算法笔记:将数组按符号排序
题目:
给定一个int数组,长度为n,数组中每个元素为随机整数,可能为负数,可能为0,可能为正数,要求将数组按照符号排序,所有的负数在左边,正数在右边,零在中间,负数和负数之间不需要有序,正数和正数之间也不需要有序。
数据约束:
0 < n <= 300000000
例子:
输入:
[0, 3, 5, -10, -1]
输出:
下面任意一个都是合法输出:
[-10, -1, 0, 3, 5]
[-1, -10, 0, 3, 5]
[-10, -1, 0, 5, 3]
[-1, -10, 0, 5, 3]
这道题中的难点是出现了三种类型的数值,不能简单地采用两个指针从两端向中间收缩的遍历方式,除非使用额外的空间(这个空间还不是临时的,而是在函数执行完毕仍然可能被占用的)。
即新申请一个长度为n的int数组,因为int数组中元素默认值为0,相当于不用考虑0的情况,将三种情况转为了两种情况,就比较容易处理了,只需要将原数组中的值按照负数放在新数组的左端,正数放在新数组的右端即可,这种方式时间复杂度为O(n),只需要遍历一遍数组即可,但是需要额外的至少4n字节的内存空间。
实现代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | package org.cc11001100.alg.sortBySymbol;/** * 需要额外空间的按符号排序,时间复杂度是O(n),但是需要额外的内存空间n * * @author CC11001100 */public class SortBySymbolSolutionNeedMoreMemory implements SortBySymbol { // 拷贝到一个新的数组中 public int[] sortBySymbol(int[] nums) { int[] result = new int[nums.length]; int left = 0, right = result.length - 1; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] < 0) { result[left++] = nums[i]; } else if (nums[i] > 0) { result[right--] = nums[i]; } } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { SortBySymbol sortBySymbol = new SortBySymbolSolutionNeedMoreMemory();// int[] nums = RandomIntArrayGenerator.random(100000000);// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// nums = sortBySymbol.sortBySymbol(nums);// long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;// System.out.println(cost);// System.out.println(SortBySymbolJudge.judge(nums));// for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {// System.out.println(nums[i]);// } SortBySymbolJudge.judge(sortBySymbol); }} |
上面的代码只是实现了基本的要求,我们肯定能够做到更好对吧,对于用到了额外空间的解法,我们应该想一下是否可以不使用额外空间就解决这个问题呢?
上面说了,这个问题复杂就复杂在要在一个数组中操纵三种类型的数据,指针不够用,那么我们可以将这个问题转化一下,比如可以将问题分为两步:
1. 先按照负数和非负数(包括零和正数)进行排序,这一步将负数的顺序排好了,但是零和正数还是无序的。
2. 再按照零和正数排序,排完之后整体有序了。
这样每一步都是两种类型的数据,使用两个指针完全够用了,而且不需要使用到额外的内存了,缺点就是需要多遍历一遍数组,时间复杂度是O(2n),约掉常数复杂度仍然是O(n)。
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 | package org.cc11001100.alg.sortBySymbol;/** * 不需要额外空间,但是需要扫描两次数组,时间复杂度是O(2n),但是不需要额外空间 * * @author CC11001100 */public class SortBySymbolSolutionTwoTimesSort implements SortBySymbol { // 将整个排序过程看做是两个步骤,先按负数和非负数排序,然后将非负数部分按照零和正数排序 public int[] sortBySymbol(int[] nums) { int left = negativeAndNotNegativeSort(nums); zeroAndPositiveSort(nums, left); return nums; } // 负数和非负数排序 private int negativeAndNotNegativeSort(int[] nums) { int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1; while (left <= right) { if (nums[left] >= 0) { right = findFirstNegativeIndexFromRight(nums, right); if (right < left) { break; } swap(nums, left, right); left++; right--; } else { left++; } } return left; } private int findFirstNegativeIndexFromRight(int[] nums, int right) { while (right >= 0) { if (nums[right] < 0) { return right; } right--; } return -1; } private void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b) { int t = nums[a]; nums[a] = nums[b]; nums[b] = t; } // 零和正数排序 private void zeroAndPositiveSort(int[] nums, int left) { int right = nums.length - 1; while (left <= right) { if (nums[left] != 0) { right = findFirstZeroIndexFromRight(nums, right); if (right < left) { break; } swap(nums, left, right); left++; right--; } else { left++; } } } private int findFirstZeroIndexFromRight(int[] nums, int right) { while (right >= 0) { if (nums[right] == 0) { return right; } else { right--; } } return -1; } public static void main(String[] args) { SortBySymbol sortBySymbol = new SortBySymbolSolutionTwoTimesSort();// int[] nums = RandomIntArrayGenerator.random(100000000);// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// sortBySymbol.sortBySymbol(nums);// long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;// System.out.println(cost);// System.out.println(SortBySymbolJudge.judge(nums));// for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {// System.out.println(nums[i]);// } SortBySymbolJudge.judge(sortBySymbol); }} |
写一个类测试代码是否正确,首先为了测试方便将两个类的类型统一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | package org.cc11001100.alg.sortBySymbol;public interface SortBySymbol { int[] sortBySymbol(int[] nums);} |
然后是生成测试数据的类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | package org.cc11001100.alg.sortBySymbol;/** * 用于生成测试数据 * * @author CC11001100 */public class RandomIntArrayGenerator { public static int[] random(int length) { int[] result = new int[length]; for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) { int n = (int) (Math.random() * 100); int t = n % 5; if (t < 2) { // n ∈ [0, 1] n *= -1; } else if (t == 2) { // n == 2 n = 0; } else { // n ∈ [3, 4] // n = n; } result[i] = n; } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = random(20); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { System.out.println(nums[i]); } }} |
然后是测评类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 | package org.cc11001100.alg.sortBySymbol;/** * 用于评测SortBySymbol输出结果是否正确 * * @author CC11001100 */public class SortBySymbolJudge { public static boolean judge(int[] nums) { int index = 0; if (nums[index] < 0) { while (index < nums.length) { if (nums[index] >= 0) { break; } index++; } } if (index < nums.length && nums[index] == 0) { while (index < nums.length) { if (nums[index] > 0) { break; } index++; } } while (index < nums.length) { if (nums[index] <= 0) { return false; } index++; } return index == nums.length; } public static void judge(SortBySymbol sortBySymbol) { int[] numLengths = new int[]{ 1, 2, 3, 5, 10, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 100000000, 100000000, 200000000, 200000000, 200000000, 300000000 }; for (int i = 0; i < numLengths.length; i++) { int[] nums = RandomIntArrayGenerator.random(numLengths[i]); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); nums = sortBySymbol.sortBySymbol(nums); long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; boolean judgeResult = judge(nums); System.out.println("num length=" + numLengths[i] + ", cost=" + cost + "ms, judge=" + judgeResult); } }} |
测评结果:
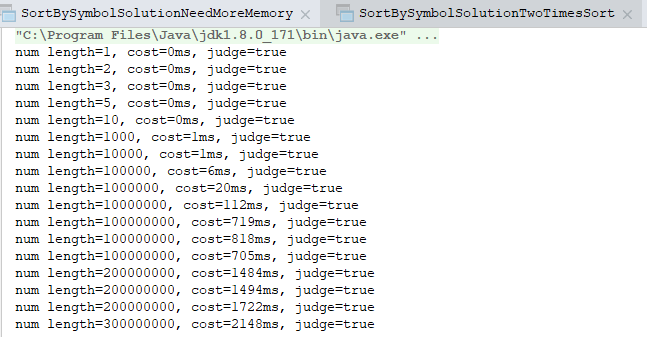
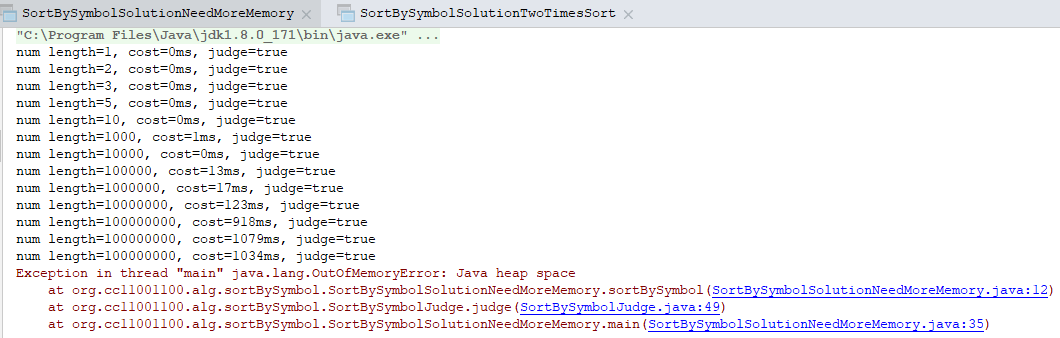
可以看到,对于使用额外内存的解法当数据量足够大时它就撑不住了,很多问题就是这样,没有CPU资源可以跑慢一点,终究还是能够跑起来的,但是没有内存资源根本跑都跑不起来。
.




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架