bind、apply、call 的区别和应用
面试中几乎每次都会问到一个js中关于call、apply、bind的问题,比如…
- 怎么利用call、apply来求一个数组中最大或者最小值
- 如何利用call、apply来做继承
- apply、call、bind的区别和主要应用场景

首先,要明白这三个函数的存在意义👉 改变函数执行时的上下文,也就是改变函数运行时的this指向。
let obj = {name: 'tom'};
function Child(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Child.prototype = {
constructor: Child,
showName: function () {
console.log(this.name)
}
}
var child = new Child('jerry');
child.showName();//jerry
child.showName.call(obj); //tom
child.showName.apply(obj); //tom
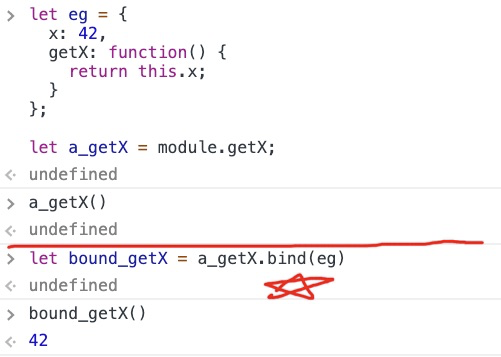
let bind = child.showName.bind(obj); // 返回一个函数
console.log(bind)
bind(); // tom
bind
区别👇
- call、apply与bind的差别
call和apply改变了函数的this上下文后便执行该函数,而bind则是返回改变了上下文后的一个函数。
- call、apply的区别(参数的区别)
call和apply的第一个参数都是要改变上下文的对象,
call从第二个参数开始以参数列表的形式展现,apply则是把除了改变上下文对象的参数放在一个数组里,作为它的第二个参数。
应用👇
1、 将伪数组转化为数组
什么是伪数组?
(例如通过document.getElementsByTagName获取的元素、含有length属性的对象) 具有length属性,并且可以通过0、1、2…下标来访问其中的元素
但是没有Array中的push、pop等方法。就可以利用call,apply来转化成真正的数组,就可以使用数组的方法了。
常见伪数组有:含有length属性的对象,dom节点, 函数的参数arguments。
function fn() { return Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); } console.log(fn(1,2,3,4,5)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let obj4 = { 0: 1, 1: 'thomas', 2: 13, length: 3 // 一定要有length属性 }; console.log(Array.prototype.slice.call(obj4)); // [1, "thomas", 13]
2、数组拼接,添加

用 apply方法,给arr1 添加 arr2。

3、判断变量类型
let arr1 = [1,2,3]; let str1 = 'string'; let obj1 = {name: 'thomas'};
function isArray(obj) { return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Array]'; } console.log(fn1(arr1)); // true
// 判断类型的方式,这个最常用语判断array和object,null(因为typeof null等于object) console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arr1)); // [object Array] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(str1)); // [object String] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(obj1)); // [object Object] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(null)); // [object Null]
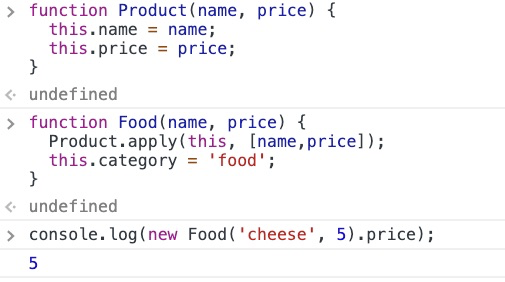
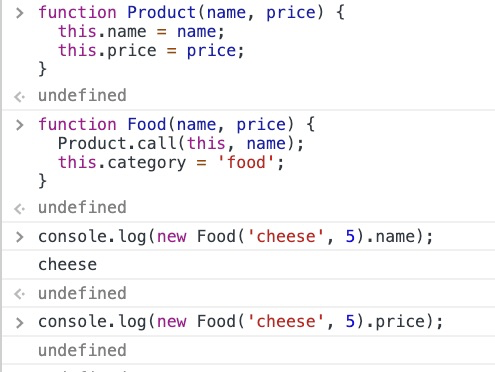
4、利用call和apply实现继承
function Animal(name){ this.name = name; this.showName = function(){ console.log(this.name); } } function Cat(name){ Animal.call(this, name); } // Animal.call(this) 的意思就是使用this对象代替Animal对象,那么Cat中就有Animal的所有属性和方法了,Cat对象就能够直接调用Animal的方法以及属性了 var cat = new Cat("TONY"); cat.showName(); //TONY
5、多继承
function Class1(a,b) { this.showclass1 = function(a,b) { console.log(`class1: ${a},${b}`); } } function Class2(a,b) { this.showclass2 = function(a,b) { console.log(`class2: ${a},${b}`); } } function Class3(a,b,c) { Class1.call(this); Class2.call(this); } let arr10 = [2,2]; let demo = new Class3(); demo.showclass1.call(this,1); // class1: 1,undefined demo.showclass1.call(this,1,2); // class1: 1,2 demo.showclass2.apply(this,arr10); // class2: 2,2
bind: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function/bind
apply: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function/apply
call: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function/call



