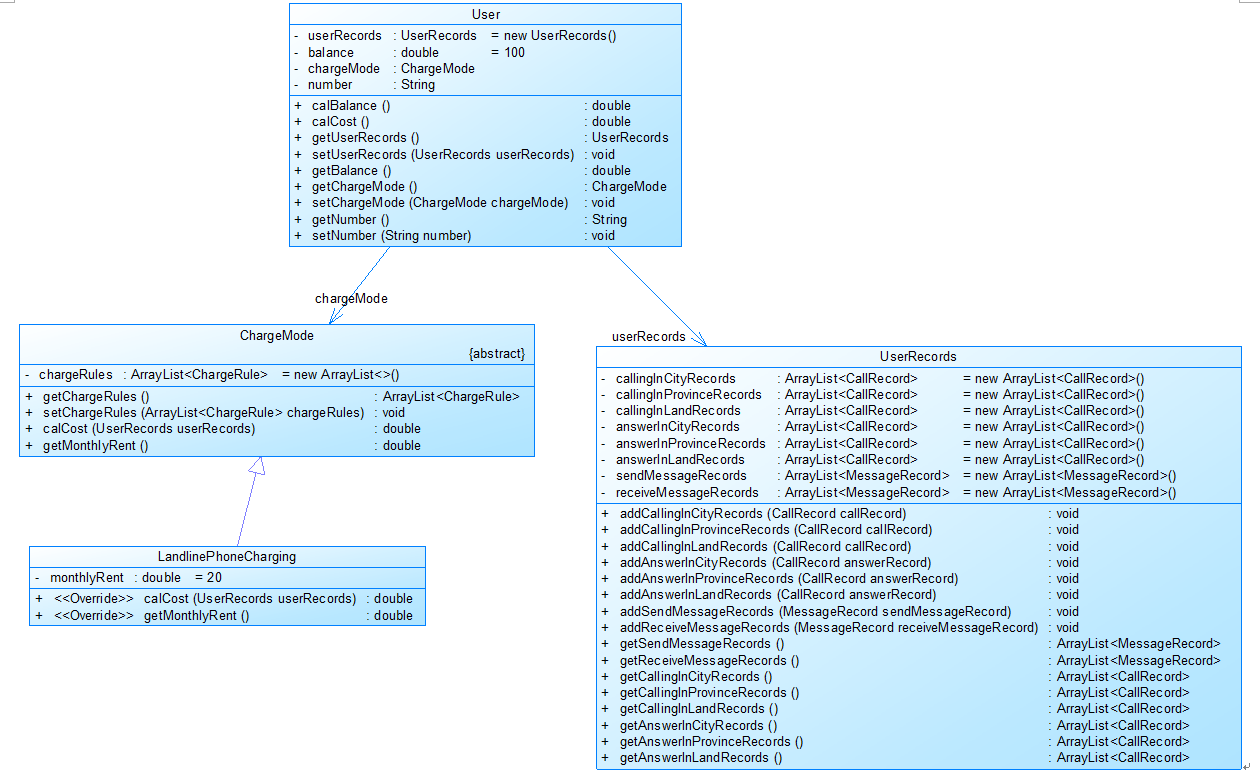
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。
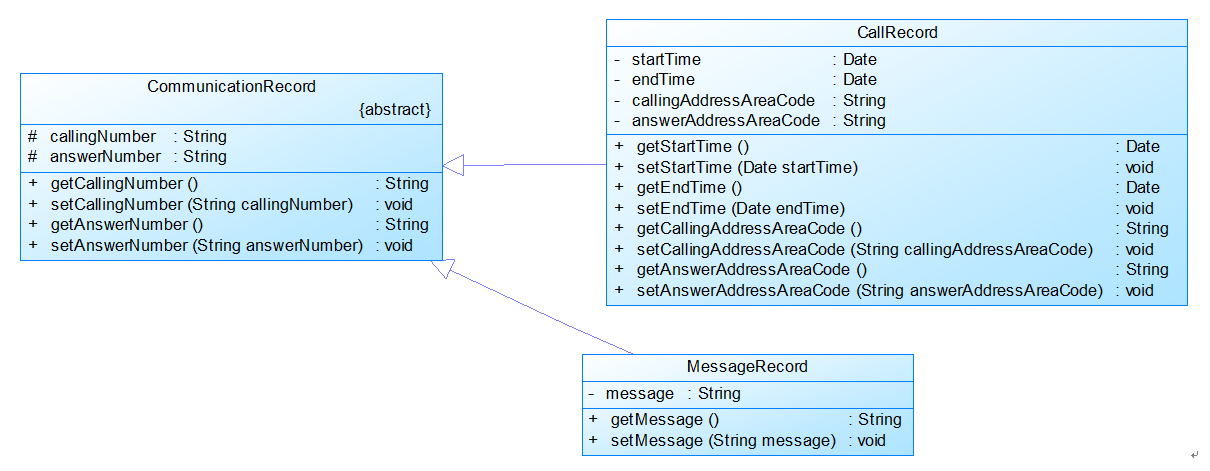
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。
CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。
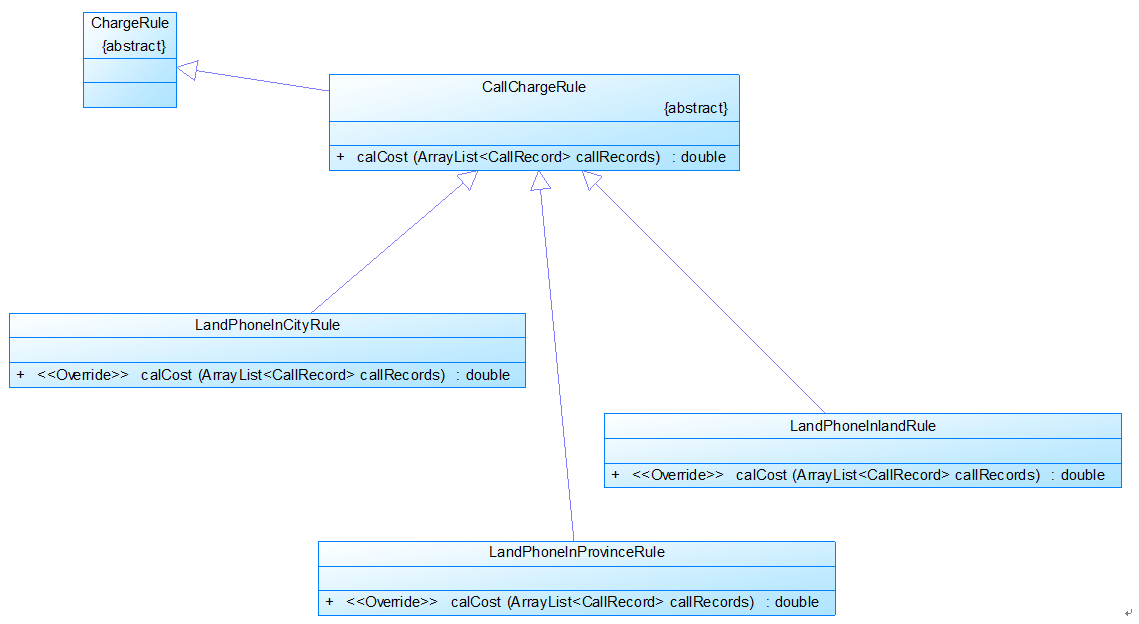
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是
座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
后续扩展说明:
后续题目集将增加手机用户,手机用户的计费方式中除了与座机计费类似的主叫通话费之外,还包含市外接听电话的漫游费以及发短信的费用。在本题的设计时可统一考虑。
通话记录中,手机需要额外记录拨打/接听的地点的区号,比如:
座机打手机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 13305862264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
手机互打:t-主叫号码 拨号地点 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-18907910010 0791 13305862264 0371 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
短信的格式:m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you
题目分析:
本题主要针对座机拨打,因此不用考虑其他计费情况。本题作为电信计费系列的第一道题,首先便是需要充分的理解上述的类图,清楚各个类之间的关系,以及它们各自的作用。之后便是正则表达式的运用,可以筛选有效的信息,并且在正确的排序之后加以存储记录。再者还需要正确的理解题目意思,比如拨打座机属于哪个位置,市内省内还是省外,这些都要进行判断处理,然后根据各自的计费规则进行计算,循环将答案输出。而判断这些信息的最好方式,就是将字符串进行分割处理,根据所给的格式进行位置判断,然后进行存储计算等处理。
源码展示:
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<String> information1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> information2 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
String str = input.nextLine();
while (!str.equals("end")) {
String regex1 = "u-(07)(9[0-9]|(01))[0-9]{7,8} [0-3]";
String regex2 = "t-0\\d{9,11}\\s0\\d{9,11}((\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|(1[0-2]))\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|3[0-1])\\s(([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2})";
if (str.matches(regex1))
{
String[] str1 = str.split("-");
String str2 = str1[1];
String[] str3 = str2.split(" ");
if (!information1.contains(str3[0]))
information1.add(str3[0]);
} else if (str.matches(regex2))
{
String[] str1 = str.split("-");
String str2 = str1[1];
information2.add(str2);
}
str = input.nextLine();
}
Collections.sort(information1);
for (String i : information1)
{
User user = new User();
user.setNumber(i);
users.add(user);
}
for (User i:users)
{
for(String j:information2)
{
String[] k=j.split(" ");
if(i.number.equals(k[0]))
{
CallRecord callRecord=new CallRecord();
callRecord.setCallingNumber(k[0]);
callRecord.setAnswerNumber(k[1]);
callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode(k[0].substring(0,4));
callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(k[1].substring(0,4));
String startTime=k[2]+" "+k[3];
String endTime=k[4]+" "+k[5];
String regex="[1-9]\\d{3}.([1-9]|1[0-2]).([1-9]|[1-2][0-9]|3[0-1])\\s+(2[0-3]|[0-1]\\d):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d";
if(startTime.matches(regex)&&endTime.matches(regex))
{
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss");
Date s1 = null;
try {
s1 = format.parse(startTime);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
callRecord.setStartTime(s1);
Date s2 = null;
try {
s2 = format.parse(endTime);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
callRecord.setEndTime(s2);
if(judgeAddress(k[0])==judgeAddress(k[1])&&judgeAddress(k[0])!=3)
i.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord);
else if((judgeAddress(k[0])!=judgeAddress(k[1]))&&judgeAddress(k[0])!=3&&judgeAddress(k[1])!=3)
i.getUserRecords().addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord);
else
i.getUserRecords().addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord);
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<users.size();i++)
{
LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging =new LandlinePhoneCharging();
users.get(i).setChargeMode(landlinePhoneCharging);
users.get(i).calBalance();
if(i==users.size()-1)
System.out.print(users.get(i).getNumber()+" "+users.get(i).calCost()+" "+users.get(i).getBalance());
else
System.out.println(users.get(i).getNumber()+" "+users.get(i).calCost()+" "+users.get(i).getBalance());
