C#读书笔记:线程,任务和同步
前言
学习C#两个多月了,像当初实习做PHP开发一样,也是由着一个个Feature需求,慢慢掌握了很多相关的编程技巧。本次主要记录下学习C# 多线程的相关知识。
参考书籍:《Csharp高级编程(第7版)》
1.使用线程的原因

不过运行多个线程也要注意一些问题:他们可以同时运行,但是如果线程访问相同的数据,就很容易出问题,必须实现同步机制。
2.理解线程
线程是程序中独立的指令流。C#编写的程序都有一个入口点(即Main()方法),程序从该方法的第一条开始执行,直到方法返回为止。这种程序结构非常适合用于一个有任务序列的程序,但是程序常常需要同时完成多个任务。
这就要用到多个线程,比如Word的拼写检查器的工作原理是这样的:一个线程等待用户输入,另一个线程进行后台搜索,第3个线程将写入的数据保存在临时文件中,第4个线程从Internet上下载其他数据。
理解线程很重要的一点其实是理解线程和进程的关系:

3.创建线程的方式
- 异步委托
创建线程的一种简单地方式是定义委托,并异步调用它。委托是方法的类型安全的引用,它使用线程池来完成异步任务。
代码实例:
使用投票的例子,并检查委托是否完成了它的任务。等待异步委托结果的四种方式:
(1)轮询
Delegate类提供了BeginInvoke()方法,通过其返回类型IAsyncResult ,可以获取委托的相关信息,并检验它是否完成了任务。只要委托没有完成其任务,程序的主线程就继续执行while循环。
(2)等待句柄
使用与IAsyncResult 相关联的等待句柄。使用AsyncWaitHandle属性可以访问等待句柄,该属性可以返回一个WaitHandle类型的对象,它可以等待委托线程完成其任务。
(3)异步回调
(4)Lambda表达式
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace Wrox.ProCSharp.Threading
{
class Program
{
static int TakesAWhile(int data, int ms)
{
Console.WriteLine("TakesAWhile started");
Thread.Sleep(ms);
Console.WriteLine("TakesAWhile completed");
return ++data;
}
//要从委托中调用这个方法,必须定义一个有相同参数和返回类型的的委托
public delegate int TakesAWhileDelegate(int data, int ms);
static void Main()
{
// synchronous
// TakesAWhile(1, 3000);
TakesAWhileDelegate d1 = TakesAWhile;
// (1)polling轮询
//IAsyncResult ar = d1.BeginInvoke(1, 3000, null, null);
//while (!ar.IsCompleted)
//{
// // doing something else
// Console.Write(".");
// Thread.Sleep(50);
//}
//int result = d1.EndInvoke(ar);
//Console.WriteLine("result: {0}", result);
// (2)wait handle
//IAsyncResult ar = d1.BeginInvoke(1, 3000, null, null);
//while (true)
//{
// Console.Write(".");
// if (ar.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(50, false))
// {
// Console.WriteLine("Can get the result now");
// break;
// }
//}
//int result = d1.EndInvoke(ar);
//Console.WriteLine("result: {0}", result);
// (3)async callback
//d1.BeginInvoke(1, 3000, TakesAWhileCompleted, d1);
//for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
//{
// Console.Write(".");
// Thread.Sleep(50);
//}
//(4)Lambda expression:可以直接访问作用域外的变量d1,所以不需要把一个值赋予BeginInvoke()方法的最后一个参数
d1.BeginInvoke(1, 3000,
ar =>
{
int result = d1.EndInvoke(ar);
Console.WriteLine("result: {0}", result);
},
null);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
Console.Write(".");
Thread.Sleep(50);
}
}
static void TakesAWhileCompleted(IAsyncResult ar)
{
if (ar == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("ar");
TakesAWhileDelegate d1 = ar.AsyncState as TakesAWhileDelegate;
Trace.Assert(d1 != null, "Invalid object type");
int result = d1.EndInvoke(ar);
Console.WriteLine("result: {0}", result);
}
}
}
运行结果:

代码实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace Wrox.ProCSharp.Threading
{
public class MyThread
{
private string data;
public MyThread(string data)
{
this.data = data;
}
public void ThreadMain()
{
Console.WriteLine("Running in a thread, data: {0}", data);
}
}
public struct Data
{
public string Message;
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
FirstThread();
//var t1 = new Thread(Prio);
