列举常见的递归问题
因为今天我重新看了递归的教学视频,但发现好像很多都很容易忘,所以我想把所有常见的递归算法题给整理一下。
1.全排列
输入:"aac"
输出:[aac,aac , aca, aca,caa]
思路就是可以选择每个下标的字母作为开头。
public static List<String> getAll(String str) { if(str.equals("") || str == null){ return null; } List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Character> set = new ArrayList<Character>(); for (Character character : str.toCharArray()) { set.add(character); } process(set,"",list); return list; } public static void process(ArrayList<Character> set, String path, List<String> list){ if(set.isEmpty()){ list.add(path); return; } for (int index = 0; index < set.size(); index++) { String pick = path+set.get(index); ArrayList<Character> next = new ArrayList<>(set); next.remove(index); process2(next, pick, list); } } }
2.全排列,不要有重复
这里要注意判断是否选过的HashSet<Character> picks,这个点我想了好久才想通,因为在for循环里面,其实是在循环每个位置作为开头,所以在循环的时候,比如当我们选了‘a’之后,我们就不能再选‘a’作为开头字母了,所以我觉得从循环这个点去理解HashSet<Character> picks会比较好。
public static List<String> getAll(String str) { if(str.equals("") || str == null){ return null; } List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Character> set = new ArrayList<Character>(); for (Character character : str.toCharArray()) { set.add(character); } process1(set,"",list); return list; } public static void process1(ArrayList<Character> set, String path, List<String> list){ if(set.isEmpty()){ list.add(path); return; } HashSet<Character> picks = new HashSet<>(); for (int index = 0; index < set.size(); index++) { if (!picks.contains(set.get(index))) { picks.add(set.get(index)); String pick = path+set.get(index); ArrayList<Character> next = new ArrayList<>(set); next.remove(index); process1(next, pick, list); } } } }
3.解码
输入: "12" 输出: 2 解释: 它可以解码为 "AB"(1 2)或者 "L"(12)。
这个其实跟全排列的思路是一样的,就是我们去遍历给的数字字符串,我们可以判断是否选当前字符,还是选择当前字符加下一位字符。其实我有点想太多了,其实就是递归的时候加上一些if语句。
