Spring Cloud学习笔记【九】配置中心Spring Cloud Config
Spring Cloud Config 是 Spring Cloud 团队创建的一个全新项目,用来为分布式系统中的基础设施和微服务应用提供集中化的外部配置支持,它分为服务端与客户端两个部分。其中服务端也称为分布式配置中心,它是一个独立的微服务应用,用来连接配置仓库并为客户端提供获取配置信息、加密 / 解密信息等访问接口;而客户端则是微服务架构中的各个微服务应用或基础设施,它们通过指定的配置中心来管理应用资源与业务相关的配置内容,并在启动的时候从配置中心获取和加载配置信息。Spring Cloud Config 实现了对服务端和客户端中环境变量和属性配置的抽象映射,所以它除了适用于 Spring 构建的应用程序之外,也可以在任何其他语言运行的应用程序中使用。由于 Spring Cloud Config 实现的配置中心默认采用 Git 来存储配置信息,所以使用 Spring Cloud Config 构建的配置服务器,天然就支持对微服务应用配置信息的版本管理,并且可以通过 Git 客户端工具来方便的管理和访问配置内容。当然它也提供了对其他存储方式的支持,比如:GIT仓库、SVN 仓库、本地化文件系统。
下面我们将构建一个基于 Git 存储的分布式配置中心,并对客户端进行改造,让其能够从配置中心获取配置信息并绑定到代码中。
准备工作
准备一个 Git 仓库,在 Github 上面创建了一个文件夹 config-repo 用来存放配置文件,为了模拟生产环境,我们创建以下三个配置文件:
1 // 开发环境 2 config-server-dev.yml 3 // 测试环境 4 config-server-test.yml 5 // 生产环境 6 config-server-prod.yml
每个配置文件中都写一个属性 info.profile, 属性值分别是 dev/test/prod
Server 端
创建一个基础的 Spring Boot 工程,命名为:service-config-server
POM依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId> 4 </dependency> 5 <dependency> 6 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 7 <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> 8 </dependency>
配置文件
在 application.yml 中添加配置服务的基本信息以及 Git 仓库的相关信息
server:
port: 9300
spring:
application:
name: service-config-server
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/carry-chan/spring-cloud # 配置git仓库的地址
search-paths: config-repo # git仓库地址下的相对地址,可以配置多个,用,分割。
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://admin:123456@localhost:8761/eureka/
Spring Cloud Config 也提供本地存储配置的方式。我们只需要设置属性spring.profiles.active=native,Config Server会从默认的src/main/resource目录下检索配置文件。也可以通过spring.cloud.config.server.native.searchLocations=file:E:/properties/属性来制定配置文件的位置。虽然 Spring Cloud Config 提供了这样的功能,但是为了支持更好的管理内容和版本控制的功能,还是推荐使用 Git 的方式。
如果我们的 Git 仓库需要权限访问,那么可以通过配置下面的两个属性来实现
spring.cloud.config.server.git.username:访问 Git 仓库的用户名
spring.cloud.config.server.git.password:访问 Git 仓库的用户密码
启动类
1 package com.carry.springcloud; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer; 6 7 @EnableConfigServer 8 @SpringBootApplication 9 public class ServiceConfigServerApplication { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 SpringApplication.run(ServiceConfigServerApplication.class, args); 13 } 14 }
到此 Server 端相关配置已经完成。
测试
启动eureka-server、service-config-server,浏览器直接访问 http://localhost:9300/config-server/dev 返回信息如下:
{
"name": "config-server",
"profiles": [
"dev"
],
"label": null,
"version": "beb220098b44c60cf99277f064a19d52e7ebeb91",