}
}
public static int judgeAddress(String s)
{
String s1;
int num;
s1=s.substring(0,4);
num=Integer.parseInt(s1);
if(num==791)
return 1;
else if((num>=790&&num<=799)||num==701)
return 2;
else
return 3;
}
}
class User
{
UserRecords userRecords=new UserRecords();
double balance=100;
ChargeMode chargeMode;
String number;
public double calBalance()
{
double sum=this.balance;
double cost1=chargeMode.calCost(userRecords);
double cost2=chargeMode.getMonthlyRent();
this.balance=sum-cost1-cost2;
return Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f",balance));
}
public double calCost()
{
double cost=chargeMode.calCost(userRecords);
return Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f",cost));
}
public UserRecords getUserRecords()
{
return userRecords;
}
public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords)
{
this.userRecords = userRecords;
}
public double getBalance()
{
return balance;
}
public ChargeMode getChargeMode()
{
return chargeMode;
}
public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode)
{
this.chargeMode = chargeMode;
}
public String getNumber()
{
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number)
{
this.number=number;
}
}
class UserRecords
{
ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> answerCityRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> answerProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> answerLandRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> sendMessageRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> receiveMessageRecords=new ArrayList<>();
public void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addAnswerCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
answerCityRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addAnswerProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
answerProvinceRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addAnswerLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
answerLandRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addSendMessageRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
sendMessageRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addReceiveMessageRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
receiveMessageRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords()
{
return callingInCityRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords()
{
return callingInProvinceRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords()
{
return callingInLandRecords;
}
}
abstract class ChargeMode
{
public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
public abstract double getMonthlyRent();
}
class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode
{
double monthlyRent=20;
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules=new ArrayList<>();
LandPhoneInCityRule landPhoneInCityRule=new LandPhoneInCityRule();
LandPhoneInProvinceRule landPhoneInProvinceRule=new LandPhoneInProvinceRule();
LandPhoneInLandRule landPhoneInLandRule=new LandPhoneInLandRule();
chargeRules.add(landPhoneInCityRule);
chargeRules.add(landPhoneInProvinceRule);
chargeRules.add(landPhoneInLandRule);
double a=chargeRules.get(0).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords());
double b=chargeRules.get(1).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords());
double c=chargeRules.get(2).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords());
return a+b+c;
}
@Override
public double getMonthlyRent()
{
return monthlyRent;
}
}
abstract class CommunicationRecord
{
protected String callingNumber;
protected String answerNumber;
public String getCallingNumber()
{
return callingNumber;
}
public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber)
{
this.callingNumber=callingNumber;
}
public String getAnswerNumber()
{
return answerNumber;
}
public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber)
{
this.answerNumber=answerNumber;