public static int numDecodings(String s) { if(s == null || s.equals("")) return 0; char[] ch = s.toCharArray(); return process(ch, 0); } public static int process(char[] ch, int index){ if(index == ch.length){ return 1; } if(ch[index] == '0'){ return 0; } if(ch[index] == '1'){ int res = process(ch,index+1); if(index+1 < ch.length){ res+= process(ch,index+2); } return res; } if(ch[index] == '2'){ int res = process(ch.index+1); if(index+1 < ch.length && ch[index] <'6'){ res += process(ch,index+2); } return res; } return process(ch,index+1); } }
4.背包问题
给定两个长度为N的数组weights和values,weights[i]和values[i]分别表示i号物品的重量和价值,
给定一个正数bag,表示一个载重bag的袋子,你装的物品不能超过这个重量,返回你能装下最大价值是多少
这个也是一个很经典的题目
public static int maxValue1(int[] c, int[] p, int bag) { return process1(c, p, 0, 0, bag); } public static int process1(int[] weights, int[] values, int i, int alreadyweight, int bag) { if (alreadyweight > bag) { return 0; } if (i == weights.length) { return 0; } return Math.max( process1(weights, values, i + 1, alreadyweight, bag), values[i] + process1(weights, values, i + 1, alreadyweight + weights[i], bag)); }
5.选牌
两位绝顶聪明的选手做选牌的游戏,桌子上放着代表这价值的卡牌,轮流拿牌,但是只能拿最左边或者最右边的牌。
public static int win(int[] arr){ if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { return 0; } return Math.max(xianshou(arr, 0, arr.length-1), houshou(arr, 0, arr.length-1)); } public static int xianshou(int[] arr, int L ,int R){ if(L == R){ return arr[L]; } return Math.max(arr[L]+houshou(arr, L+1, R), arr[R]+houshou(arr, L, R-1)); } public static int houshou(int[] arr,int L ,int R){ if(L == R){ return 0; } return Math.min(xianshou(arr, L-1, R), xianshou(arr, L, R-1)); }
public static int win2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] f = new int[arr.length][arr.length];
int[][] s = new int[arr.length][arr.length];
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
f[j][j] = arr[j];
for (int i = j - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(arr[i] + s[i + 1][j], arr[j] + s[i][j - 1]);
