netty(5)高级篇-私有协议栈
来源:《Netty权威指南》 作者:李林峰
一、私有协议介绍
由于现代软件的复杂性,一个大型软件系统往往会被人为地拆分称为多个模块,另外随着移动互联网的兴起,网站的规模越来越大,业务功能越来越多,往往需要集群和分布式部署。模块之间的通信就需要进行跨节点通信。
传统的Java应用中节点通信的常用方式:
- rmi远程服务调用
- Java Socket + Java序列化
- RPC框架 Thrift、Apache的Avro等
- 利用标准的公有协议进行跨节点调用,例如HTTP+XML,Restful+JSON或WebService
下面使用Netty设计私有协议
除了链路层的物理连接外,还需要对请求和响应消息进行编解码。 在请求和应答之外,还需要控制和管理类指令,例如链路建立的握手信息,链路检测的心跳信息。这些功能组合到一起后,就会形成私有协议。
- 每个Netty节点(Netty进程)之间建立长连接,使用Netty协议进行通信。
- Netty节点没有客户端和服务端的区别,谁首先发起连接,谁就是客户端。
1. 网络拓扑图:

2. 协议栈功能描述:
- 基于Netty的NIO通信框架,提供高性能的异步通信能力;
- 提供消息的编解码框架,实现POJO的序列化和反序列化
- 提供基于IP地址的白名单接入认证机制;
- 链路的有效性校验机制;
- 链路的断线重连机制;
3. 通信模型:
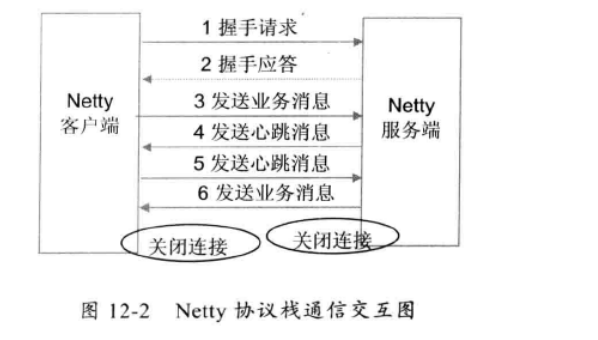
具体步骤:
- Netty协议栈客户端发送握手请求信息,携带节点ID等有效身份认证信息;
- Netty协议服务端对握手请求消息进行合法性校验,包括节点ID有效性校验、节点重复登录校验和IP地址合法性校验,校验通过后,返回登录成功的握手应答消息;
- 链路建立成功之后,客户端发送业务消息;
- 链路成功之后,服务端发送心跳消息;
- 链路建立成功之后,客户端发送心跳消息;
- 链路建立成功之后,服务端发送业务消息;
- 服务端退出时,服务端关闭连接,客户端感知对方关闭连接后,被动关闭客户端连接。
4. 消息定义
类似于http协议,消息分为消息头和消息体。其中消息体是一个Object类型,消息头则如下所示:
| 名称 | 类型 | 长度 | 描述 |
| length | 整型 int | 32 | 消息长度,整个消息,包括消息头和消息体 |
| sessionId | 长整型long | 64 | 集群节点内全局唯一,由会话ID生成器生成 |
| type | Byte | 8 |
0: 表示请求消息 1: 业务响应消息 2: 业务ONE WAY消息(即是请求又是响应消息) 3: 握手请求消息 4: 握手应答消息 5: 心跳请求消息 6: 心跳应答消息 |
| priority | Byte | 8 | 消息优先级: 0-255 |
| attachment | Map<String,Object> | 变长 | 可选字段,用于扩展消息头 |
5. 支持的字段类型:

6. Netty协议的编解码规范
编码规范:
(1) crcCode: java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(int value),如果采用其它缓存区实现,必须与其等价
(2) length: java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(int value),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(3) sessionID: java.nio.ByteBuffer.putLong(long value),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(4) type: java.nio.ByteBuffer.put(byte b),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(5) priority: java.nio.ByteBuffer.put(byte b),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(6) attachment: 如果长度为0,表示没有可选附件,则将长度编码为0,即java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(0),如果大于0,表示有附件需要编码,具体规则如下:
首先对附件的个数进行编码,java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(attachment.size());
然后对Key进行编码,先编码长度,然后再将它转换成byte数组之后编码内容,具体代码如下:
String key = null; byte[] value = null; for (Map.Entry<String, Object> param: attachment:entrySet()) { key = param.getKey(); buffer.writeString(key); value = marshaller.writeObject(param.getValue()); buffer.writeBinary(value); } key = null; value = null;
(7) body的编码: 通过JBoss Marshalling将其序列化为byte数组,然后调用java.nio.ByteBuffer.put(byte[] src);将其写入ByteBuffer缓冲区中。
在所有的内容都编码完成之后更新消息头的length字段。
解码规范:
(1) crcCode: java.nio.ByteBuffer.getInt()获取校验码字段,如果采用其它缓存区实现,必须与其等价
(2) length: java.nio.ByteBuffer.getInt()获取Netty消息的长度,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(3) sessionID: java.nio.ByteBuffer.getLong()获取会话ID,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(4) type: java.nio.ByteBuffer.get()获取消息类型,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(5) priority: java.nio.ByteBuffer.get()获取消息优先级,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
(6) attachment: 它的解码规则为-首先创建一个新的attachment对象,调用java.nio.ByteBuffer.getInt()获取附件的长度,如果为0,说明附件为空,解码结束,解析解消息体,否则,根据长度通过for循环进行解码。
(7) body: 使用JBoss marshaller对其进行解码
7. 链路的建立
不区分客户端和服务端:如果A节点需要B节点的服务,但是A和B之间还没有建立物理链路,则由调用方主动发起连接,此时调用方为客户端,被调用方为服务端。
使用简单的黑白名单进行认证,实际环境中,应该使用密钥,用户名密码等方式。
客户端发送请求消息:
- 消息头的type字段为3;
- 可选附件个数为0;
- 消息体为空;
- 握手消息的长度为22个字节;
服务端接收到握手请求消息,如果IP校验通过,返回握手成功应答给客户端,应用层链路建立成功。握手应答消息:
- 消息头type为4
- 可选附件个数为0
- 消息体为byte类型的结果,"0"表示认证成功,"-1"表示认证失败。
链路成功建立后,客户端和服务端就可以相互发送业务消息了。
8. 链路的关闭
由于采用长连接通信,正常的业务运行期间,双方通过心跳和业务消息维持链路,任何一方不需要主动关闭连接。
但是,在以下情况下,客户端和服务端需要关闭连接。
(1) 当对方宕机或者重启时,会主动释放链路,另一方读取到操作系统的通知信号,得到对方REST链路,需要关闭连接,释放自身的句柄等资源。由于采用TCP全双工通信,通信双方都需要关闭连接,释放资源;
(2) 消息在读写过程中,发生了I/O异常,需要主动关闭连接;
(3) 心跳消息读写过程中发生了I/O异常,需要主动关闭连接;
(4) 心跳超时,需要主动关闭连接;
(5) 发生编码异常等不可恢复的错误时,需要主动关闭连接;
9. 可靠性设计
