关于事务、ThreadLocal应用、CompletionService的一些总结
一、ThreadLocal的本质:
Thread 类组合一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap 所以ThreadLocalMap 是ThreadLocal 的内部类, ThreadLocalMap 是ThreadLocal 自己实现的一个key、value map结构,初始化Entry 长度16、其中key 基于弱引用。key 是 一个ThreadLocal 实例。所以单纯的说ThreadLocal 的 key 为线程本身压根就是不贴切的。
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
/**
* The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
*/
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
*/
private Entry[] table;看一下get 方法
其中getMap 就是拿到Thread 类实例中所组合的ThreadLocalMap ,getEntry 就是把线程所关联的ThreadLocal 类实例作为key 来搞数据。而value对应线程的变量副本,每个线程可能存在多个ThreadLocal
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
set方法 很简单
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}二 Spring的事务管理器如何玩儿的 ThreadLocal
以DataSourceTransactionManager 这个管理器为例。
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionManager.DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionManager.DataSourceTransactionObject)transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
if(txObject.getConnectionHolder() == null || txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Connection newCon = this.dataSource.getConnection();
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
if(con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = this.determineTimeout(definition);
if(timeout != -1) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
if(txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(this.getDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
} catch (Throwable var7) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource);
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", var7);
}
}这个Connection 就是我们常见的jdbc的连接, 主要是利用jdbc接口设置事务不自动提交 ,而有spring来控制何时提交、何时回滚。如果是新的连接创建, 那么bindResource 方法就把Connection 的holder 扔到ThreadLocalMap 里面了。 当线程间切换时,保证了连接资源的 一致性。
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");
Map<Object, Object> map = (Map)resources.get();
if(map == null) {
map = new HashMap();
resources.set(map);
}
Object oldValue = ((Map)map).put(actualKey, value);
if(oldValue instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder)oldValue).isVoid()) {
oldValue = null;
}
ThreadLocal可能存在的 内存泄漏问题
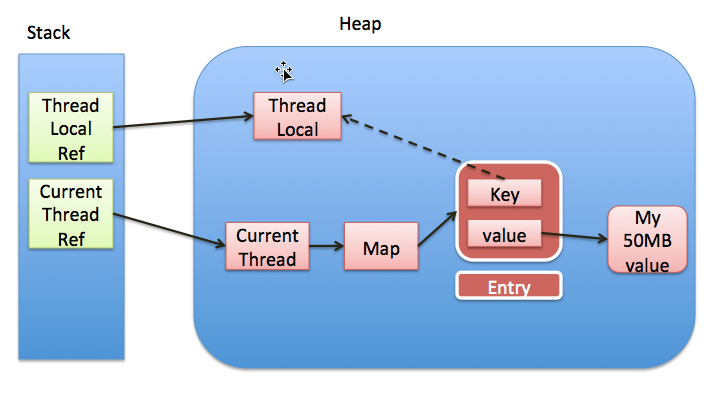
当把threadlocal实例置为null以后,没有任何强引用指向threadlocal实例,所以threadlocal将会被gc回收. 但是,我们的value却不能回收,因为存在一条从current thread连接过来的强引用. 只有当前thread结束以后, current thread就不会存在栈中,强引用断开, Current Thread, Map, value将全部被GC回收.