s[i][j] = Math.min(f[i + 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return Math.max(f[0][arr.length - 1], s[0][arr.length - 1]);
}

这里的动态的填二维表很牛逼,它是从下往上开始填。
6.N皇后问题
public static int num1(int n) { if(n < 1) return 0; int[] record = new int[n]; return process(n, 0, record); } public static int process(int n , int i ,int[] record){ if(i == n){ return 1; } int res = 0; for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if(isValid(record,i ,j)){ record[i] = j; res +=process(n, i+1, record); } } return res; } public static boolean isValid(int[] record, int i ,int j){ for (int k = 0; k < i; k++) { if(record[k] == j || Math.abs(k-i) == Math.abs(record[k] - j) ){ return false; } } return true; } public static int num2(int n) { if(n<2 || n>32) return 0; int limit = n == 32 ? -1 : (1<<n) -1; return process(limit,0,0,0); } public static int process(int limit, int colLim, int leftDaLim, int rightDaLim){ if(colLim == limit){ return 1; } int positon = limit & ~(colLim | leftDaLim | rightDaLim); int mostRightPos = 0; int res = 0; while(positon != 0){ mostRightPos = positon & (~positon +1); positon = positon - mostRightPos; res += process(limit, colLim | mostRightPos, (leftDaLim| mostRightPos )<<1, (rightDaLim | mostRightPos )>>>1); } return res; }
判断是否处于相同的斜对角线,只要知道两个点的行列,
比如点1(a,b)和点2(b,c),|a-c|==|b-d|

7.机器人走路
给定一个数值,机器人每次只能前进一步和后退一步,指定机器人只能走k步,返回机器人能走到指定位置的路径数。
输入:n=
输出:
public static int walk(int N, int s, int e, int k){ return process2(N,s,e,k); } public static int process(int N ,int cur, int e, int rest){ if(rest == 0){ return rest == e ? 1 : 0 ; } if (cur == 1) { return process(N, cur+1, e, rest-1); } if (cur == N) { return process(N, N-1, e, rest-1); } return process(N, cur+1, e, rest-1)+process(N, cur-1, e, rest-1); } public static int process2(int N ,int cur, int e, int rest){ int[][] dp = new int[rest+1][N+1]; //解决第一行的dp表 dp[0][e] = 1; //遍历行 for (int i = 1; i <= rest; i++) { //遍历列 for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) { if(j == 1){ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j+1]; }else if (j == N){ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]; }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j+1]; } } } return dp[e][rest]; }