//t1.Name = "First";
//var t2 = new Thread(Prio);
//t2.Name = "Second";
//t1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
//t2.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest;
//t1.Start();
//t2.Start();
//var t1 = new Thread(ThreadMain);
//t1.Name = "MyNewThread1";
//t1.IsBackground = true;
//t1.Start();
//Console.WriteLine("Main thread ending now...");
//var d = new Data { Message = "Info" };
//var t2 = new Thread(ThreadMainWithParameters);
//t2.Start(d);
//var obj = new MyThread("info");
//var t3 = new Thread(obj.ThreadMain);
//t3.Start();
}
static void Prio()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
}
static void ThreadMain()
{
Console.WriteLine("Thread {0} started", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
Thread.Sleep(3000);
// Console.WriteLine("Running in the thread {0}, id: {1}.", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("Thread {0} completed", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
}
static void ThreadMainWithParameters(object o)
{
Data d = (Data)o;
Console.WriteLine("Running in a thread, received {0}", d.Message);
}
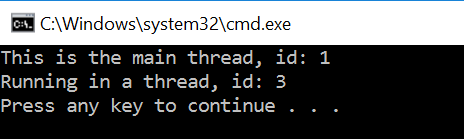
static void FirstThread()
{
new Thread(() => Console.WriteLine("Running in a thread, id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId)).Start();
Console.WriteLine("This is the main thread, id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
}
}
运行结果:
代码实例:
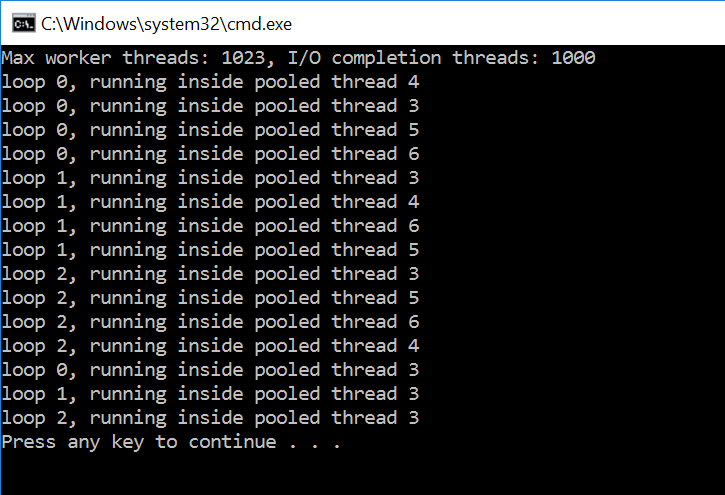
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Wrox.ProCSharp.Threading
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int nWorkerThreads;
int nCompletionPortThreads;
ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out nWorkerThreads, out nCompletionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine("Max worker threads: {0}, I/O completion threads: {1}", nWorkerThreads, nCompletionPortThreads);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(JobForAThread);
}
Thread.Sleep(3000);
}
static void JobForAThread(object state)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("loop {0}, running inside pooled thread {1}", i,
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Thread.Sleep(50);
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
代码实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
namespace TaskSamples
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// ParallelDemo();
SimpleTask();
// ContinuationTask();
// ParentAndChild();
// ResultsFromTasks();
Thread.Sleep(5000);
//ParentAndChild();
// HierarchyTasks("c:\\");
//Parallel.f
//Task t1 = new Task(() => Console.WriteLine("running in a task"));
//Task t2 = new Task(() => Console.WriteLine("running in a task"));
//for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
//{
// Task t1 = new Task(o =>
// {
// Console.WriteLine("running in a task {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// Thread.Sleep(500);
// Console.WriteLine("still running {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// }, "data", TaskCreationOptions.None);
