虚树
虚树(Virtual Tree)
题目引入
题目大意:一颗树,上面有 \(k\) 个资源点,拆一些边,使得 \(1\) 号点不能到达任何资源点。现在要使得拆除的边的权值和最小。总共有 \(m\) 次询问,每次给出资源点。
$n\le 2.5\times 10^5,m\le 5\times 10^5,\sum k_i\le 5\times 10^5 $
这个题是虚树的模板题。接下来以这题为例介绍虚树。
正片开始
我们把上面题中的资源点称为 关键点。
暂且不考虑虚树,我们考虑怎么暴力求解。
发现可以直接DP,我们设 \(dp[i]\) 表示使得 \(i\) 不与子树中关键点连通的最小代价,那么容易得到:
其中 \(w(u,v)\) 为 \(u\) 到 \(v\) 的边权。这个复杂度易证是 \(O(nm)\) 的,还完全不行不行。
我们发现两个事情:1.如果一个点的子树完全没有关键点,那么我们显然完全不需要DP这个子树。2.发现 \(k\) 的总数是 \(O(n)\) 级别的。
所以综上我们知道肯定是将原树按照关键点浓缩出一棵巨小的树,来快速求解问题。稍加思索可知,我们只需要保存关键点及其LCA的信息即可。
我们按照dfs序将关键点排序,那么显然所有相邻的两个关键点的LCA与关键点的并等价于所有关键点互相的LCA与关键点的并。
证明一下:
我们设 \(a,b,c\) 满足 \(dfn[a]<dfn[b]<dfn[c]\) 。
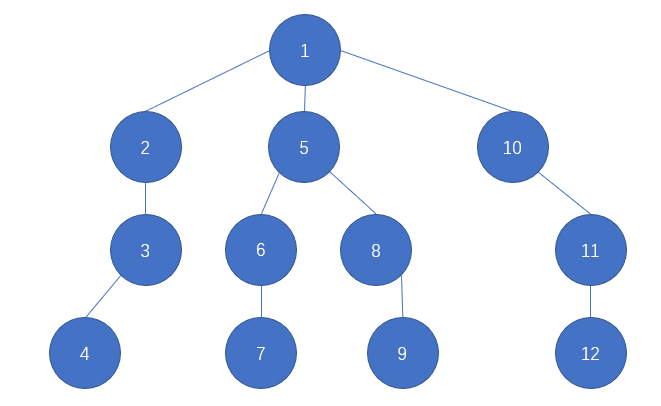
其中节点编号与dfs序对应。接下来我们证明 \(a,c\) 的LCA必定是某个关键点,或者是某两个相邻的关键点的LCA。
如果 \(a\) 不为 \(c\) 的祖先,比如 \(a=4,b=7,c=12\) 或 \(a=6,b=7,c=9\),此时如果 \(a\) 为 \(b\) 的祖先,那么 \(a\) 在 \(LCA(b,c)\) 的 \(b\) 所在子树,有 \(LCA(b,c)=LCA(a,c)\)。如果 \(a\) 不为 \(b\) 的祖先,则 \(a\) 在 \(LCA(b,c)\) 及之上的dfs序小于 \(b\) 所在子树的子树,那么显然可知 \(LCA(a,b)=LCA(a,c)\),两种情况都符合条件。
否则由于 \(a\) 为 \(c\) 祖先,两者LCA为 \(a\) ,也符合条件。
综上可知:所有相邻的两个关键点的LCA与关键点的并等价于所有关键点互相的LCA与关键点的并。
那么我们可以对于每对相临的关键点求LCA,然后进行一番操作,这种做法我们在文章最后介绍,先介绍常规方法。
其实对于一棵虚树,它只要满足原树的祖先关系,那么它怎么建,建几个点都没有任何关系。所以对于这道题,我们图方便的话可以直接率先将 \(1\) 号点加入虚树。
接下来介绍一种用单调栈建立虚树的做法。我们使用单调栈维护虚树上的一条链,不断切换链的同时更新祖先关系以建立虚树。
我先提供一次示例图片(图中点编号与dfs序对应)
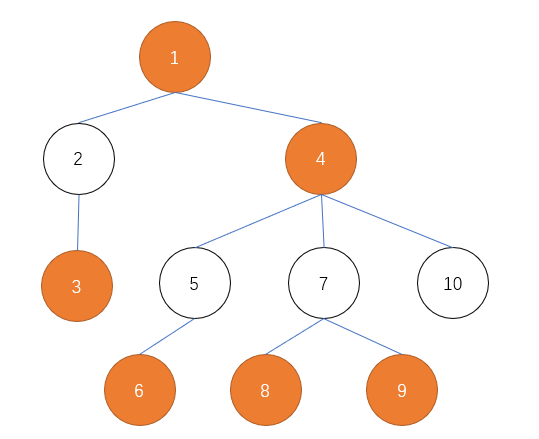
我们先按照dfs序将关键点(图中橙色的点)排序。然后先将第一个关键点入栈,目前栈中节点为 \(1\)。
step1: 接下来我们看到 \(3\) ,求一下相邻关键点的LCA(也等价于求了栈顶元素和当前点的LCA),发现是 \(1\) ,为栈顶元素,显然已经在虚树中了,不用额外操作。随后 \(3\) 入栈。栈中 \(1,3\) 。
step2: \(4\) 号,求LCA,发现是 \(1\) ,但不是栈顶元素,可以得知当前点与上一个点已经换链了。直接栈顶和次栈顶也就是LCA连边 \(1\leftrightarrow 3\) ,弹出 \(3\) 。随后 \(4\) 入栈,目前栈中元素 \(1,4\) 。
step3: 6号的情况同step1,直接 \(6\) 入栈。
step4: 同step2,弹出 \(6\) 并连边LCA,\(8\) 入栈。
step5: 类似step2,但是发现次栈顶不是LCA,弹出 \(8\) 并连边LCA, 我们把LCA \(7\) 入栈,并把 \(9\) 入栈。
那么我们总结一下:
当相邻关键点的LCA为dfs序小的那一个,也就是栈顶元素,那么我们直接把当前点入栈。
否则,我们需要换链,一直弹出直到次栈顶的dfs序小于LCA,我们将栈顶和LCA连边并弹出,然后LCA入栈。如果LCA在此之前已经入栈,则只需弹出栈顶并连边LCA即可,而当次栈顶等于LCA时可以得出LCA在之前已经入栈的结论。最后也要将当前点入栈。
需要注意的是,最后跑完之后,栈中还存在一条链,我们直接把边连接上。以及由于是多测,我们考虑对于每个第一次入栈的点重置其链式前向星的头指针。
给出建虚树的参考代码:
inline void build(){
std::sort(h+1,h+1+k,[](int x,int y){
return dfn[x]<dfn[y];
});
//G2.head[h[1] ] = -1;
sta[top=1]=h[1];
for(int i=2;i<=k;++i){
int f=LCA(h[i],sta[top]);
if(f!=sta[top]){
while(dfn[f]<dfn[sta[top-1] ]){
G2.add(sta[top],sta[top-1]) ;--top;
}
if(f!=sta[top-1]){
//G2.head[f]=-1;
G2.add(f,sta[top]); sta[top]=f;
}else{
G2.add(f,sta[top--]);
}
}
//G2.head[h[i] ]=-1;
sta[++top]=h[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<top;++i){