}
}
class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord
{
private Date startTime;
private Date endTime;
private String callingAddressAreaCode;
private String answerAddressAreaCode;
public Date getStartTime()
{
return startTime;
}
public void setStartTime(Date startTime)
{
this.startTime = startTime;
}
public Date getEndTime()
{
return endTime;
}
public void setEndTime(Date endTime)
{
this.endTime = endTime;
}
public String getCallingAddressAreaCode()
{
return callingAddressAreaCode;
}
public void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode)
{
this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode;
}
public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode()
{
return answerAddressAreaCode;
}
public void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode)
{
this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode;
}
}
class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord
{
private String message;
public String getMessage()
{
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message)
{
this.message = message;
}
}
abstract class ChargeRule
{
public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords)
{
return 1;
}
}
class LandPhoneInCityRule extends ChargeRule
{
double cost = 0;
public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)
{
for(CallRecord i:callRecords)
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else
Time = Time/60000;
cost+=Time*0.1;
}
return cost;
}
}
class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends ChargeRule
{
double cost = 0;
public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)
{
for(CallRecord i:callRecords)
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else
Time = Time/60000;
cost+=Time*0.3;
}
return cost;
}
}
class LandPhoneInLandRule extends ChargeRule
{
double cost = 0;
public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)
{
for(CallRecord i:callRecords)
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else Time = Time/60000;
cost+=Time*0.6;
}
return cost;
}
}
类图:
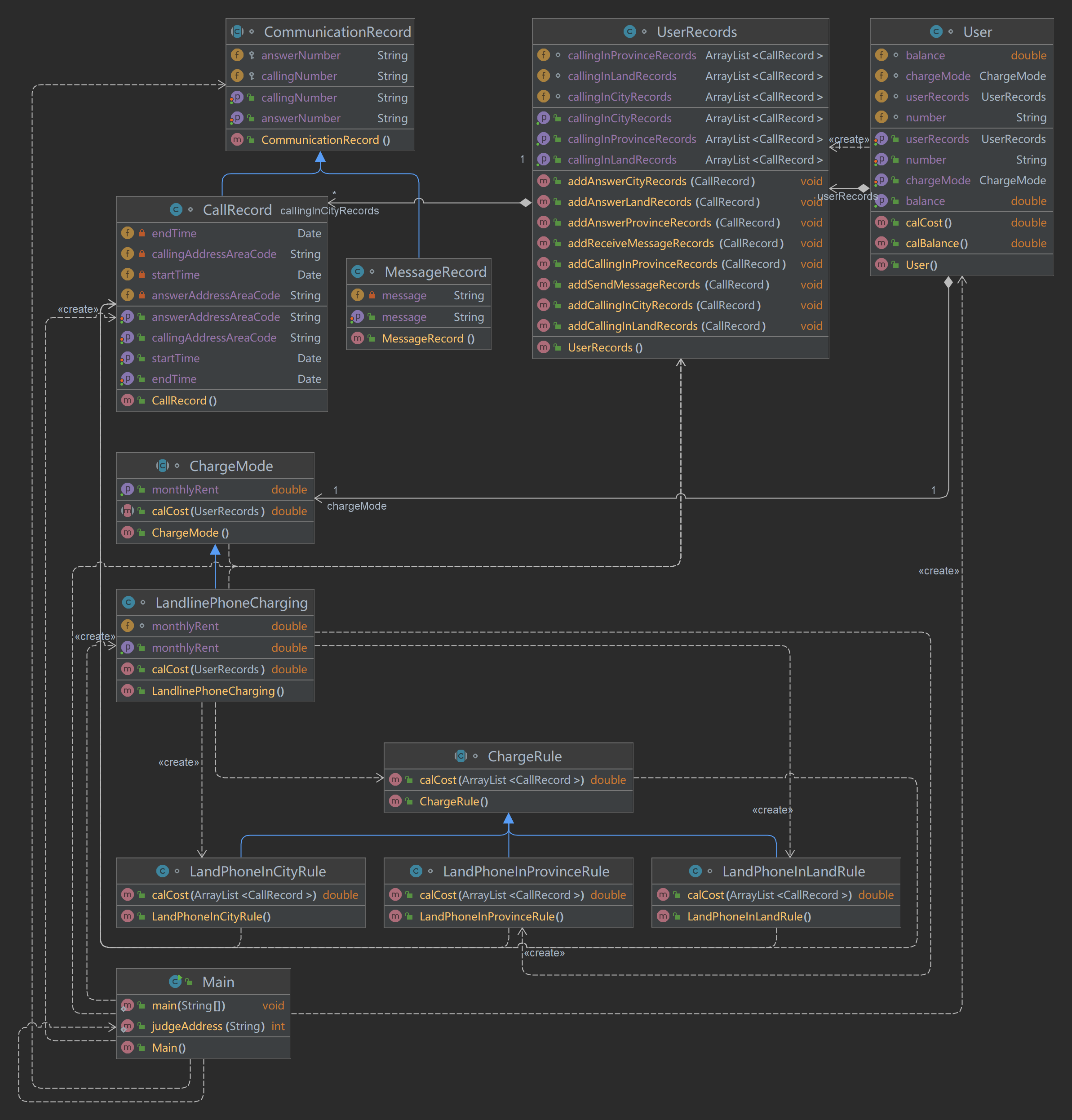
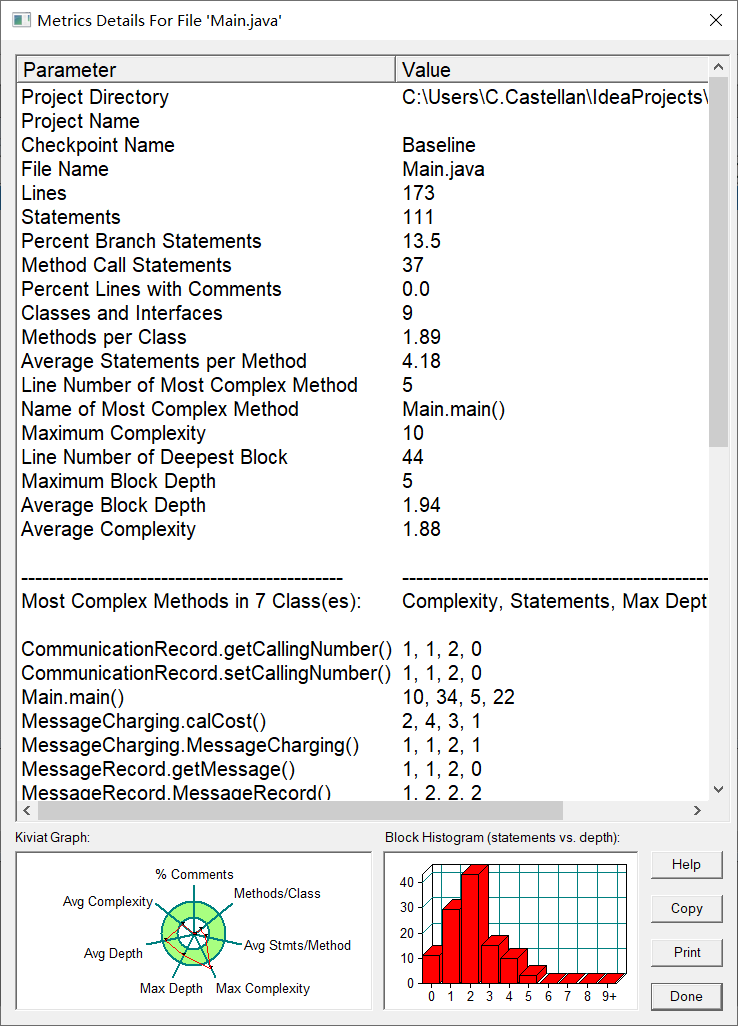
SourceMonitor生成的报表内容:
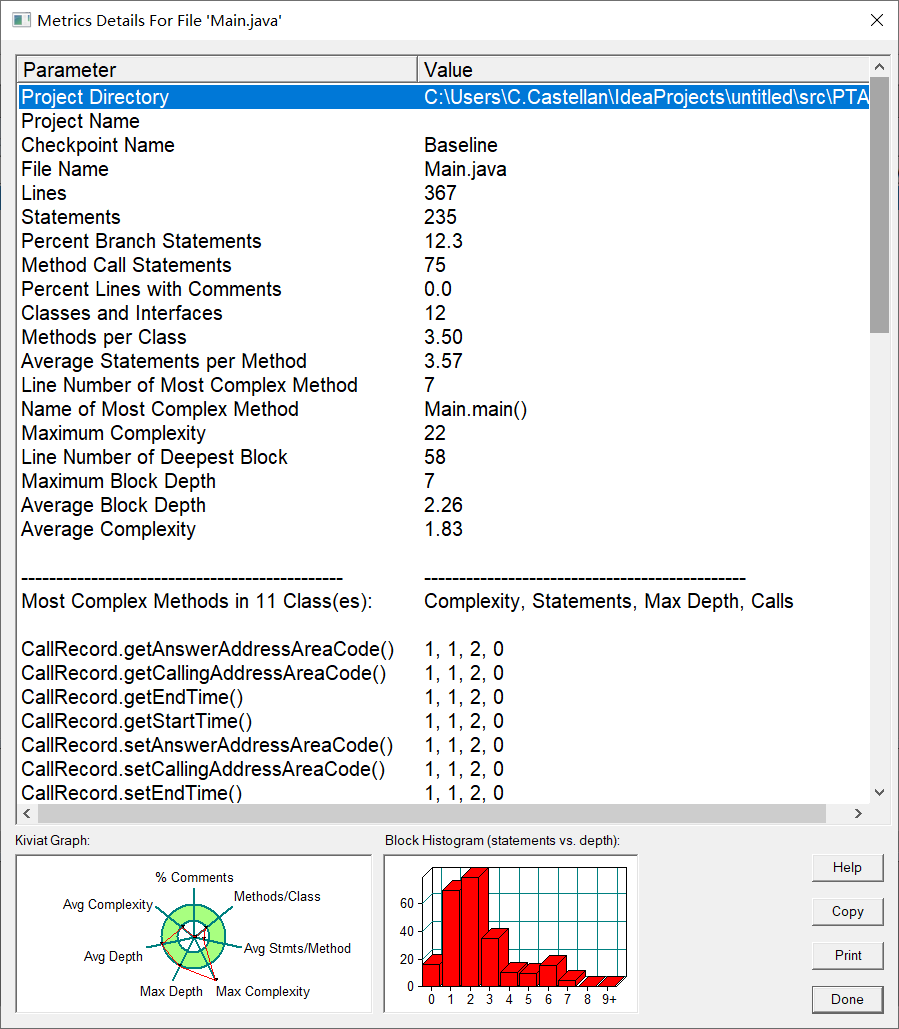
本题心得:
本题在了解各类之间的关系以及作用上还是花了很多时间,通过在SourceMonitor生成的报表内容来看,max complexity这一点上还是超出了范围,本题的主函数的代码多用于循环操作进行,增加了代码的时间复杂度,还需要进一步的优化。
②题目集七
7-1 电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费
题目:
实现南昌市电信分公司的计费程序,假设该公司针对手机和座机用户分别采取了两种计费方案,分别如下:
1、针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式(与电信计费系列1内容相同):
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
假设本市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
2、针对手机用户采用实时计费方式:
月租15元,市内省内接电话均免费,市内拨打市内电话0.1元/分钟,市内拨打省内电话0.2元/分钟,市内拨打省外电话0.3元/分钟,省内漫游打电话0.3元/分钟,省外漫游接听0.3元/分钟,省外漫游拨打0.6元/分钟;
注:被叫电话属于市内、省内还是国内由被叫电话的接听地点区号决定,比如以下案例中,南昌市手机用户13307912264在区号为020的广州接听了电话,主叫号码应被计算为拨打了一个省外长途,同时,手机用户13307912264也要被计算省外接听漫游费:
u-13307912264 1
t-079186330022 13307912264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
输入格式:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,含手机和座机用户
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题在电信计费系列1基础上增加类型1-手机实时计费。
手机设置0或者座机设置成1,此种错误可不做判断。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
输入格式增加手机接打电话以及收发短信的格式,手机接打电话的信息除了号码之外需要额外记录拨打/接听的地点的区号,比如:
座机打手机:
t-主叫号码 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 13305862264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
手机互打:
t-主叫号码 拨号地点 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-18907910010 0791 13305862264 0371 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
输出格式:
根据输入的详细通讯信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月费用(精确到小数点后2位,单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条通讯、短信信息均单独计费后累加,不是将所有信息累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
本题只做格式的错误判断,无需做内容上不合理的判断,比如同一个电话两条通讯记录的时间有重合、开户号码非南昌市的号码等,此类情况都当成正确的输入计算。但时间的输入必须符合要求,比如不能输入2022.13.61 28:72:65。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3,可根据理解自行调整:

图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。

图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。
CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。

图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是
座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
注意:以上图中所定义的类不是限定要求,根据实际需要自行补充或修改。
题目分析:
本题在电信计费系列题目1的基础上增加了手机计费规则,可以座机拨打手机、手机拨打座机、手机拨打手机等,需要考虑的点很多,其中最重要的就是手机的位置区号所属的判断:拨打手机分别在市内、省内、省外拨打时所需的花费各不相同,同时要根据接听电话的所在区号判断收费;接听手机的收费也根据其所在区位;接听手机在市内或者省内时,无需另付漫游费,但当它在省外接听省外电话时,接听电话还需要付省外接听漫游费。只要理清了上述几点计费规则,本题的解题思路将会清晰很多。
源码展示:
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<String> information = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords=new ArrayList<>();
String str = input.nextLine();
String regex1 = "u-((0\\d{9,11}\\s0)|(1\\d{10}\\s1))";
String regex2 = "0\\d{9,11}\\s0\\d{9,11}((\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|(1[0-2]))\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|3[0-1])\\s(([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2})";
String regex3 = "0\\d{9,11}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}((\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|(1[0-2]))\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|3[0-1])\\s(([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2})";
String regex4 = "1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s0\\d{9,11}((\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|(1[0-2]))\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|3[0-1])\\s(([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2})";
String regex5 = "1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}((\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|(1[0-2]))\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|3[0-1])\\s(([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])){2})";
while (!str.equals("end")) {
if (str.matches(regex1))
{
String[] str1 = str.split("-");
String str2 = str1[1];
if (!information.contains(str2))
information.add(str2);
}
else if (str.matches("t-"+regex2)||str.matches("t-"+regex3)||str.matches("t-"+regex4)||str.matches("t-"+regex5))
{
String[] str1 = str.split("-");
String str2 = str1[1];
String[] str3=str2.split(" ");
CallRecord callRecord=new CallRecord(str3);
callRecords.add(callRecord);
}
str = input.nextLine();
}
Collections.sort(information);
for (String i : information)
{
User user = new User();
String[] str3 = i.split(" ");
if(Integer.parseInt(str3[1])==0)
user.setChargeMode(new LandlinePhoneCharging());
else
user.setChargeMode(new NewLandlinePhoneCharging());
user.setNumber(str3[0]);
users.add(user);
}
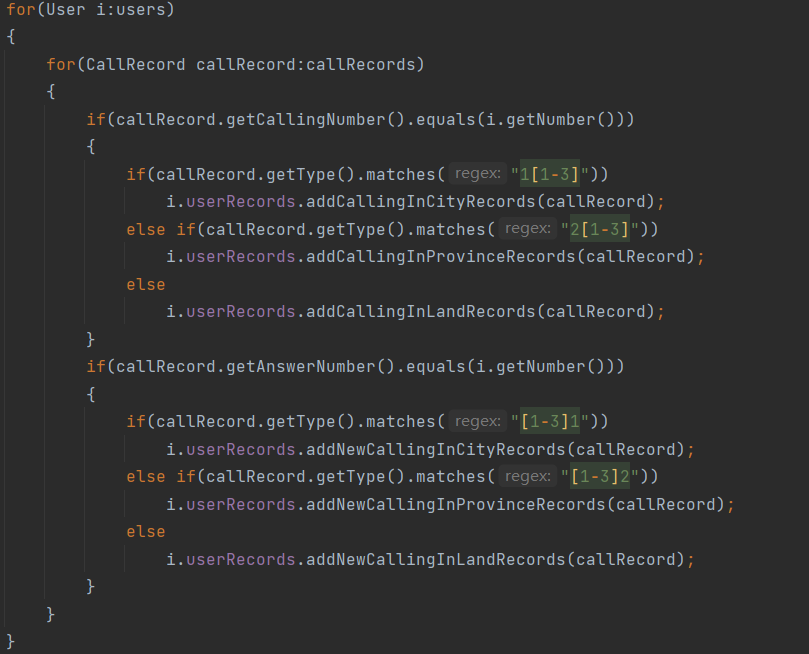
for(User i:users)
{
for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords)
{
if(callRecord.getCallingNumber().equals(i.getNumber()))
{
if(callRecord.getType().matches("1[1-3]"))
i.userRecords.addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord);
else if(callRecord.getType().matches("2[1-3]"))
i.userRecords.addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord);
else
i.userRecords.addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord);
}
if(callRecord.getAnswerNumber().equals(i.getNumber()))
{
if(callRecord.getType().matches("[1-3]1"))
i.userRecords.addNewCallingInCityRecords(callRecord);
else if(callRecord.getType().matches("[1-3]2"))
i.userRecords.addNewCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord);
else
i.userRecords.addNewCallingInLandRecords(callRecord);
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<users.size();i++)
{
if(i!=users.size()-1)
System.out.println(users.get(i).getNumber()+" "+users.get(i).calCost()+" "+users.get(i).calBalance());
else
System.out.print(users.get(i).getNumber()+" "+users.get(i).calCost()+" "+users.get(i).calBalance());
}
}
}
class User
{
UserRecords userRecords=new UserRecords();
double balance=100;
int mode;
ChargeMode chargeMode;
String number;