// // t1.RunSynchronously();
// t1.Start();
//}
//Console.WriteLine("start sleep main");
//Thread.Sleep(3000);
//Console.WriteLine("main thread");
}
static void ResultsFromTasks()
{
var t1 = new Task<Tuple<int,int>>(TaskWithResult, Tuple.Create<int, int>(8, 3));
t1.Start();
Console.WriteLine(t1.Result);
t1.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("result from task: {0} {1}", t1.Result.Item1, t1.Result.Item2);
}
static Tuple<int, int> TaskWithResult(object division)
{
Tuple<int, int> div = (Tuple<int, int>)division;
int result = div.Item1 / div.Item2;
int reminder = div.Item1 % div.Item2;
Console.WriteLine("task creates a result...");
return Tuple.Create<int, int>(result, reminder);
}
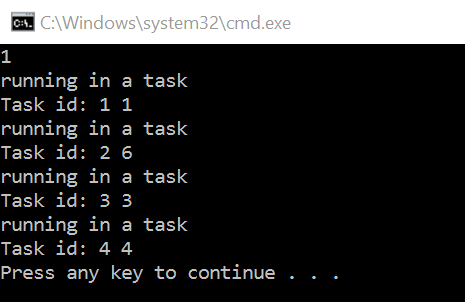
static void SimpleTask()
{
// using task factory
TaskFactory tf = new TaskFactory();
Task t1 = tf.StartNew(TaskMethod);
// using the task factory via a task
Task t2 = Task.Factory.StartNew(TaskMethod);
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// using Task constructor
Task t3 = new Task(TaskMethod);
// t3.Start();
t3.RunSynchronously();
Task t4 = new Task(TaskMethod, TaskCreationOptions.PreferFairness);
t4.Start();
}
static void ContinuationTask()
{
Task t1 = new Task(DoOnFirst);
Task t2 = t1.ContinueWith(DoOnSecond);
Task t3 = t1.ContinueWith(DoOnSecond);
Task t4 = t2.ContinueWith(DoOnSecond);
Task t5 = t1.ContinueWith(DoOnError, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted);
t1.Start();
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
static void DoOnFirst()
{
Console.WriteLine("doing some task {0}", Task.CurrentId);
Thread.Sleep(3000);
}
static void DoOnSecond(Task t)
{
Console.WriteLine("task {0} finished", t.Id);
Console.WriteLine("this task id {0}", Task.CurrentId);
Console.WriteLine("do some cleanup");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
}
static void DoOnError(Task t)
{
Console.WriteLine("task {0} had an error!", t.Id);
Console.WriteLine("my id {0}", Task.CurrentId);
Console.WriteLine("do some cleanup");
}
static void ParentAndChild()
{
Task parent = new Task(ParentTask);
parent.Start();
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine(parent.Status);
Thread.Sleep(4000);
Console.WriteLine(parent.Status);
}
static void ParentTask()
{
Console.WriteLine("task id {0}", Task.CurrentId);
Task child = new Task(ChildTask); // , TaskCreationOptions.DetachedFromParent);
child.Start();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("parent started child");
// Thread.Sleep(3000);
}
static void ChildTask()
{
// Console.WriteLine("task id {0}, parent: {1}", Task.Current.Id, Task.Current.Parent.Id);
Console.WriteLine("child");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
Console.WriteLine("child finished");
}
static void TaskMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("running in a task");
Console.WriteLine("Task id: {0} {1}", Task.CurrentId, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
static void ParallelDemo()
{
// Parallel.For(0, 5, i => Console.WriteLine(i));