G2.add(sta[i],sta[i+1]);
}
}
这个复杂度是 \(O(k\log k)\) 的,然后我们在虚树上做之前的DP就可以AC了。
会了建虚树,就相当于多了一个工具罢,和圆方树和点分树一样都是重构树,难点在于怎么利用,而不是其本身,多练练题就通了。
补充:后来发现其实过河拆桥式的清空前向星,几种写法都可以吧,但是我觉得好像这样更加美妙一点。
本题完整代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define filein(a) freopen(#a".in","r",stdin)
#define fileot(a) freopen(#a".out","w",stdout)
#define sky fflush(stdout);
#define Better_IO 1
namespace IO{
inline bool blank(const char &c){
return c==' ' or c=='\n' or c=='\t' or c=='\r' or c==EOF;
}
#if Better_IO==true
char buf[(1<<20)+3],*p1(buf),*p2(buf);
char buf2[(1<<20)+3],*p3(buf2);
const int lim=1<<20;
inline char gc(){
if(p1==p2) p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,lim,stdin);
return p1==p2?EOF:*p1++;
}
#define pc putchar
#else
#define gc getchar
#define pc putchar
#endif
inline void gs(char *s){
char ch=gc();
while(blank(ch) ) {ch=gc();}
while(!blank(ch) ) {*s++=ch;ch=gc();}
*s=0;
}
inline void gs(std::string &s){
char ch=gc();s+='#';
while(blank(ch) ) {ch=gc();}
while(!blank(ch) ) {s+=ch;ch=gc();}
}
inline void ps(char *s){
while(*s!=0) pc(*s++);
}
inline void ps(const std::string &s){
for(auto it:s)
if(it!='#') pc(it);
}
template<class T>
inline void read(T &s){
s=0;char ch=gc();bool f=0;
while(ch<'0'||'9'<ch) {if(ch=='-') f=1;ch=gc();}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9') {s=s*10+(ch^48);ch=gc();}
if(ch=='.'){
db p=0.1;ch=gc();
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9') {s=s+p*(ch^48);ch=gc();}
}
s=f?-s:s;
}
template<class T,class ...A>
inline void read(T &s,A &...a){
read(s);read(a...);
}
};
using IO::read;
using IO::gs;
using IO::ps;
const int N=2.5e5+3,M=5e5+3;
const ll inf=1e18;
int n,m;
struct EdgeList{
struct Edge{
int v,w;
};
int Etot;
int head[N],nxt[M];
Edge to[M];
EdgeList(){
Etot=-1;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head) );
}
inline void join(int u,int v,int w=0){
nxt[++Etot]=head[u];
head[u]=Etot;
to[Etot]={v,w};
}
inline void add(int u,int v,int w=0){
join(u,v,w);join(v,u,w);
}
}G1,G2;
int idx;
ll mi[N];
int dfn[N],fa[N][20+3],dep[N];
void dfs1(int u,int f){
dfn[u]=++idx;
dep[u]=dep[f]+1;
fa[u][0]=f;
for(int i=0;i<20;++i){
fa[u][i+1]=fa[fa[u][i] ][i];
}
for(int i=G1.head[u];~i;i=G1.nxt[i]){
int v=G1.to[i].v;
if(v==f) continue;
mi[v]=std::min(mi[u],1ll*G1.to[i].w);
dfs1(v,u);
}
}
inline int LCA(int x,int y){
if(dep[x]<dep[y]) std::swap(x,y);
for(int i=20;i>=0;--i){
if(dep[fa[x][i] ]>=dep[y]){
x=fa[x][i];
}
if(x==y) return x;
}
