信号的字符串显示
在捕获到信号的时候,可以将其对应的字符串输出。有以下几种方法:
1. 字符串数组
使用signal.h头文件下的字符串数组sys_siglist,将信号作为下标时,字符串就是对应的信号含义:
#include <signal.h> extern const char * const sys_siglist[];
测试:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> int main(int argc, char **argv) { int i=1; while(sys_siglist[i]) { printf("SIGNO=%d: %s\n",i,sys_siglist[i]); i++; } return 0; }
运行效果如下:
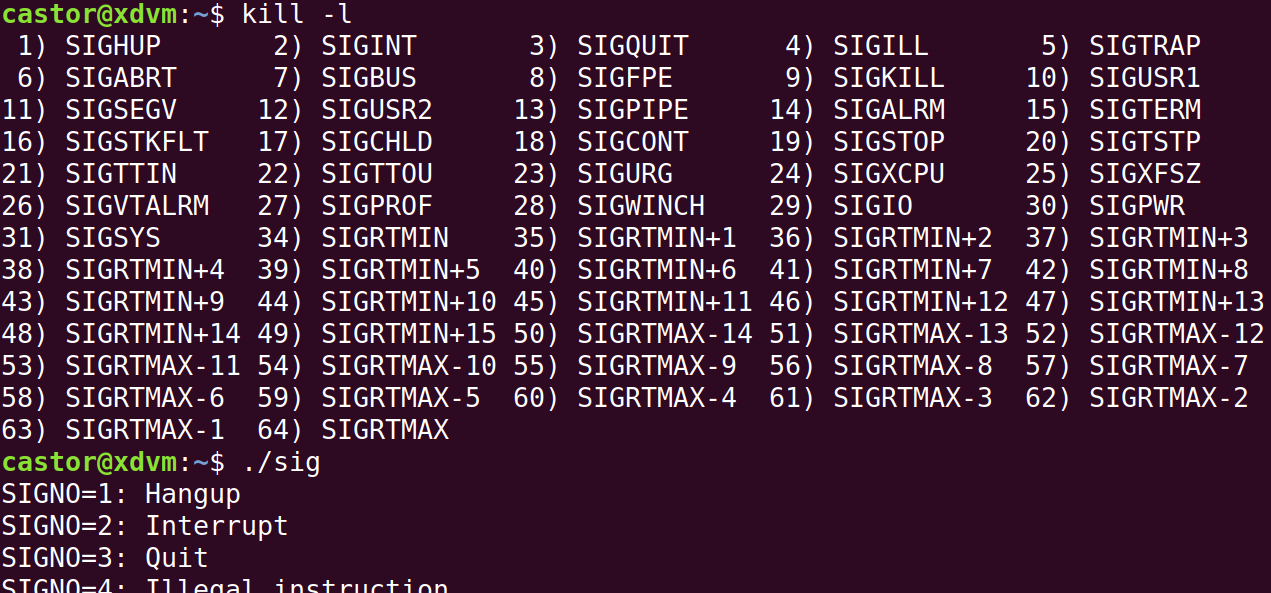
SIGNO=1: Hangup
SIGNO=2: Interrupt
SIGNO=3: Quit
SIGNO=4: Illegal instruction
SIGNO=5: Trace/breakpoint trap
SIGNO=6: Aborted
SIGNO=7: Bus error
SIGNO=8: Floating point exception
SIGNO=9: Killed
SIGNO=10: User defined signal 1
SIGNO=11: Segmentation fault
SIGNO=12: User defined signal 2
SIGNO=13: Broken pipe
SIGNO=14: Alarm clock
SIGNO=15: Terminated
SIGNO=16: Stack fault
SIGNO=17: Child exited
SIGNO=18: Continued
SIGNO=19: Stopped (signal)
SIGNO=20: Stopped
SIGNO=21: Stopped (tty input)
SIGNO=22: Stopped (tty output)
SIGNO=23: Urgent I/O condition
SIGNO=24: CPU time limit exceeded
SIGNO=25: File size limit exceeded
SIGNO=26: Virtual timer expired
SIGNO=27: Profiling timer expired
SIGNO=28: Window changed
SIGNO=29: I/O possible
SIGNO=30: Power failure
SIGNO=31: Bad system call
其实,在终端中使用kill -l也可以查看:
2. psignal函数
定义如下:
#include <signal.h> void psignal (int signo, const char *msg);
这个函数的使用同perror类似,例如,调用:
psignal(13, "signal");
将会显示“signal: Broken pipe”
3. strsignal函数
与perror和strerror两个函数类似,有psignal,其实也有strsignal函数,定义如下:
#include <string.h> char * strsignal (int signo);
效果和strerror类似。需要注意这个函数返回的字符串指针仅在下一次调用strsignal前保持不变,所以这个函数不是线程安全的。