8.金钱组合问题
给定一个int数组,数组的数值表示不同金额的面值,可以选择任一张面值的纸币,可重复使用,返回可组成target金额的方法数有多少种。
这就是一个带有范围尝试的背包问题,在我的理解就是在递归里面多了个for循环。递归代码是比较容易写出来的。
public static int coins1(int[] arr, int aim) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) { return 0; } return process(arr, 0, aim); } public static int process(int[] arr, int index, int rest ){ if(index == arr.length){ return rest == 0 ? 1 : 0; } int res = 0; for (int zhang = 0; zhang * arr[index] < rest; zhang ++) { return res += process(arr, index+1, rest - zhang * arr[index]); } return res; }
在改成动态规划的时候,也是跟平常差不多,但是每个格子依赖的格子比较多,而且要分越界的时候和不越界的时候,但整体来说也是比较简单的,找出两个会影响结果的参数,就能画出了个二维数组。
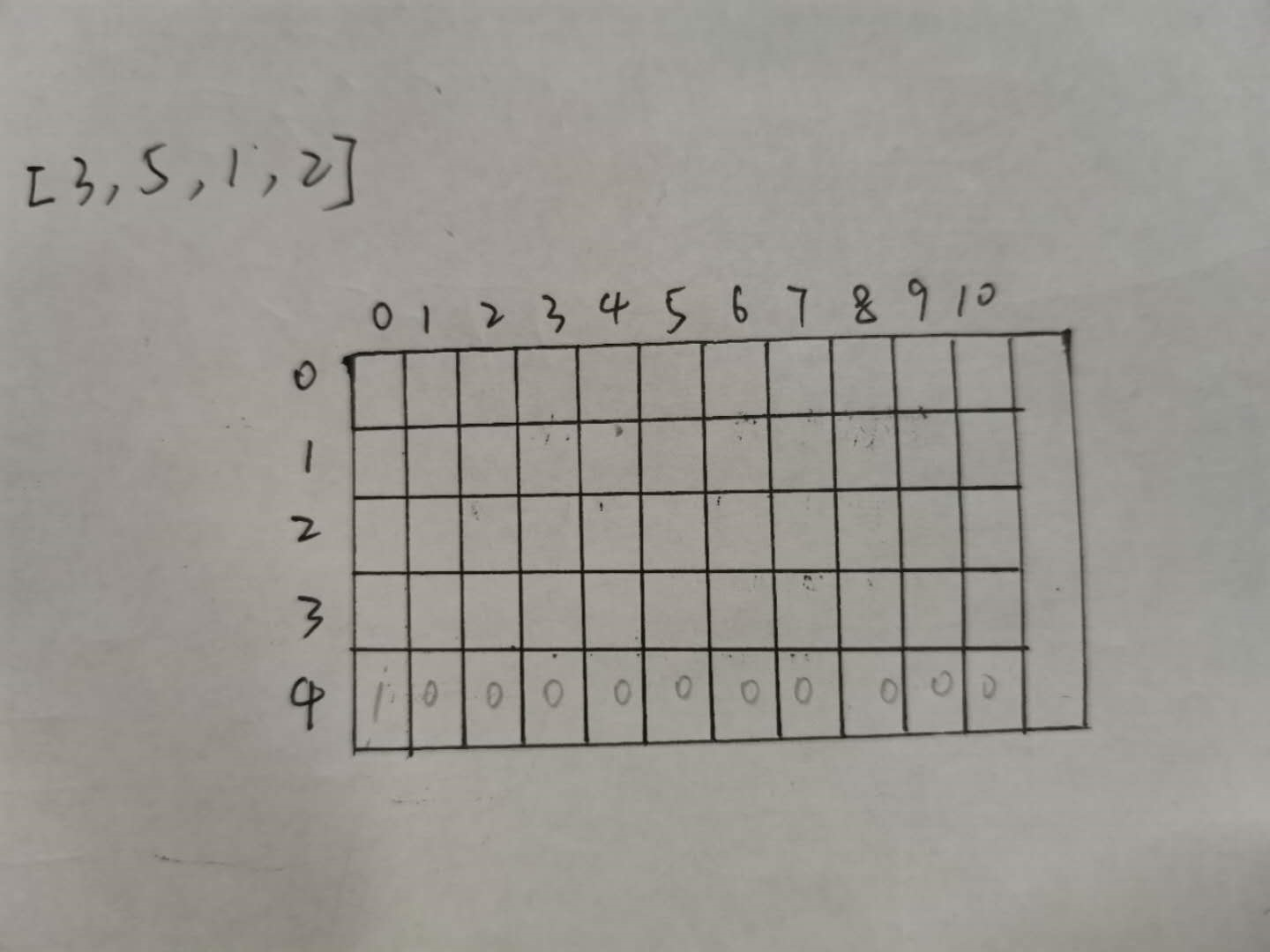
这里可以记住在范围尝试的时候填格子时的代码,这里可以学习。
public static int process22(int[] arr, int aim){ int N = arr.length; int[][] dp = new int[N+1][aim+1]; dp[N][0]= 1; for (int index = N-1; index >= 0 ; index--) { for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) { int res = 0; for (int zhang = 0; zhang * arr[index] <= rest; zhang ++) { res += dp[index+1][ rest - zhang * arr[index]]; } dp[index][rest] = res; } } return dp[0][aim]; }
然后这里还可以再继续优化,表达出来比较难,但总的来说就是每个中间的格子都会不断地去计算累加和,这个过程其实是重复计算过的,这里我们要做的就是如何去省去这个重复的过程,我们就可以利用格子距离自己arr[index]的格子,再加上自己下方的格子,这样我们的速度就很更快了。
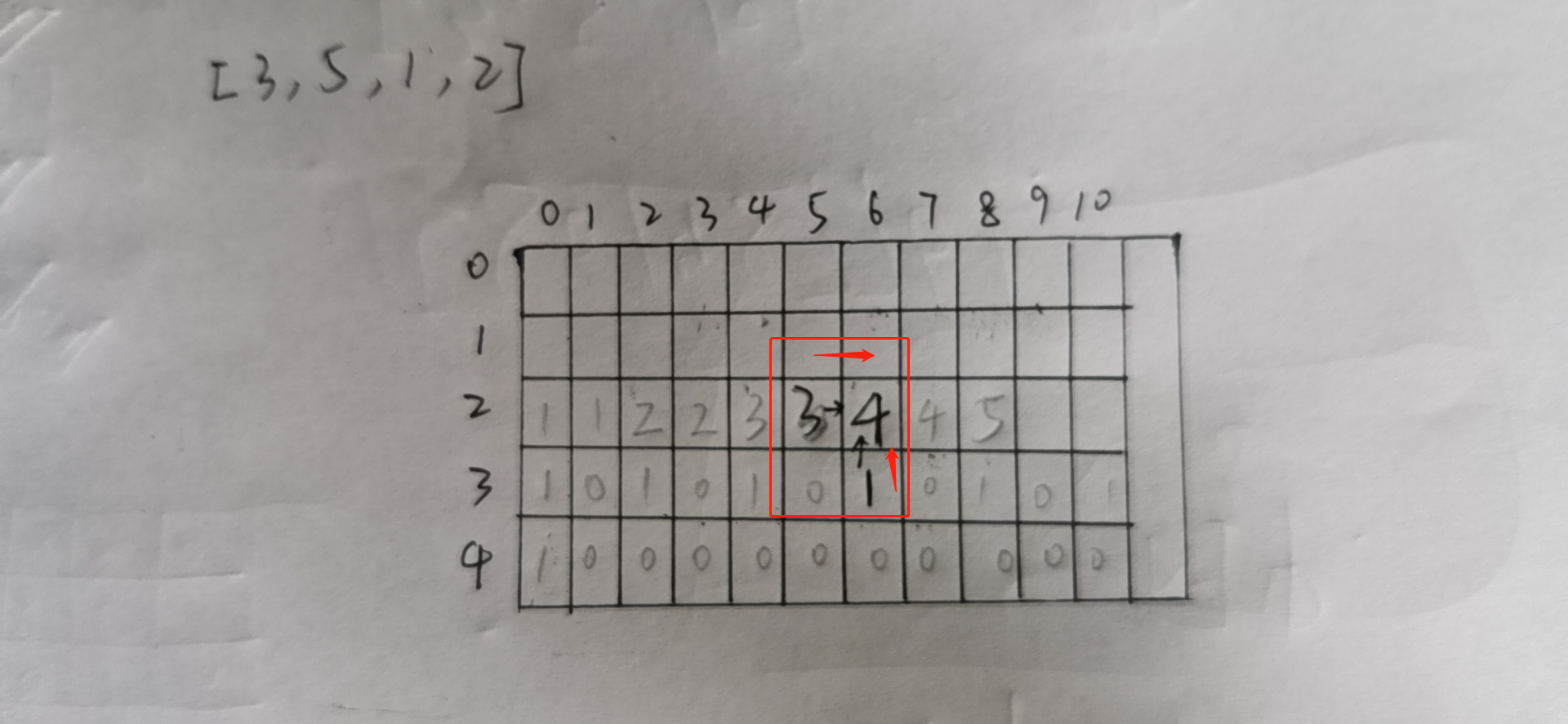
public static int processPro(int[] arr, int aim){ int N = arr.length; int[][] dp = new int[N+1][aim+1]; dp[N][0]= 1; for (int index = N-1; index >= 0 ; index--) { for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) { dp[index][rest] = dp[index+1][rest]; if(rest - arr[index] >=0){ dp[index][rest] += dp[index][rest-arr[index]]; } } } return dp[2][5]; }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号