for(int i=20;i>=0;--i){
if(fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i]){
x=fa[x][i];
y=fa[y][i];
}
}
return fa[x][0];
}
bool cr[N];
int h[N];
int sta[N],top,k;
inline void build(){
std::sort(h+1,h+1+k,[](int x,int y){
return dfn[x]<dfn[y];
});
sta[top=1]=h[1];
for(int i=2;i<=k;++i){
int f=LCA(h[i],sta[top]);
if(f!=sta[top]){
while(dfn[f]<dfn[sta[top-1] ]){
G2.add(sta[top],sta[top-1]) ;--top;
}
if(f!=sta[top-1]){
//G2.head[f]=-1;
G2.add(f,sta[top]); sta[top]=f;
}else{
G2.add(f,sta[top--]);
}
}
//G2.head[h[i] ]=-1;
sta[++top]=h[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<top;++i){
G2.add(sta[i],sta[i+1]);
}
}
ll dfs2(int u,int f){
//std::cerr<<f<<' '<<u<<'\n';
ll res=0,ans=0;
for(int i=G2.head[u];~i;i=G2.nxt[i]){
int v=G2.to[i].v;
if(v==f) continue;
res+=dfs2(v,u);
}
if(cr[u]){
ans=mi[u];
}else{
ans=std::min(mi[u],res);
}
G2.head[u]=-1;
cr[u]=0;
return ans;
}
int main(){
filein(a);fileot(a);
read(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) mi[i]=inf;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
int u,v,w;
read(u,v,w);
G1.add(u,v,w);
}
dfs1(1,0);
int Q; read(Q);
while(Q--){
read(k);
for(int i=1;i<=k;++i){
read(h[i]);
cr[h[i] ]=1;
}
G2.Etot=-1;
build();
printf("%lld\n",dfs2(sta[1],sta[1]) );
}
return 0;
}
虚虚树法
我们之前提到了我们可以直接对排序后相邻的关键点求LCA,然后用标记数组判重,把数组复制一份负的,最后再按照dfs序(此时还需记录每个点退出的时间戳)排一次序,就得到了欧拉序列。然后在欧拉序列上跑DP即可。但是这样会需要排序两次,常数就是两倍了,还是不推荐。
参考代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define filein(a) freopen(#a".in","r",stdin)
#define fileot(a) freopen(#a".out","w",stdout)
#define sky fflush(stdout);
#define Better_IO 1
namespace IO{
inline bool blank(const char &c){
return c==' ' or c=='\n' or c=='\t' or c=='\r' or c==EOF;
}
#if Better_IO==true
char buf[(1<<20)+3],*p1(buf),*p2(buf);
char buf2[(1<<20)+3],*p3(buf2);
const int lim=1<<20;
inline char gc(){
if(p1==p2) p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,lim,stdin);
return p1==p2?EOF:*p1++;
}
#define pc putchar
#else
#define gc getchar
#define pc putchar
#endif
inline void gs(char *s){
char ch=gc();
while(blank(ch) ) {ch=gc();}
while(!blank(ch) ) {*s++=ch;ch=gc();}
*s=0;
}
inline void gs(std::string &s){
char ch=gc();s+='#';
while(blank(ch) ) {ch=gc();}
while(!blank(ch) ) {s+=ch;ch=gc();}
}
inline void ps(char *s){
while(*s!=0) pc(*s++);
}
inline void ps(const std::string &s){
for(auto it:s)
if(it!='#') pc(it);
}
template<class T>
inline void read(T &s){
s=0;char ch=gc();bool f=0;