ThreadLocal在dubbo分布式调用跟踪中使用
在dubbo 中monitor 是一个单独的模块部署, 即使挂了也不耽误provider 和和consumer 继续暧昧。
在Dubbo的核心领域模型中:
1. Protocol是服务域,它是Invoker暴露和引用的主功能入口,它负责Invoker的生命周期管理。
2. Invoker是实体域,它是Dubbo的核心模型,其它模型都向它靠扰,或转换成它,它代表一个可执行体,可向它发起invoke调用,它有可能是一个本地的实现,也可能是一个远程的实现,也可能一个集群实现。
3. Invocation是会话域,它持有调用过程中的变量,比如方法名,参数等。
在dubbo-monitor-api 中:MonitorFilter 实现了Filter:
// 调用过程拦截
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//如果配置了监控中心
if (invoker.getUrl().hasParameter(Constants.MONITOR_KEY)) {
RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext(); // 提供方必须在invoke()之前获取context信息
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 记录起始时间戮
getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).incrementAndGet(); // 并发计数
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); // 让调用链往下执行
collect(invoker, invocation, result, context, start, false);
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
collect(invoker, invocation, null, context, start, true);
throw e;
} finally {
getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).decrementAndGet(); // 并发计数
}
} else { //没有配置监控中心
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}看一下如何做的信息采集collect 方法: 主要逻辑是根据是服务提供方还是消费方获取监控采集参数, 并发送到监控中心。
// 信息采集
private void collect(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation, Result result, RpcContext context, long start, boolean error) {
try {
// ---- 服务信息获取 ----
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; // 计算调用耗时
int concurrent = getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).get(); // 当前并发数
String application = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.APPLICATION_KEY);
String service = invoker.getInterface().getName(); // 获取服务名称
String method = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); // 获取方法名
URL url = invoker.getUrl().getUrlParameter(Constants.MONITOR_KEY);
Monitor monitor = monitorFactory.getMonitor(url);
int localPort;
String remoteKey;
String remoteValue;
if (Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE.equals(invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.SIDE_KEY))) {
// ---- 服务消费方监控 ----
context = RpcContext.getContext(); // 消费方必须在invoke()之后获取context信息
localPort = 0;
remoteKey = MonitorService.PROVIDER;
remoteValue = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
} else {
// ---- 服务提供方监控 ----
localPort = invoker.getUrl().getPort();
remoteKey = MonitorService.CONSUMER;
remoteValue = context.getRemoteHost();
}
String input = "", output = "";
if (invocation.getAttachment(Constants.INPUT_KEY) != null) {
input = invocation.getAttachment(Constants.INPUT_KEY);
}
if (result != null && result.getAttachment(Constants.OUTPUT_KEY) != null) {
output = result.getAttachment(Constants.OUTPUT_KEY);
}
monitor.collect(new URL(Constants.COUNT_PROTOCOL,
NetUtils.getLocalHost(), localPort,
service + "/" + method,
MonitorService.APPLICATION, application,
MonitorService.INTERFACE, service,
MonitorService.METHOD, method,
remoteKey, remoteValue,
error ? MonitorService.FAILURE : MonitorService.SUCCESS, "1",
MonitorService.ELAPSED, String.valueOf(elapsed),
MonitorService.CONCURRENT, String.valueOf(concurrent),
Constants.INPUT_KEY, input,
Constants.OUTPUT_KEY, output));
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to monitor count service " + invoker.getUrl() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}重点在于:
if (invocation.getAttachment(Constants.INPUT_KEY) != null) {
input = invocation.getAttachment(Constants.INPUT_KEY);
}
if (result != null && result.getAttachment(Constants.OUTPUT_KEY) != null) {
output = result.getAttachment(Constants.OUTPUT_KEY);
}分布式调用链想要串起来, 一般有一个类似于traceId 的东西 一直往下传。在并发下, dubbo如何确认到底哪一个调用方传过来的traceId , 那就需要dubbo处理请求线程 去和traceId 绑定了。继而ThreadLocal 应运而生。其它分布式调用跟踪框架可以通过扩展dubbo 的Filter 并通过invocation 的attachment 来传递这些traceId、`
ThreadLocal在mybatis框架中的使用
SqlSession 声明周期内线程不共享
public class SqlSessionManager implements SqlSessionFactory, SqlSession {
private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// proxy
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
// 保持线程局部变量SqlSession的地方
private ThreadLocal<SqlSession> localSqlSession = new ThreadLocal<SqlSession>();
private SqlSessionManager(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
// 这个proxy是重点
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{SqlSession.class},
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
public static SqlSessionManager newInstance(Reader reader) {
return new SqlSessionManager(new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, null, null));
}
public static SqlSessionManager newInstance(Reader reader, String environment) {
return new SqlSessionManager(new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, environment,
null));
}
//...
