PAT (Basic Level) Practice 1050 螺旋矩阵
本片主要讲解螺旋矩阵的几种解法。
1 题目描述
1. 定义
本题要求将给定的
2. 输入格式
输入在第1行中给出一个正整数
3. 输出格式
输出螺旋矩阵。每行
相关题目,可以参考:
LeetCode 54. Spiral Matrix:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix/
PAT 1050螺旋矩阵:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805260223102976/problems/994805275146436608
2 思路分析
方法一:
第一步,计算行数
第二步,将
第三步,建立
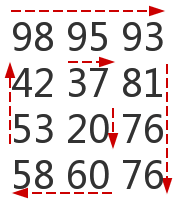
提示:由图可以发现横向和纵向交替,而且横向和纵向上数字每次减少一个。第一次横向的数字个数就是index指示, 每次到行列转换的时候: index = ( index + 1 ) % 4就可以到下一个方向了。检测每个行列的结束可以用计数加上行列状态的检查,而且每次到了行列转换的时候还要注意重置计数和改变行列的状态。
方法二:
第一步,计算行数
第二步,将
第三步,建立left>right || top>bottom。
3 代码实现
AC代码一:
def factorization(N): # 因式分解 iter = int(N**0.5) for i in range(iter, 0, -1): if N % i == 0: return N // i, i def main(): N = int(input()) input_list = list(map(int, input().split())) input_list.sort(reverse=True) # 对输入列表从大到小排序 m, n = factorization(N) result_list = [[0 for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)] # 构造二维数组,用来记录螺旋访问的结果 directions = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] # 记录四个移动方向,依次为右、下、左、上 direction_index = 0 # 记录当前方向 corr_x, corr_y = 0, -1 # 当前坐标 vertical = False # 是否在竖直方向上前进,否就是在水平方向上前进 vertical_count = m - 1 # 记录本次竖直方向上应访问的元素个数 horizontal_count = n # 记录本次水平方向上应访问的元素个数 count_line = 0 # 记录当前方向上访问过的元素个数 count = 0 # 记录已经访问过的元素总个数 while count < N: direction = directions[direction_index] corr_x += direction[0] # 前进一步 corr_y += direction[1] result_list[corr_x][corr_y] = input_list[count] # 螺旋赋值 count += 1 count_line += 1 # 记录数都加一 if vertical and count_line == vertical_count: # 判断在竖直方向是否达到尽头 vertical = False # 接下来是水平方向 direction_index = (direction_index + 1) % 4 # 下一个方向 vertical_count -= 1 # 下次的竖直方向上元素个数要减一 count_line = 0 # 下个方向上的元素个数置零 if not vertical and count_line == horizontal_count: # 如果是在水平方向上走到头了 vertical = True # 接下来走竖直方向 direction_index = (direction_index + 1) % 4 # 下一个方向 horizontal_count -= 1 # 下次的水平方向上的元素个数要减一 count_line = 0 # 下个方向的元素个数置零 for t in range(m): print(' '.join(list(map(str, result_list[t])))) main()
AC代码二:
def factorization(N): iter = int(N**0.5) for i in range(iter, 0, -1): if N % i == 0: return N // i, i def main(): N = int(input()) input_list = list(map(int, input().split())) input_list.sort(reverse=True) m, n = factorization(N) top, right, bottom, left = 0, n - 1, m - 1, 0 result_list = [[0 for i in range(n)] for i in range(m)] k = 0 while (top <= bottom) and (left <= right): for j in range(left, right): # 上边 result_list[top][j] = input_list[k] k += 1 for i in range(top, bottom + 1): # 右边 result_list[i][right] = input_list[k] k += 1 # 考虑排到最后或者为m*1的数组,下边和左边就不需要排列 if (top < bottom) and (left < right): for p in range(right - 1, left, -1): # 下边 result_list[bottom][p] = input_list[k] k += 1 for q in range(bottom, top, -1): # 左边 result_list[q][left] = input_list[k] k += 1 top += 1 right -= 1 bottom -= 1 left += 1 for t in range(m): print(' '.join(list(map(str, result_list[t])))) main()
4 参考
- PAT1050 螺旋矩阵:https://www.cnblogs.com/yfr2zaz/p/10386550.html
- PAT----1050 螺旋矩阵(两种解法):https://blog.csdn.net/qq_47534719/article/details/122233412
本文作者:Carpe_Diem2021
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/carpediem2021/p/16738581.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步