while(ch<'0'||'9'<ch) {if(ch=='-') f=1;ch=gc();}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9') {s=s*10+(ch^48);ch=gc();}
if(ch=='.'){
db p=0.1;ch=gc();
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9') {s=s+p*(ch^48);ch=gc();}
}
s=f?-s:s;
}
template<class T,class ...A>
inline void read(T &s,A &...a){
read(s);read(a...);
}
};
using IO::read;
using IO::gs;
using IO::ps;
const int N=2.5e5+3,M=5e5+3;
const ll inf=1e18;
int n,m;
struct Edge{
int v,w;
};
int Etot;
int head[N],nxt[M];
Edge to[M];
inline void join(int u,int v,int w=0){
nxt[++Etot]=head[u];
head[u]=Etot;
to[Etot]={v,w};
}
inline void add(int u,int v,int w=0){
join(u,v,w);join(v,u,w);
}
int idx;
ll mi[N];
int efn1[N],efn2[N],fa[N][20+3],dep[N];
void dfs1(int u,int f){
efn1[u]=++idx;
dep[u]=dep[f]+1;
fa[u][0]=f;
for(int i=0;i<20;++i){
fa[u][i+1]=fa[fa[u][i] ][i];
}
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=nxt[i]){
int v=to[i].v;
if(v==f) continue;
mi[v]=std::min(mi[u],1ll*to[i].w);
dfs1(v,u);
}efn2[u]=++idx;
}
inline int LCA(int x,int y){
if(dep[x]<dep[y]) std::swap(x,y);
for(int i=20;i>=0;--i){
if(dep[fa[x][i] ]>=dep[y]){
x=fa[x][i];
}
if(x==y) return x;
}
for(int i=20;i>=0;--i){
if(fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i]){
x=fa[x][i];
y=fa[y][i];
}
}
return fa[x][0];
}
bool cr[N];
int tot;
int h[N<<1];
int sta[N],top;
bool vis[N];
inline void build(){
std::sort(h+1,h+1+tot,[](int x,int y){
return efn1[x]<efn1[y];
});
int tmp=tot;
for(int i=1;i<tmp;++i){
int f=LCA(h[i],h[i+1]);
if(!vis[f] and !cr[f]){
vis[f]=1;
h[++tot]=f;
}
}
if(!vis[1]) h[++tot]=1;
tmp=tot;
for(int i=1;i<=tmp;++i){
h[++tot]=-h[i];
}
std::sort(h+1,h+1+tot,[](int x,int y){
int p1=x>0?efn1[x]:efn2[-x],p2=y>0?efn1[y]:efn2[-y];
return p1<p2;
});
}
ll f[N];
inline void efs1(){
top=0;
for(int i=1;i<=tot;++i){
//printf("%d ",h[i]);
if(h[i]>0){
sta[++top]=h[i];
f[h[i] ]=0;
}else{
int u=sta[top],p=sta[--top];
if(cr[u]) f[u]=mi[u];
else f[u]=std::min(f[u],mi[u]);
//fprintf(stderr,"%d %d\n",u,f[u]);
f[p]+=f[u];
cr[u]=vis[u]=0;
}
}//pc('\n');
printf("%lld\n",f[1]);
}
int main(){
filein(a);fileot(a);
read(n);
Etot=-1;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head) );
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) mi[i]=inf;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
int u,v,w;
read(u,v,w);
add(u,v,w);
}
dfs1(1,0);
int Q; read(Q);
while(Q--){
read(tot);
for(int i=1;i<=tot;++i){
read(h[i]);
cr[h[i] ]=1;
}
build();
efs1();
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号