"state": null,
"propertySources": [
{
"name": "https://github.com/carry-chan/spring-cloud/config-repo/config-server-dev.yml",
"source": {
"info.profile": "dev"
}
}
]
}
上述的返回的信息包含了配置文件的位置、版本、配置文件的名称以及配置文件中的具体内容,说明 Server 端已经成功获取了 Git 仓库的配置信息。
如果直接查看配置文件中的配置信息可访问 http://localhost:9300/config-server-dev.yml 返回:
info: profile: dev
修改配置文件config-server-dev.yml中配置信息为dev v0,再次在浏览器访问 http://localhost:9300/config-server-dev.yml 返回:dev v0,说明 Server 端会自动读取最新提交的内容。
仓库中的配置文件会被转换成 Web 接口,访问可以参照以下的规则:
- /{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
- /{application}-{profile}.yml
- /{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
- /{application}-{profile}.properties
- /{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
上面的 URL 会映射 {application}-{profile}.yml 对应的配置文件,其中 {label} 对应 Git 上不同的分支,默认为 master。
Client 端
创建一个基础的 Spring Boot 应用,命名为 service-config-client。
POM依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId> 4 </dependency> 5 <dependency> 6 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 7 <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> 8 </dependency> 9 <dependency> 10 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 11 <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> 12 </dependency>
配置文件
需要配置两个配置文件,application.yml 和 bootstrap.yml,配置分别如下:
application.yml
server:
port: 9400
spring:
application:
name: service-config-client
bootstrap.yml
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: config-server # 对应 {application} 部分
profile: dev # 对应 {profile} 部分
label: master # 对应 {label} 部分,即 Git 的分支。如果配置中心使用的是本地存储,则该参数无用
discovery:
enabled: true
service-id: service-config-server #springcloud config的服务名
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://admin:123456@localhost:8761/eureka/
注意:上面这些与 Spring Cloud Config 相关的属性必须配置在 bootstrap.yml 中,config 部分内容才能被正确加载。因为 config 的相关配置会先于 application.yml,而 bootstrap.yml 的加载也是先于 application.yml。
启动类
1 package com.carry.springcloud; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 6 @SpringBootApplication 7 public class ServiceConfigClientApplication { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 SpringApplication.run(ServiceConfigClientApplication.class, args); 11 } 12 }
在 Controller 中使用 @Value 注解来获取 Server 端参数的值