Parallel.For<string>(0, 20, () => "abcd",
(x, ls, str) =>
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
return "defg";
},
(str) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("action {0}", str);
});
ParallelOptions po = new ParallelOptions();
}
//static void ParentAndChild()
//{
// TaskFactory factory = new TaskFactory();
// var t1 = factory.StartNew(() =>
// {
// Console.WriteLine("parent task {0}", Task.CurrentId);
// factory.StartNew(() =>
// {
// Console.WriteLine("child task {0}", Task.CurrentId);
// Thread.Sleep(2000);
// Console.WriteLine("finished child");
// }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent);
// Console.WriteLine("finished parent");
// });
// t1.Wait();
//}
}
}
运行结果:
代码实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Wrox.ProCSharp.Threading
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
//ParallelFor();
//ParallelForeach();
ParallelInvoke();
}
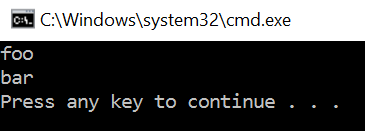
static void ParallelInvoke()
{
//并行运行多个任务:Parallel.Invoke()方法允许传递一个Action委托数组,其中指定应运行的方法
Parallel.Invoke(Foo, Bar);
}
static void Foo()
{
Console.WriteLine("foo");
}
static void Bar()
{
Console.WriteLine("bar");
}
static void ParallelForeach()
{
string[] data = {"zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten", "eleven", "twelve"};
//异步方式遍历
ParallelLoopResult result =
Parallel.ForEach<string>(data, s =>
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
});
Parallel.ForEach<string>(data,
(s, pls, l) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", s, l);
});
}
static void ParallelFor()
{
//ParallelLoopResult result =
// Parallel.For(0, 10, i =>
// {
// Console.WriteLine("{0}, task: {1}, thread: {2}", i,
// Task.CurrentId, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// Thread.Sleep(10);
// });
//Console.WriteLine(result.IsCompleted);
//ParallelLoopResult result =
// Parallel.For(10, 40, (int i, ParallelLoopState pls) =>
// {
// Console.WriteLine("i: {0} task {1}", i, Task.CurrentId);
// Thread.Sleep(10);
// if (i > 15)
// pls.Break();
// });
//Console.WriteLine(result.IsCompleted);
//Console.WriteLine("lowest break iteration: {0}", result.LowestBreakIteration);
Parallel.For<string>(0, 20,
() =>
{
// invoked once for each thread
Console.WriteLine("init thread {0}, task {1}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Task.CurrentId);
return String.Format("t{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
},
(i, pls, str1) =>
{
// invoked for each member
Console.WriteLine("body i {0} str1 {1} thread {2} task {3}", i, str1,
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId,
Task.CurrentId);
Thread.Sleep(10);
return String.Format("i {0}", i);
},
(str1) =>
{
// final action on each thread
Console.WriteLine("finally {0}", str1);
});
}
}
}
运行结果:
代码实例:
ps:在运行书中附带的sample时,报错:
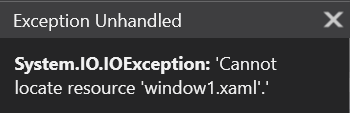
经查证,发现这是由于StartupUri中的内容与窗口名称不一致所导致。
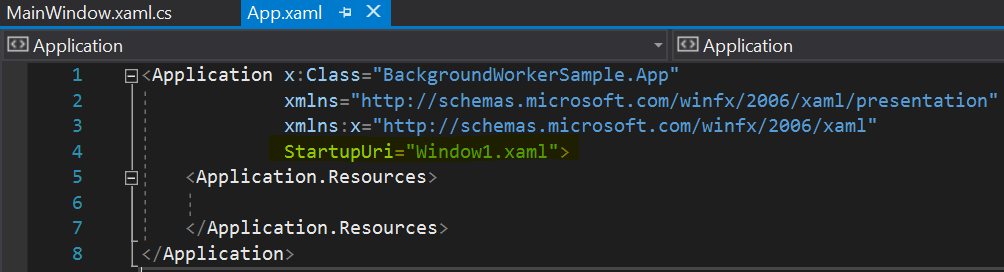
这部分的知识可以参考一篇译文:WPF教程(十)使用App.xaml


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号