网络环境是恶劣的。意外无法避免,需要在出现意外的时候正常工作或者说是恢复,需要可靠性设计的保证。
(1) 心跳机制
在凌晨等业务低谷期,如果发生网络闪断、连接被Hang住等网络问题,由于没有业务消息,应用进程很难发现。到了白天业务高峰期,会发生大量的网络通信失败,严重的会导致一段时间进程内无法处理业务消息。
为了解决这个问题,在网络空闲的时候采用心跳机制来检测链路的互通性,一旦发现了网络故障,立即关闭链路,主动重连。
设计思路:
- 当网络处于空闲时间达到了T(连续周期T没有读写消息)时,客户端主动发送Ping心跳消息给服务端;
- 如果在下一个周期T到来时客户端没有收到对方发送的Pong心跳应答消息或者读取到服务端发送的其他业务消息,则心跳失败计数器+1
- 每当客户端接收到服务的业务消息或者Pong应答消息时,将心跳失败计数器清0;连续N次没有接收到服务端的Pong消息或者业务消息,则关闭链路,间隔INTERVAL时间后发起重连操作;
- 服务端网络空闲状态持续时间达到T后,服务器端将心跳失败计数器+1;只要接收到客户端发送的Ping消息或者其他业务消息,计数器清0
- 服务器端连续N次没有接收到客户端的Ping消息或者其他业务消息,则关闭链路,释放资源,等待客户端重连。
(2) 重连机制
如果链路中断,等待INTERVAL时间后,由客户端发起重连操作,如果重连失败,间隔周期INTERVAL之后再继续重连。
无论什么场景下的重连失败,客户端必须保证自身资源被成功及时释放
重连失败,需要记录异常堆栈信息,方便问题定位。
(3) 重复登录保护
客户端握手成功之后,链路处于正常状态下,不允许客户端重复登录,以防止客户端在异常状态下反复重连导致句柄资源被耗尽。
server在接收到握手消息后,首先进行ip合法性校验,如果成功,则在缓存的地址表中查看客户端是否已经登录,如果已经登录,则拒绝重复登录,返回错误码-1,同时关闭链路,并且在服务端日志中打印错误信息。
为了防止由服务端和客户端对链路状态理解不一致的问题,当服务端连续N次心跳超时之后需要主动关闭链路,同时清空该客户端的缓存信息,保证后续的客户端可以重连。
(5) 消息缓存重发
无论是客户端还是服务端,在发生链路中断之后,恢复链路之前,缓存在消息队列的待发送的消息不能丢失。同时考虑到内存溢出风险,应该在消息缓存队列中设置上限。
10 可扩展性设计
Netty协议栈需要具备一定的扩展能力,例如统一的消息拦截、接口日志、安全、加密解密等可以被方便地添加和删除,推荐使用Servelt的FilterChain机制,考虑到性能因素,不推荐AOP。
二、Netty协议栈开发
2.1 数据结构定义
不管心跳消息、握手请求和握手应答消息都可以用NettyMessage来定义,只是type不同而已。
消息头:
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月14日 */ public final class Header { private int crcCode = 0xabef0101; private int length;// 消息长度 private long sessionID;// 会话ID private byte type;// 消息类型 private byte priority;// 消息优先级 private Map<String, Object> attachment = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // 附件 /** * @return the crcCode */ public final int getCrcCode() { return crcCode; } /** * @param crcCode the crcCode to set */ public final void setCrcCode(int crcCode) { this.crcCode = crcCode; } /** * @return the length */ public final int getLength() { return length; } /** * @param length the length to set */ public final void setLength(int length) { this.length = length; } /** * @return the sessionID */ public final long getSessionID() { return sessionID; } /** * @param sessionID the sessionID to set */ public final void setSessionID(long sessionID) { this.sessionID = sessionID; } /** * @return the type */ public final byte getType() { return type; } /** * @param type the type to set */ public final void setType(byte type) { this.type = type; } /** * @return the priority */ public final byte getPriority() { return priority; } /** * @param priority the priority to set */ public final void setPriority(byte priority) { this.priority = priority; } /** * @return the attachment */ public final Map<String, Object> getAttachment() { return attachment; } /** * @param attachment the attachment to set */ public final void setAttachment(Map<String, Object> attachment) { this.attachment = attachment; } /* * (non-Javadoc) * * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString() { return "Header [crcCode=" + crcCode + ", length=" + length + ", sessionID=" + sessionID + ", type=" + type + ", priority=" + priority + ", attachment=" + attachment + "]"; } }
消息:
/** * @author lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月14日 */ public final class NettyMessage { private Header header; private Object body; /** * @return the header */ public final Header getHeader() { return header; } /** * @param header the header to set */ public final void setHeader(Header header) { this.header = header; } /** * @return the body */ public final Object getBody() { return body; } /** * @param body the body to set */ public final void setBody(Object body) { this.body = body; } /* * (non-Javadoc) * * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString() { return "NettyMessage [header=" + header + "]"; } }
2.2 消息编解码
由于依赖于JBoss Marshalling...,添加maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.jboss.marshalling</groupId> <artifactId>jboss-marshalling</artifactId> <version>1.4.10.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.jboss.marshalling</groupId> <artifactId>jboss-marshalling-serial</artifactId> <version>1.4.10.Final</version> </dependency>