// 设置线程局部变量sqlSession的方法
public void startManagedSession() {
this.localSqlSession.set(openSession());
}
public void startManagedSession(boolean autoCommit) {
this.localSqlSession.set(openSession(autoCommit));
}
//...
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
return sqlSessionProxy.<T> selectOne(statement, parameter);
}
@Override
public <K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, String mapKey) {
return sqlSessionProxy.<K, V> selectMap(statement, mapKey);
}
//..ThreadLocal在SpringMvc中的使用
在FrameworkServlet.java 中 所有的doGet 、doPost。。。。全都委托给了processRequest 方法 统一处理。 processrequest 的核心语句是doService, 是一个模版方法, 在DispatcherServlet 有具体的实现。在doService 前后 我们看看分别干了什么有趣的事儿。在之前 首先获取了LocaleContextHodler 和 RequestContextHolder 中原来保存的LocaleContext 和RequestAttributes 并设置到previousLocaleContext 和 previousAttributes 临时属性, 然后调用buildLocaleContext 和 buildRequestAttributes 方法获取到当前请求的LocaleContext 和RequestAttributes , 并通过initContextHolders 方法将它们设置到LocaleContextHolder 和 RequestContextHolder, 然后设置了拦截器, 接着调用了最重要的 doService 方法, finally 中, 通过resetContextHolders 方法将原来的previousAttributes 和 previousLocaleContext 恢复到之前的两个holder中。 最后调用publishRequestHandledEvent 进行事件发布, 告知一些感兴趣的listener 一个请求处理已经完成。
LocaleContext : 里面存放着本地化信息, 如zh-cn
。RequestAttributes: 是spring 的一个接口, 通过他可以get、set 一些属性, 根据scope 参数判断操作是request 还是session 作用域, 这里具体使用的是ServletRequestAttributes 封装了request 、 response 、session , 根据scope 来判定从哪个作用域取数据, 我们先看看holder 是啥
public abstract class LocaleContextHolder {
private static final java.lang.ThreadLocal<org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContext> localeContextHolder;
private static final java.lang.ThreadLocal<org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContext> inheritableLocaleContextHolder;
就是一个抽象类, 但是里面有两个ThreadLocal 类型的静态属性, 可以直接拿来用。总的来说就是在调用真正的doService 之前 先把之前的本地化信息和一些作用域范围内的信息保存到临时变量中,把当前请求的以上信息放在ThreadLocal 中, 然后在我们的业务中无论是controller 还是service 可以直接拿来用, 而不用在controller 用request 去取,然后传递到service 了。 最后在finally 中又把 那些之前信息给放回了holder
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
}
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, startTime, failureCause);
}
}CompletionService 妙用
对于批量执行task切均需要拿到返回结果的时候, CompletionService是用武之地
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorCompletionService;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class CompletionServiceTest {
static int numThread =100;
static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(numThread);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//data表示批量任务
int[] data =new int[100];
for(int i=1;i<100000;i++){
int idx =i % 100;
data[idx] =i;
if(i%100==0){
testCompletionService(data);
data =new int[100];
}
}
}
private static void testCompletionService(int [] data) throws Exception{
CompletionService<Object> ecs = new ExecutorCompletionService<Object>(executor);
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++){
final Integer t=data[i];
ecs.submit(new Callable<Object>() {
public Object call() {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return t;
}
});
}
//CompletionService会按处理完后顺序返回结果
List<Object> res =new ArrayList<Object>();
for(int i = 0;i<data.length;i++ ){
Future<Object> f = ecs.take();
res.add(f.get());
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+res);
}
private static void testBasicFuture(int [] data) throws Exception{
List<Future<Object>> res =new ArrayList<Future<Object>>();
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++){
final Integer t=data[i];
Future<Object> future=executor.submit(new Callable<Object>() {
public Object call() {
return t;
}
});
res.add(future);
}
for(int i = 0;i<res.size();i++ ){
Future<Object> f = res.get(i);
Object rObject =f.get();
System.out.print(":"+rObject);
}
System.out.println("LN");
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号