public double calBalance()
{
double sum=this.balance;
double cost1=chargeMode.calCost(userRecords);
double cost2=chargeMode.getMonthlyRent();
this.balance=sum-cost1-cost2;
return Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f",balance));
}
public double calCost()
{
double cost=chargeMode.calCost(userRecords);
return Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f",cost));
}
public UserRecords getUserRecords()
{
return userRecords;
}
public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) {
this.userRecords = userRecords;
}
public ChargeMode getChargeMode() {
return chargeMode;
}
public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode)
{
this.chargeMode = chargeMode;
}
public String getNumber()
{
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number)
{
this.number=number;
}
public int getMode() {
return mode;
}
public void setMode(int mode) {
this.mode = mode;
}
}
class UserRecords
{
ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> newCallingInCityRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> newCallingInProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> newCallingInLandRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> sendMessageRecords=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CallRecord> receiveMessageRecords=new ArrayList<>();
public void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addNewCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
newCallingInCityRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addNewCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
newCallingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addNewCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
newCallingInLandRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addSendMessageRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
sendMessageRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public void addReceiveMessageRecords(CallRecord callRecord)
{
receiveMessageRecords.add(callRecord);
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords()
{
return callingInCityRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords()
{
return callingInProvinceRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords()
{
return callingInLandRecords;
}
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getNewCallingInCityRecords(){ return newCallingInCityRecords; }
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getNewCallingInProvinceRecords(){ return newCallingInProvinceRecords; }
public ArrayList<CallRecord> getNewCallingInLandRecords(){ return newCallingInLandRecords; }
}
abstract class ChargeMode
{
protected ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules = new ArrayList<>();
public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
public abstract double getMonthlyRent();
}
class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode
{
double monthlyRent=20;
public LandlinePhoneCharging() {
chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule());
chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule());
chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInLandRule());
}
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double cost = 0;
for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) {
cost += rule.calCost(userRecords);
}
return cost;
}
@Override
public double getMonthlyRent() {
return monthlyRent;
}
}
class NewLandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode
{
double monthlyRent = 15;
public NewLandlinePhoneCharging()
{
chargeRules.add(new newLandPhoneInCityRule());
chargeRules.add(new newLandPhoneInProvinceRule());
chargeRules.add(new newLandPhoneInLandRule());
}
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double cost = 0;
for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) {
cost += rule.calCost(userRecords);
}
return cost;
}
@Override
public double getMonthlyRent() {