JBossMarshallingFactory:
import org.jboss.marshalling.*; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author Administrator * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public final class MarshallingCodecFactory { /** * 创建Jboss Marshaller * * @return * @throws IOException */ protected static Marshaller buildMarshalling() throws IOException { final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling .getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial"); final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration(); configuration.setVersion(5); Marshaller marshaller = marshallerFactory .createMarshaller(configuration); return marshaller; } /** * 创建Jboss Unmarshaller * * @return * @throws IOException */ protected static Unmarshaller buildUnMarshalling() throws IOException { final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling .getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial"); final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration(); configuration.setVersion(5); final Unmarshaller unmarshaller = marshallerFactory .createUnmarshaller(configuration); return unmarshaller; } }
增加JBossMarshalling序列化对象->ByteBuf工具
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler.Sharable; import org.jboss.marshalling.Marshaller; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月14日 */ @Sharable public class MarshallingEncoder { private static final byte[] LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER = new byte[4]; Marshaller marshaller; public MarshallingEncoder() throws IOException { marshaller = MarshallingCodecFactory.buildMarshalling(); } // 使用marshall对Object进行编码,并且写入bytebuf... protected void encode(Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { try { //1. 获取写入位置 int lengthPos = out.writerIndex(); //2. 先写入4个bytes,用于记录Object对象编码后长度 out.writeBytes(LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER); //3. 使用代理对象,防止marshaller写完之后关闭byte buf ChannelBufferByteOutput output = new ChannelBufferByteOutput(out); //4. 开始使用marshaller往bytebuf中编码 marshaller.start(output); marshaller.writeObject(msg); //5. 结束编码 marshaller.finish(); //6. 设置对象长度 out.setInt(lengthPos, out.writerIndex() - lengthPos - 4); } finally { marshaller.close(); } } }
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import org.jboss.marshalling.ByteOutput; import java.io.IOException; /** * {@link ByteOutput} implementation which writes the data to a {@link ByteBuf} * * */ class ChannelBufferByteOutput implements ByteOutput { private final ByteBuf buffer; /** * Create a new instance which use the given {@link ByteBuf} */ public ChannelBufferByteOutput(ByteBuf buffer) { this.buffer = buffer; } @Override public void close() throws IOException { // Nothing to do } @Override public void flush() throws IOException { // nothing to do } @Override public void write(int b) throws IOException { buffer.writeByte(b); } @Override public void write(byte[] bytes) throws IOException { buffer.writeBytes(bytes); } @Override public void write(byte[] bytes, int srcIndex, int length) throws IOException { buffer.writeBytes(bytes, srcIndex, length); } /** * Return the {@link ByteBuf} which contains the written content * */ ByteBuf getBuffer() { return buffer; } }
增加JBossMarshalling反序列化对象<-ByteBuf工具