1 package com.carry.springcloud; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; 4 import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope; 5 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; 6 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 7 8 import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; 9 10 @RestController 11 public class ClientController { 12 13 @Value("${info.profile}") 14 private String profile; 15 16 @GetMapping("/info") 17 public Mono<String> hello() { 18 return Mono.justOrEmpty(profile); 19 } 20 }
测试
依次启动项目eureka-server、service-config-server、service-config-client,访问 http://localhost:9400/info 返回dev 说明已经正确的从 Server 端获取到了参数。
手动修改Git仓库中 config-server-dev.yml 的值,再次访问 http://localhost:9400/info 依旧返回dev,这是因为 Spring Cloud Config 分服务端和客户端,服务端负责将 Git 中存储的配置文件发布成 REST 接口,客户端可以从服务端 REST 接口获取配置。但客户端并不能主动感知到配置的变化,从而主动去获取新的配置。客户端如何去主动获取新的配置信息呢,Spring Cloud 已经给我们提供了解决方案,每个客户端通过 POST 方法触发各自的 /actuator/refresh。
Refresh功能
修改客户端即 service-config-client 项目
添加依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> 4 </dependency>
增加了spring-boot-starter-actuator包,spring-boot-starter-actuator是一套监控的功能,可以监控程序在运行时状态,其中就包括/actuator/refresh的功能。
开启更新机制
需要给加载变量的类上面加 @RefreshScope,在客户端执行/actuator/refresh的时候就会更新此类下面的变量值。
1 package com.carry.springcloud; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; 4 import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope; 5 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; 6 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 7 8 import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; 9 10 @RestController 11 @RefreshScope 12 public class ClientController { 13 14 @Value("${info.profile}") 15 private String profile; 16 17 @GetMapping("/info") 18 public Mono<String> hello() { 19 return Mono.justOrEmpty(profile); 20 } 21 }
配置
Spring Boot 1.5.X 以上默认开通了安全认证,所以要在配置文件 application.yml 中添加以下配置以将/actuator/refresh这个 Endpoint 暴露出来
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: refresh
测试
重启 service-config-client 项目
访问 http://localhost:9400/info 返回dev
我将 Git 上对应配置文件里的值改为dev v0
执行 curl -X POST http://localhost:9400/actuator/refresh,返回["config.client.version","info.profile"]
再次访问 http://localhost:9400/info 返回dev v0
这就说明客户端已经得到了最新的值,Refresh 是有效的。
Webhook
现在虽然可以不用重启服务就更新配置了,但还是需要我们手动操作,这样还是不可取的。所以,这里就要用到git的webhooks来达到自动更新配置。
打开git上配置仓库的地址,添加webhooks
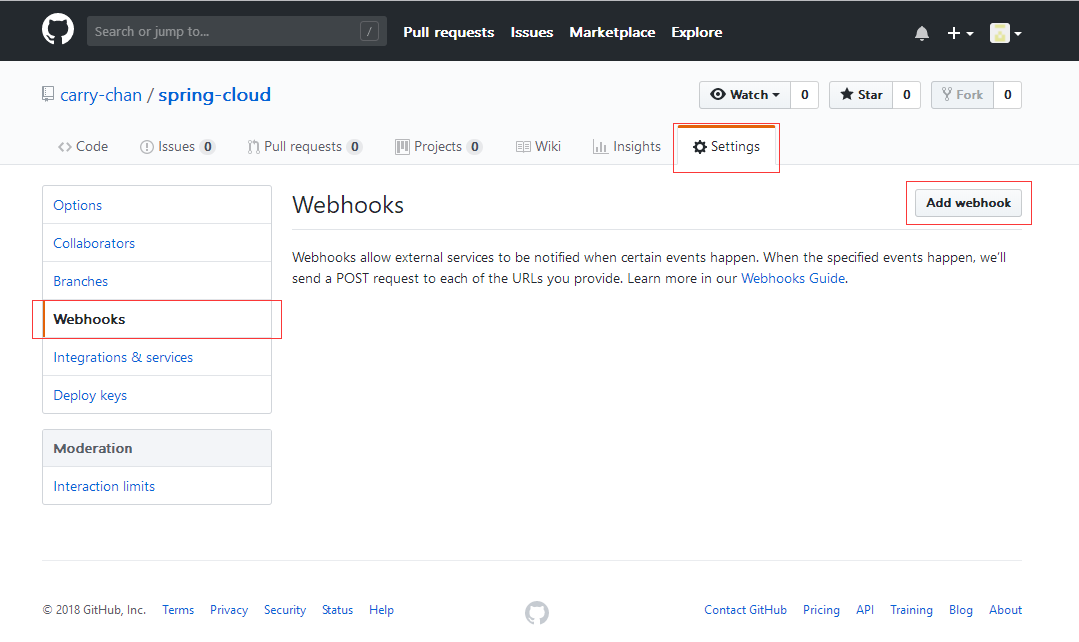
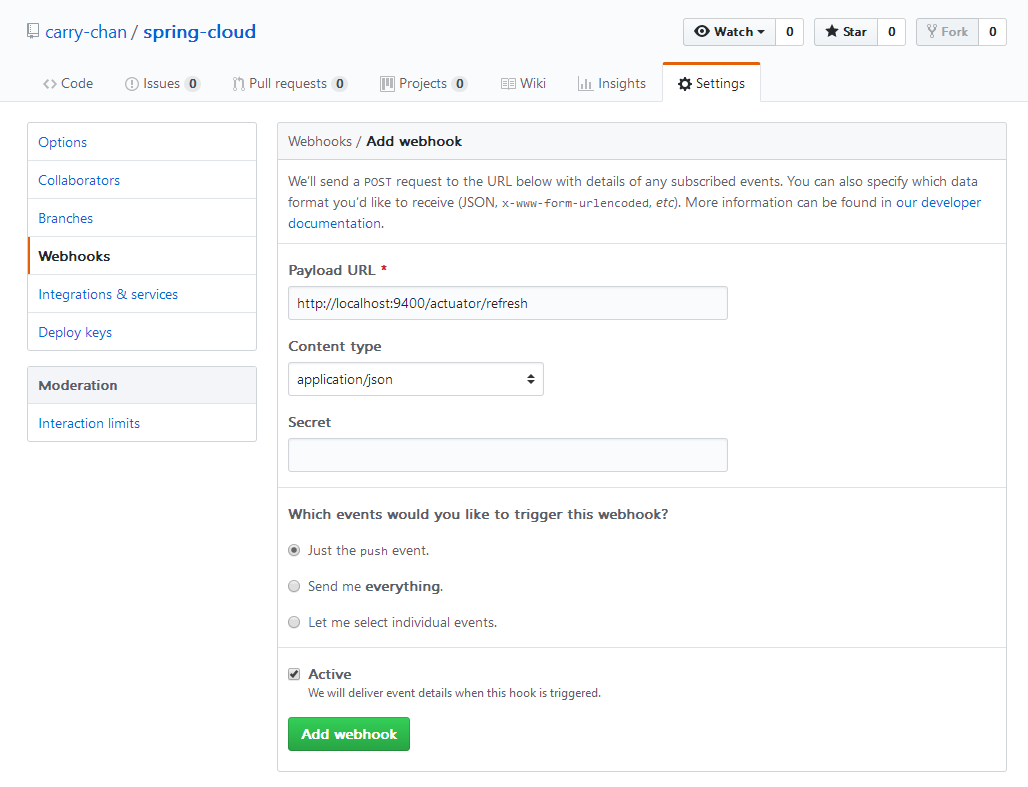
上面的Payload URL就填写我们的配置中心触发刷新的地址,当然这里不能写localhost,要外网访问地址才行。还有这里面有个Secret的秘钥验证,如果这里填写的话,在配置文件上要写上encrypt.key与之对应。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号