return monthlyRent;
}
}
abstract class CommunicationRecord
{
protected String callingNumber;
protected String answerNumber;
public String getCallingNumber() {
return callingNumber;
}
public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber)
{
this.callingNumber=callingNumber;
}
public String getAnswerNumber() {
return answerNumber;
}
public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber)
{
this.answerNumber=answerNumber;
}
}
class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord
{
Date startTime;
Date endTime;
String callingAddressAreaCode;
String answerAddressAreaCode;
public Date getStartTime()
{
return startTime;
}
public Date getEndTime()
{
return endTime;
}
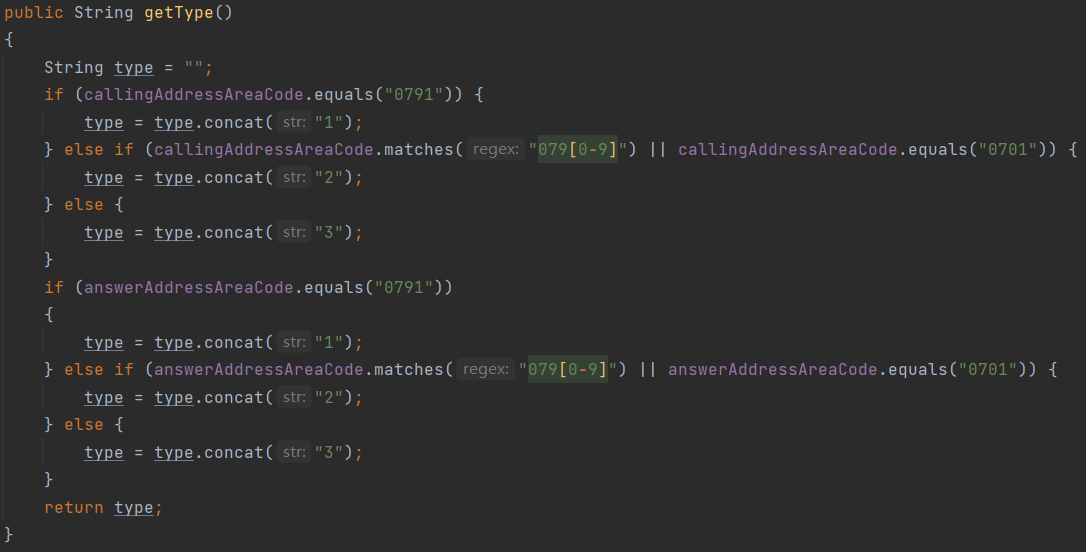
public String getType()
{
String type = "";
if (callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) {
type = type.concat("1");
} else if (callingAddressAreaCode.matches("079[0-9]") || callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) {
type = type.concat("2");
} else {
type = type.concat("3");
}
if (answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0791"))
{
type = type.concat("1");
} else if (answerAddressAreaCode.matches("079[0-9]") || answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) {
type = type.concat("2");
} else {
type = type.concat("3");
}
return type;
}
public CallRecord(String[] s)
{
String s1="",s2="",s3="",s4="";
if (s.length == 6)
{
s1 = s[2];
s2 = s[3];
s3 = s[4];
s4 = s[5];
setCallingNumber(s[0]);
setAnswerNumber(s[1]);
callingAddressAreaCode = s[0].substring(0,4);
answerAddressAreaCode = s[1].substring(0,4);
}
else if (s.length == 7)
{
s1 = s[3];
s2 = s[4];
s3 = s[5];
s4 = s[6];
if (s[0].charAt(0) == '0')
{
setCallingNumber(s[0]);
setAnswerNumber(s[1]);
callingAddressAreaCode = s[0].substring(0, 4);
answerAddressAreaCode = s[2];
}
else
{
setCallingNumber(s[0]);
setAnswerNumber(s[2]);
callingAddressAreaCode = s[1];
answerAddressAreaCode = s[2].substring(0, 4);
}
}
else if (s.length == 8)
{
s1 = s[4];
s2 = s[5];
s3 = s[6];
s4 = s[7];
setCallingNumber(s[0]);
setAnswerNumber(s[2]);
callingAddressAreaCode = s[1];
answerAddressAreaCode = s[3];
}
String regex="[1-9]\\d{3}.([1-9]|1[0-2]).([1-9]|[1-2][0-9]|3[0-1])\\s+(2[0-3]|[0-1]\\d):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d";
String str1=s1 + " " + s2;
String str2=s3 + " " + s4;
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss");
if(str1.matches(regex)&&str2.matches(regex))
{
try
{
startTime = simpleDateFormat.parse(str1);
endTime = simpleDateFormat.parse(str2);
}
catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord
{
private String message;
public String getMessage()
{
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message)
{
this.message = message;
}
}
abstract class ChargeRule
{
abstract public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
}
class LandPhoneInCityRule extends ChargeRule
{
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double cost = 0;
for(CallRecord i:userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords())
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else
Time = Time/60000;
if (i.getType().equals("11"))
cost += Time * 0.1;
else if (i.getType().equals("12"))
cost += Time * 0.3;
else if (i.getType().equals("13"))
cost += Time * 0.6;
}
return cost;
}
}
class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends ChargeRule
{
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double cost = 0;
for(CallRecord i:userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords())
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else
Time = Time/60000;
cost+=Time*0.3;
}
return cost;
}
}
class LandPhoneInLandRule extends ChargeRule
{
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double cost = 0;
for(CallRecord i:userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords())
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else Time = Time/60000;