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import org.jboss.marshalling.ByteInput; import org.jboss.marshalling.Unmarshaller; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.StreamCorruptedException; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月14日 */ public class MarshallingDecoder { private final Unmarshaller unmarshaller; /** * Creates a new decoder whose maximum object size is {@code 1048576} bytes. * If the size of the received object is greater than {@code 1048576} bytes, * a {@link StreamCorruptedException} will be raised. * * @throws IOException */ public MarshallingDecoder() throws IOException { unmarshaller = MarshallingCodecFactory.buildUnMarshalling(); } protected Object decode(ByteBuf in) throws Exception { //1. 读取第一个4bytes,里面放置的是object对象的byte长度 int objectSize = in.readInt(); ByteBuf buf = in.slice(in.readerIndex(), objectSize); //2 . 使用bytebuf的代理类 ByteInput input = new ChannelBufferByteInput(buf); try { //3. 开始解码 unmarshaller.start(input); Object obj = unmarshaller.readObject(); unmarshaller.finish(); //4. 读完之后设置读取的位置 in.readerIndex(in.readerIndex() + objectSize); return obj; } finally { unmarshaller.close(); } } }
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import org.jboss.marshalling.ByteInput; import java.io.IOException; /** * {@link ByteInput} implementation which reads its data from a {@link ByteBuf} */ class ChannelBufferByteInput implements ByteInput { private final ByteBuf buffer; public ChannelBufferByteInput(ByteBuf buffer) { this.buffer = buffer; } @Override public void close() throws IOException { // nothing to do } @Override public int available() throws IOException { return buffer.readableBytes(); } @Override public int read() throws IOException { if (buffer.isReadable()) { return buffer.readByte() & 0xff; } return -1; } @Override public int read(byte[] array) throws IOException { return read(array, 0, array.length); } @Override public int read(byte[] dst, int dstIndex, int length) throws IOException { int available = available(); if (available == 0) { return -1; } length = Math.min(available, length); buffer.readBytes(dst, dstIndex, length); return length; } @Override public long skip(long bytes) throws IOException { int readable = buffer.readableBytes(); if (readable < bytes) { bytes = readable; } buffer.readerIndex((int) (buffer.readerIndex() + bytes)); return bytes; } }
下面根据上述所说的进行对消息编解码:
import demo.protocol.netty.struct.NettyMessage; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Map; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/19. */ public class NettyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<NettyMessage> { MarshallingEncoder marshallingEncoder; public NettyMessageEncoder() throws IOException { this.marshallingEncoder = new MarshallingEncoder(); } @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, NettyMessage msg, ByteBuf sendBuf) throws Exception { if (null == msg || null == msg.getHeader()) { throw new Exception("The encode message is null"); } //---写入crcCode--- sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getCrcCode())); //---写入length--- sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getLength())); //---写入sessionId--- sendBuf.writeLong((msg.getHeader().getSessionID())); //---写入type--- sendBuf.writeByte((msg.getHeader().getType())); //---写入priority--- sendBuf.writeByte((msg.getHeader().getPriority())); //---写入附件大小--- sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getAttachment().size())); String key = null; byte[] keyArray = null; Object value = null; for (Map.Entry<String, Object> param : msg.getHeader().getAttachment() .entrySet()) { key = param.getKey(); keyArray = key.getBytes("UTF-8"); sendBuf.writeInt(keyArray.length); sendBuf.writeBytes(keyArray); value = param.getValue(); // marshallingEncoder.encode(value, sendBuf); } // for gc key = null; keyArray = null; value = null; if (msg.getBody() != null) { marshallingEncoder.encode(msg.getBody(), sendBuf); } else sendBuf.writeInt(0); // 之前写了crcCode 4bytes,除去crcCode和length 8bytes即为更新之后的字节 sendBuf.setInt(4, sendBuf.readableBytes() - 8); } }
import demo.protocol.netty.struct.Header; import demo.protocol.netty.struct.NettyMessage; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public class NettyMessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder { MarshallingDecoder marshallingDecoder; public NettyMessageDecoder(int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength) throws IOException { super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength); marshallingDecoder = new MarshallingDecoder(); } @Override protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception { ByteBuf frame = (ByteBuf) super.decode(ctx, in); if (frame == null) { return null; } NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage(); Header header = new Header(); header.setCrcCode(frame.readInt()); header.setLength(frame.readInt()); header.setSessionID(frame.readLong()); header.setType(frame.readByte()); header.setPriority(frame.readByte()); int size = frame.readInt(); if (size > 0) { Map<String, Object> attch = new HashMap<String, Object>(size); int keySize = 0; byte[] keyArray = null; String key = null; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { keySize = frame.readInt(); keyArray = new byte[keySize]; frame.readBytes(keyArray); key = new String(keyArray, "UTF-8"); attch.put(key, marshallingDecoder.decode(frame)); } keyArray = null; key = null; header.setAttachment(attch); } if (frame.readableBytes() > 4) { message.setBody(marshallingDecoder.decode(frame)); } message.setHeader(header); return message; } }
关键在于解码器继承了LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,三个参数:
ch.pipeline().addLast( new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
第一个参数:1024*1024: 最大长度
第二个参数: 从第4个bytes开始表示是长度
第三个参数: 有4个bytes的长度表示是长度
2.3 握手和安全认证
Netty的机制大多是基于Handler链。
client端在通道激活时构建login请求:
/** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public class LoginAuthRespHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private final static Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(LoginAuthRespHandler.class); /** * 本地缓存 */ private Map<String, Boolean> nodeCheck = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>(); private String[] whitekList = {"127.0.0.1", "192.168.1.104"}; /** * Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#fireChannelRead(Object)} to forward to * the next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}. * <p> * Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior. */ @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg; // 如果是握手请求消息,处理,其它消息透传 if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_REQ .value()) { String nodeIndex = ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString(); NettyMessage loginResp = null; // 重复登陆,拒绝 if (nodeCheck.containsKey(nodeIndex)) { loginResp = buildResponse((byte) -1); } else { InetSocketAddress address = (InetSocketAddress) ctx.channel() .remoteAddress(); String ip = address.getAddress().getHostAddress(); boolean isOK = false; for (String WIP : whitekList) { if (WIP.equals(ip)) { isOK = true; break; } } loginResp = isOK ? buildResponse((byte) 0) : buildResponse((byte) -1); if (isOK) nodeCheck.put(nodeIndex, true); } LOG.info("The login response is : " + loginResp + " body [" + loginResp.getBody() + "]"); ctx.writeAndFlush(loginResp); } else { ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } } private NettyMessage buildResponse(byte result) { NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage(); Header header = new Header(); header.setType(MessageType.LOGIN_RESP.value()); message.setHeader(header); message.setBody(result); return message; } public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); nodeCheck.remove(ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString());// 删除缓存 ctx.close(); ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause); } }
server端判断是否是login请求,并对ip进行验证:
/** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public class LoginAuthReqHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(LoginAuthReqHandler.class); /** * Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#fireChannelActive()} to forward to the * next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}. * <p/> * Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior. */ @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.writeAndFlush(buildLoginReq()); } /** * Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#fireChannelRead(Object)} to forward to * the next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}. * <p/> * Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior. */ @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg; // 如果是握手应答消息,需要判断是否认证成功 if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_RESP .value()) { byte loginResult = (byte) message.getBody(); if (loginResult != (byte) 0) { // 握手失败,关闭连接 ctx.close(); } else { LOG.info("Login is ok : " + message); ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } } else //调用下一个channel链.. ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } /** * 构建登录请求 */ private NettyMessage buildLoginReq() { NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage(); Header header = new Header(); header.setType(MessageType.LOGIN_REQ.value()); message.setHeader(header); return message; } public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause); } }
2.4 心跳机制检测
握手成功之后,由客户端主动发送心跳消息,服务端接收到心跳消息之后,返回应答,由于心跳消息的目的是为了检测链路的可用性,因此不需要携带消息体。
/** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public class HeartBeatReqHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(HeartBeatReqHandler.class); //使用定时任务发送 private volatile ScheduledFuture<?> heartBeat; @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg; // 当握手成功后,Login响应向下透传,主动发送心跳消息 if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_RESP .value()) { //NioEventLoop是一个Schedule,因此支持定时器的执行,创建心跳计时器 heartBeat = ctx.executor().scheduleAtFixedRate( new HeartBeatReqHandler.HeartBeatTask(ctx), 0, 5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } else if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP .value()) { LOG.info("Client receive server heart beat message : ---> " + message); } else ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } //Ping消息任务类 private class HeartBeatTask implements Runnable { private final ChannelHandlerContext ctx; public HeartBeatTask(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { this.ctx = ctx; } @Override public void run() { NettyMessage heatBeat = buildHeatBeat(); LOG.info("Client send heart beat messsage to server : ---> " + heatBeat); ctx.writeAndFlush(heatBeat); } private NettyMessage buildHeatBeat() { NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage(); Header header = new Header(); header.setType(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ.value()); message.setHeader(header); return message; } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); if (heartBeat != null) { heartBeat.cancel(true); heartBeat = null; } ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause); } }
import demo.protocol.netty.MessageType; import demo.protocol.netty.struct.Header; import demo.protocol.netty.struct.NettyMessage; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public class HeartBeatRespHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(HeartBeatRespHandler.class); @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg; // 返回心跳应答消息 if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ .value()) { LOG.info("Receive client heart beat message : ---> " + message); NettyMessage heartBeat = buildHeatBeat(); LOG.info("Send heart beat response message to client : ---> " + heartBeat); ctx.writeAndFlush(heartBeat); } else ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } private NettyMessage buildHeatBeat() { NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage(); Header header = new Header(); header.setType(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP.value()); message.setHeader(header); return message; } }