cost+=Time*0.6;
}
return cost;
}
}
class newLandPhoneInCityRule extends ChargeRule
{
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double cost = 0;
for(CallRecord i:userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords())
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else Time = Time/60000;
if (i.getType().equals("11"))
cost += Time * 0.1;
else if (i.getType().equals("12"))
cost += Time * 0.2;
else if (i.getType().equals("13"))
cost += Time * 0.3;
}
return cost;
}
}
class newLandPhoneInProvinceRule extends ChargeRule
{
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double cost = 0;
for(CallRecord i:userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords())
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else Time = Time/60000;
if (i.getType().equals("21"))
cost += Time * 0.3;
else if (i.getType().equals("22"))
cost += Time * 0.3;
else if (i.getType().equals("23"))
cost += Time * 0.3;
}
return cost;
}
}
class newLandPhoneInLandRule extends ChargeRule
{
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double cost = 0;
for(CallRecord i:userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords())
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else Time = Time/60000;
cost+=Time*0.6;
}
for(CallRecord i:userRecords.getNewCallingInLandRecords())
{
long Time = i.getEndTime().getTime()-i.getStartTime().getTime();
if(Time%60000!=0)
Time = Time/60000+1;
else Time = Time/60000;
cost+=Time*0.3;
}
return cost;
}
}
类图:
SourceMonitor生成的报表内容:
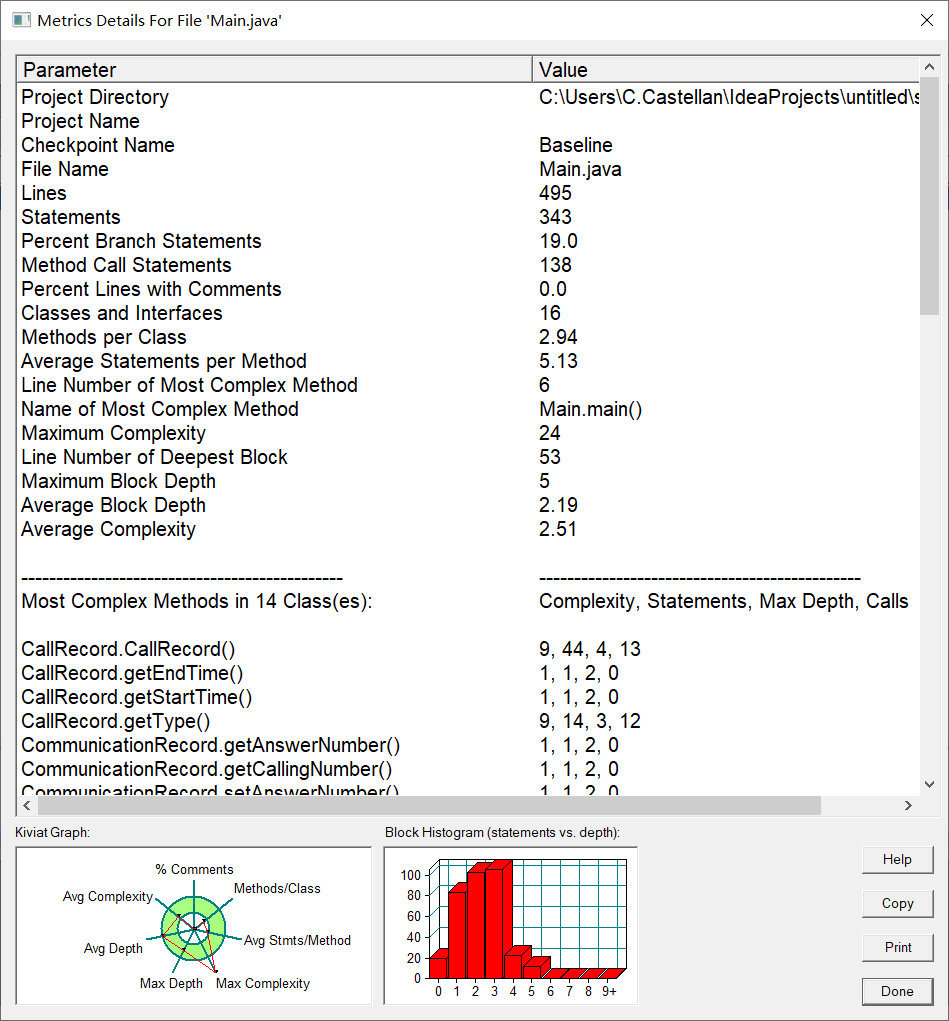
本题心得:
本题需要考虑的点确实很多,花了不少时间才全部弄清计费的方式,起先在上题的代码基础上编写完后交了上去,发现代码的时间复杂度太高,一直卡在了题目要求的400ms上下,导致获得的分数起伏不定,然后重构了一番代码,将主函数上的代码缩减,成功减少了时间复杂度。
③题目集八
7-1 电信计费系列3-短信计费
题目:
实现一个简单的电信计费程序,针对手机的短信采用如下计费方式:
1、接收短信免费,发送短信0.1元/条,超过3条0.2元/条,超过5条0.3元/条。
2、如果一次发送短信的字符数量超过10个,按每10个字符一条短信进行计算。
输入格式:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市手机用户开户的信息,每行一个用户。
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐 3-手机短信计费)
例如:u-13305862264 3
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题只针对类型3-手机短信计费。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的短信信息,短信的格式:
m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容 (短信内容只能由数字、字母、空格、英文逗号、英文句号组成)
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi.
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you.
注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
输出格式:
根据输入的详细短信信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月短信费用(精确到小数点后2位,单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条短信信息均单独计费后累加,不是将所有信息累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
本题只做格式的错误判断,无需做内容上不合理的判断,比如同一个电话两条通讯记录的时间有重合、开户号码非南昌市的号码等,此类情况都当成正确的输入计算。但时间的输入必须符合要求,比如不能输入2022.13.61 28:72:65。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3,可根据理解自行调整:

图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。

图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。
CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。

图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是
座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
注意:以上图中所定义的类不是限定要求,根据实际需要自行补充或修改。
题目分析:
过了前两题之后,本题就显得稍微简单了许多,因为不需要考虑座机和电话的情况,只需要考虑短信即可,整体需要注意的点就是短信的内容,其中是包括,.空格等内容的,还有就是短信数量的记录,然后根据次数据进行计算,解决了以上两点,然后再以之前代码基础上稍作更改,就能轻松的拿下这道题了。
源码展示:
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<String> information1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> information2 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
String str = input.nextLine();
while (!str.equals("end")) {
String regex1 = "u-((0\\d{9,11})|(1\\d{10}))\\s3";
String regex2 = "m-1\\d{10}\\s1\\d{10}[ 0-9a-z,.A-Z]+";
if (str.matches(regex1))
{
String[] str1 = str.split("-");
String str2 = str1[1];
String[] str3 = str2.split(" ");
if (!information1.contains(str3[0]))
information1.add(str3[0]);
} else if (str.matches(regex2))
{
String[] str1 = str.split("-");
String str2 = str1[1];
information2.add(str2);
}
str = input.nextLine();
}