心跳超时的机制非常简单,直接利用Netty的ReadTimeoutHandler进行实现,当一定周期内(50s)没有接收到任何对方消息时,需要主动关闭链路。如果是客户端,则重新发起连接,如果是服务端,则释放资源,清除客户端登录缓存信息,等待服务器端重连。
2.5 断线重连机制
在client感知到断连事件之后,释放资源,重新发起连接,具体代码如以下部分

首先监听网络断连事件,如果Channel关闭,则执行后续的重连任务,通过Bootstrap重新发起连接,客户端挂在closeFuture上监听链路关闭信号,一旦关闭,则创建定时器,重连。
服务端在监听到断连事件后,还需要清空缓存中的登录认证注册信息,以保证后续客户端可以正常重连。
2.6 客户端代码
public final class NettyConstant { public static final String REMOTEIP = "127.0.0.1"; public static final int PORT = 8080; public static final int LOCAL_PORT = 12088; public static final String LOCALIP = "127.0.0.1"; }
import demo.protocol.netty.NettyConstant; import demo.protocol.netty.codec.NettyMessageDecoder; import demo.protocol.netty.codec.NettyMessageEncoder; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.timeout.ReadTimeoutHandler; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public class NettyClient { private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(NettyClient.class); private ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors .newScheduledThreadPool(1); EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception { // 配置客户端NIO线程组 try { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast( new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4)); ch.pipeline().addLast("MessageEncoder", new NettyMessageEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler", new ReadTimeoutHandler(50)); ch.pipeline().addLast("LoginAuthHandler", new LoginAuthReqHandler()); ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler", new HeartBeatReqHandler()); } }); // 发起异步连接操作 ChannelFuture future = b.connect( new InetSocketAddress(host, port), new InetSocketAddress(NettyConstant.LOCALIP, NettyConstant.LOCAL_PORT)).sync(); // 当对应的channel关闭的时候,就会返回对应的channel。 // Returns the ChannelFuture which will be notified when this channel is closed. This method always returns the same future instance. future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { // 所有资源释放完成之后,清空资源,再次发起重连操作 executor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); try { connect(NettyConstant.PORT, NettyConstant.REMOTEIP);// 发起重连操作 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } } /** * @param args * @throws Exception */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { new NettyClient().connect(NettyConstant.PORT, NettyConstant.REMOTEIP); } }
2.7 服务端
import demo.protocol.netty.NettyConstant; import demo.protocol.netty.codec.NettyMessageDecoder; import demo.protocol.netty.codec.NettyMessageEncoder; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel; import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler; import io.netty.handler.timeout.ReadTimeoutHandler; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月15日 */ public class NettyServer { private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(NettyServer.class); public void bind() throws Exception { // 配置服务端的NIO线程组 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100) .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws IOException { ch.pipeline().addLast( new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyMessageEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler", new ReadTimeoutHandler(50)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoginAuthRespHandler()); ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler", new HeartBeatRespHandler()); } }); // 绑定端口,同步等待成功 b.bind(NettyConstant.REMOTEIP, NettyConstant.PORT).sync(); LOG.info("Netty server start ok : " + (NettyConstant.REMOTEIP + " : " + NettyConstant.PORT)); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { new NettyServer().bind(); } }
三、测试
3.1 正常测试
启动server端,再启动client端
2016-12-19 20:52:23 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:44 - Receive client heart beat message : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=18, sessionID=0, type=5, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:23 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:47 - Send heart beat response message to client : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=0, sessionID=0, type=6, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:28 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:44 - Receive client heart beat message : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=18, sessionID=0, type=5, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:28 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:47 - Send heart beat response message to client : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=0, sessionID=0, type=6, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:33 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:44 - Receive client heart beat message : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=18, sessionID=0, type=5, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:33 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:47 - Send heart beat response message to client : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=0, sessionID=0, type=6, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:38 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:44 - Receive client heart beat message : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=18, sessionID=0, type=5, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:38 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:47 - Send heart beat response message to client : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=0, sessionID=0, type=6, priority=0, attachment={}]] 2016-12-19 20:52:43 INFO HeartBeatRespHandler:44 - Receive client heart beat message : ---> NettyMessage [header=Header [crcCode=-1410399999, length=18, sessionID=0, type=5, priority=0, attachment={}]]
3.2 服务端宕机重启
关闭服务端,client由于心跳,一直报错:
io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel$AnnotatedConnectException: Connection refused: no further information: /127.0.0.1:8080 at sun.nio.ch.SocketChannelImpl.checkConnect(Native Method) at sun.nio.ch.SocketChannelImpl.finishConnect(SocketChannelImpl.java:717) at io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel.doFinishConnect(NioSocketChannel.java:347) at io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioChannel$AbstractNioUnsafe.finishConnect(AbstractNioChannel.java:340) at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKey(NioEventLoop.java:627) at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeysOptimized(NioEventLoop.java:551) at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeys(NioEventLoop.java:465) at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.run(NioEventLoop.java:437) at io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor$5.run(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java:873) at io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultThreadFactory$DefaultRunnableDecorator.run(DefaultThreadFactory.java:144) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
需要测试信息如下:
(1) 客户端是否能够正常发起重连
(2) 重连之后,不再重连
(3) 断连期间,心跳定时器停止工作,不再发送心跳请求消息
(4) 服务器重启成功后,允许客户端重新登录
(5) 服务器重启成功之,客户端能够重连和握手成功
(6) 重连成功之后,双方的心跳能够正常护法
(7) 性能指标:重连期间,客户端能源得到了正常回收,不会导致句柄等资源泄露
使用vituralvm或者Jconsole工具,监控断连期间,cpu,线程,堆内存等资源占用正常.
重连之后,可以继续通信
3.3 客户端断开重连
也可以重新启动,且清空缓存信息,清空代码在LoginAuthHandler中的异常捕获部分:
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); nodeCheck.remove(ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString());// 删除缓存 ctx.close(); ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause); }