Collections.sort(information1);
for (String i : information1)
{
User user = new User();
user.setNumber(i);
user.setChargeMode(new MessageCharging());
users.add(user);
}
for (User i:users)
{
for(String j:information2)
{
String[] k=j.split(" ");
if(i.number.equals(k[0]))
{
MessageRecord messageRecord=new MessageRecord(j);
messageRecord.setCallingNumber(k[0]);
i.userRecords.addSendMessageRecords(messageRecord);
}
}
}
for(User user:users)
System.out.println(user.getNumber()+" "+user.calCost()+" "+user.calBalance());
}
}
class User
{
UserRecords userRecords=new UserRecords();
double balance=100;
ChargeMode chargeMode;
String number;
public double calBalance()
{
double sum=this.balance;
double cost1=chargeMode.calCost(userRecords);
this.balance=sum-cost1;
return Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f",balance));
}
public double calCost()
{
double cost=chargeMode.calCost(userRecords);
return Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f",cost));
}
public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode)
{
this.chargeMode = chargeMode;
}
public String getNumber()
{
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number)
{
this.number=number;
}
}
class UserRecords
{
ArrayList<MessageRecord> SendMessageRecords=new ArrayList<>();
public void addSendMessageRecords(MessageRecord messageRecord)
{
SendMessageRecords.add(messageRecord);
}
public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords() {
return SendMessageRecords;
}
public void setSendMessageRecords(ArrayList<MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords) {
SendMessageRecords = sendMessageRecords;
}
}
class MessageCharging extends ChargeMode
{
public MessageCharging()
{
chargeRules.add(new MessageRule());
}
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords)
{
double sumCost = 0;
for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) {
sumCost += rule.calCost(userRecords);
}
return sumCost;
}
}
abstract class ChargeMode
{
ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules = new ArrayList<>();
public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
}
abstract class CommunicationRecord
{
protected String callingNumber;
public String getCallingNumber()
{
return callingNumber;
}
public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber)
{
this.callingNumber=callingNumber;
}
}
class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord
{
private String message;
public MessageRecord(String input) {
super();
this.message = input.substring(24);
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
abstract class ChargeRule
{
abstract public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords);
}
class MessageRule extends ChargeRule {
@Override
public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) {
double Cost;
int num = 0;
for(MessageRecord m : userRecords.getSendMessageRecords())
{
int length = m.getMessage().length();
num+=length/10;
if (length%10!=0)
num++;
}
if(num<=3)
Cost=num * 0.1;
else if(num <= 5)
Cost=0.3+0.2*(num-3);
else
Cost=0.7+0.3*(num-5);
return Cost;
}
}
类图:
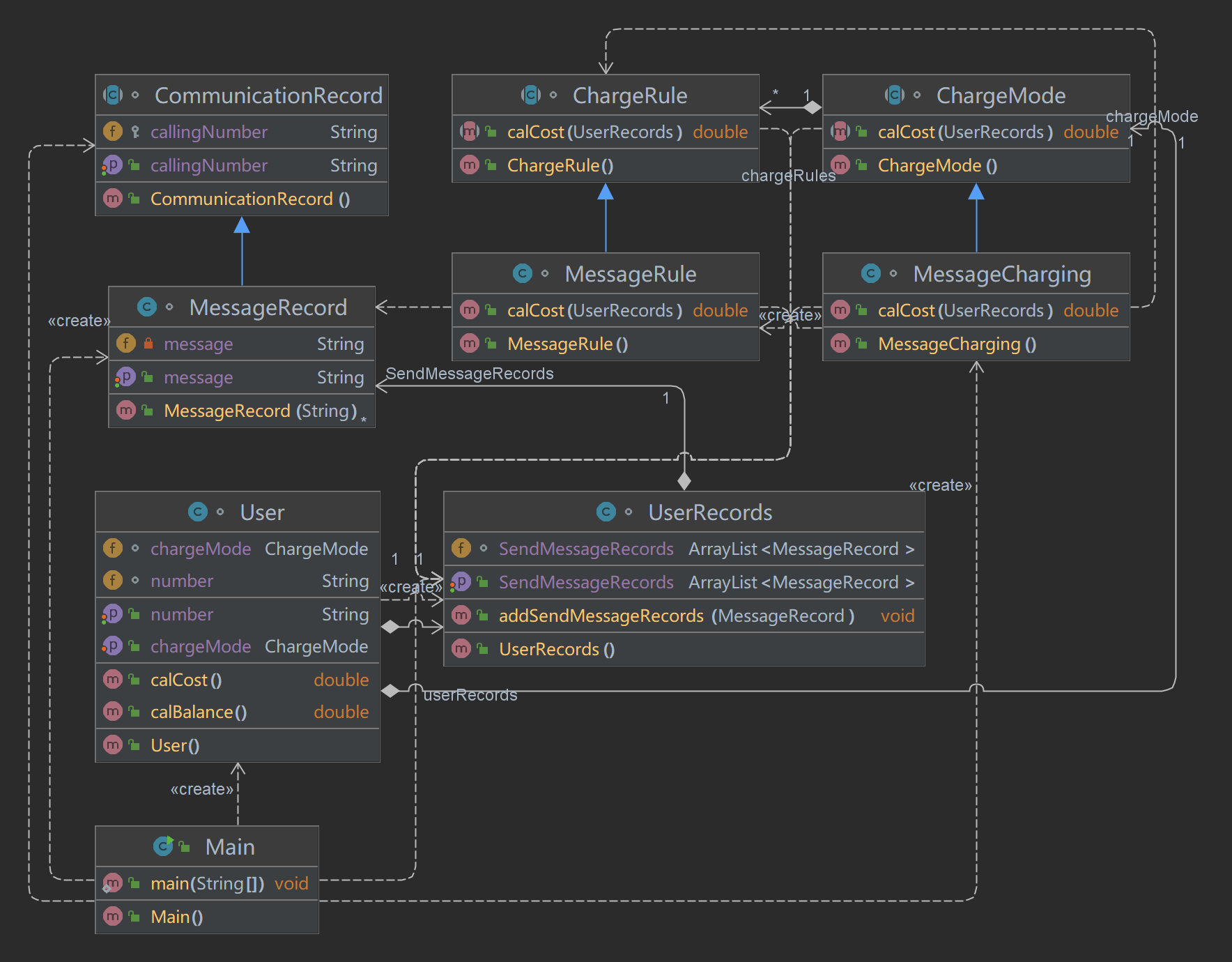
SourceMonitor生成的报表内容:
本题心得:
由于前面的题目集已经做好了铺垫,本题解决起来也更加轻松点,短信的内容以及用户等判断比起前面来说也不是很复杂,只需要做一些删改即可,总体来说还是很轻松的解决了的。
3.采坑心得
本次题目集主要的踩坑点就是手机收费的区号判断,需要明确拨打电话和接通电话的区号所属,然后明确两者之间的收费判断标准,关于区号的判断可以根据切割字符串后的位置进行记录并判断,比如根据split(“ ”)来获取字符数组长度,根据长度和位置来判断是手机打手机,电话打手机,还是电话打电话,由此来决定区号、starttime和endtime 的位置,每次得到的都是一个callrecord,只需要调一个函数,得到一个返回值,然后在存入一个存储Callrecord的数组即可。再者就是关于主函数应减少使用过多的循环以及复杂冗余的代码,因为这样会导致时间复杂度过高而难通过测试点,可以将大部分函数都重构于其他类中,然后进行调用,这样既减少了代码的冗余性,也增加了代码的复用性。
4.改进建议
在本次题目集中的类图中其实有许多冗余的地方,没必要全权按照老师所给的类图进行编程,可以适当的删改,这样便于自己理解和使用。本次代码的复杂度和可复用性其实还有很多可优化的空间,比如尽量避免在main方法中编写大量代码,这样提高代码的时间复杂度,可以尝试多设计类,多调用类的方法。
5.总结
本次是该学期最后一次的题目集,虽然不及上一次多边形题目集的难度,但是也所学颇多,这次考察了对于类图的还原能力和扩展能力,让我认识到了类图的理解以及类与类的关系的重要性。要使得代码能够具有良好的可读性和可复用性,以上的理解都缺一不可。希望之后这些能够真正的融会贯通,便写出高质量的代码。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· SpringCloud带你走进微服务的世界