C#基础-类
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp4
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 类的实例化:对象
Student stu = new Student();
// 给对象赋值
stu.name = "Joe";
stu.stuNo = 1001;
stu.age = 21;
Console.WriteLine("学生的姓名:" + stu.name);
Console.WriteLine("学生的学号:" + stu.stuNo);
Console.WriteLine("学生的年龄:" + stu.age);
}
}
// 定义类的两种方法,
//1/在源文件基础上添加
//2/单独在文件添加
public class Student
{
// 定义变量
public string name;
public int stuNo;
public int age;
}
}
定义类的两种方法,
1.在源文件基础上添加
public class Student
{
// 定义变量
public string name;
public int stuNo;
public int age;
}
2.单独在文件添加

类的实例化
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 类的实例化:对象
Student stu = new Student();
// 给对象赋值
stu.name = "Joe";
stu.stuNo = 1001;
stu.age = 21;
Console.WriteLine("学生的姓名:" + stu.name);
Console.WriteLine("学生的学号:" + stu.stuNo);
Console.WriteLine("学生的年龄:" + stu.age);
}
构造函数
构造函数分为无参构造函数与有参构造函数
新建一个Student类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Student
{
public string name;
public int stuno;
public int age;
//无参构造函数
public Student()
{
}
//有参构造函数
public Student(string _name,int _stuno,int _age)
{
name = _name;
stuno = _stuno;
age = _age;
}
}
}
无参构造函数与有参构造函数实例化
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student(); // 无参数的实例化对象
Student stu2 = new Student("Joe",1001,12); //有参数的实例化对象
Console.WriteLine("学生的姓名:" + stu2.name);
Console.WriteLine("学生的学号:" + stu2.stuno);
Console.WriteLine("学生的年龄:" + stu2.age);
}
}
}
this表示访问类本身的数据
//有参构造函数
public Student(string _name,int _stuno,int _age)
{
// this表示访问类本身的数据
this.name = _name;
this.stuno = _stuno;
this.age = _age;
}
调用类中方法
Program.cs
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
Console.WriteLine(stu.Say()); // 调用类中的方法
Console.WriteLine(stu.DoWork("老师")); //有参数
}
}
}
Student.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Student
{
public string Say()
{
string strResult = "这是说话的方法的返回值";
return strResult;
}
public string DoWork(string job)
{
string str = "我做的工作是:" + job;
return str;
}
}
}
调用类中的方法
类中方法
class Student
{
public string Say()
{
string strResult = "这是说话的方法的返回值";
return strResult;
}
public string DoWork(string job)
{
string str = "我做的工作是:" + job;
return str;
}
}
如何调用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
Console.WriteLine(stu.Say()); // 调用类中的方法
Console.WriteLine(stu.DoWork("老师")); //有参数
}
没有返回类型的方法
public void Do()
{
Console.WriteLine("无返回类型的方法");
}
在主程序中调用
stu.Do(); //没有返回类型
类的实例化应用,设计两个数的加减法
Program.cs
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Operater op = new Operater(89, 34);
Console.WriteLine(op.Add());
Console.WriteLine(op.Sub());
}
}
}
Operater.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Operater
{
public int num1;
public int num2;
public Operater(int _num1,int _num2)
{
this.num1 = _num1;
this.num2 = _num2;
}
public int Add()
{
return this.num1 + this.num2;
}
public int Sub()
{
return this.num1 - this.num2;
}
}
}
ref与out参数
ref的使用,ref为引用参数
新建一个Person类,在里面添加ChangeAge方法:
class Person
{
public void ChangeAge(ref int age) // ref为引用参数
{
age = age + 10;
}
}
主程序调用ChangeAge
引用原数据,输出结果为29;不加ref结果不变为19
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int myage = 19;
Person p = new Person();
p.ChangeAge(ref myage); //引用原数据,输出结果为29;不加ref结果不变为19
Console.WriteLine(myage);
}
out也是引用参数,使用时不需要赋值,直接调用即可
class Person
{
public void ChangeWeight(out double d)
{
d = 120;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double dweight;
Person p = new Person();
p.ChangeWeight(out dweight);
Console.WriteLine(dweight); //输出为120
}
params 表示是一个可变的数组
public void ShowInfo(string str,params int[] showages)
{
foreach(int i in showages)
{
Console.WriteLine("年龄:" + i);
}
}
int[] myages = {12,14,35,64,32,43};
Person p = new Person();
p.ShowInfo("",myages);
静态方法
static关键字
static表示静态字段,静态字段长期驻留在内存中
public class Person
{
// static表示静态的字段
public static string Country;
}
static静态直段Person可以直接访问
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person.Country = "China";
}
静态字段可以通过静态方法修改
public static void ChangeCountry()
{
Person.Country = "American";
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person.Country = "China";
Console.WriteLine(Person.Country); //输出"China"
Person.ChangeCountry();
Console.WriteLine(Person.Country); //输出"American"
}
在类的实例化方法中访问实例化字段用this关键字,静态字段直接访问
// 实例化字段
public string name;
public Person(string _name)
{
this.name = _name;
}
// 实例化方法
public void ShowInfo()
{
// name是实例化字段 Country是静态字段
Console.WriteLine("我的姓名:" + this.name + ",我来自:" + Country);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person.Country = "China";
Person p = new Person("Jake");
p.ShowInfo();
}
静态类
在静态类中不允许出现实例化方法和字段
public static class Operater
{
public static int result;
public static int Add(int a,int b)
{
result = a+b;
return result;
}
}
方法重载
重载
方法的重载必须要求方法的名字和返回类型必须一致
方法的参数个数或参数类型不一致
public class Person
{
// 充话费
public void Chong(string str,double d)
{
Console.WriteLine("给:" + str + "冲了:" + d);
}
// 重载
// 方法的重载必须要求方法的名字和返回类型必须一致
public void Chong(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine("给{0}充话费",str);
}
public void Chong(double d)
{
Console.WriteLine("冲了{0}钱", d);
}
}
主程序安照下面调用都是合理的
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 重载效果
Person p = new Person();
p.Chong(12);
p.Chong("小王");
p.Chong("晓明",89);
}
命名空间
1.在解决方案中新建一个项目Test
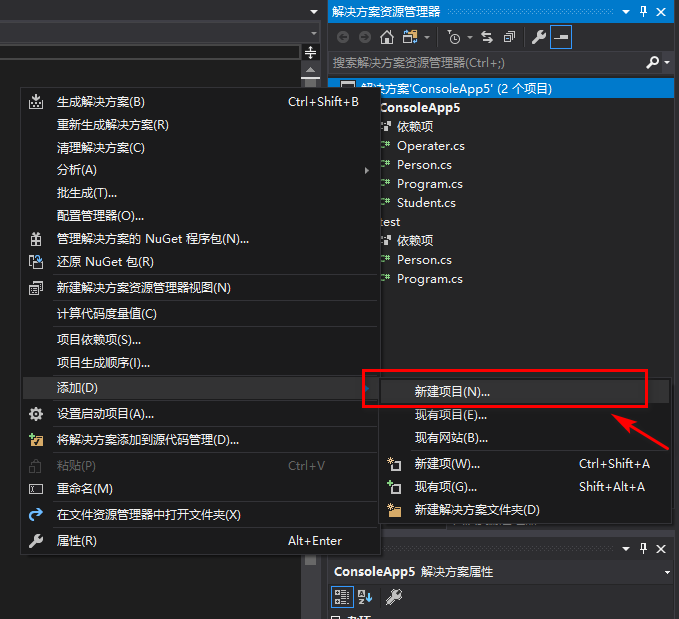
2.在新的项目中可以创建与第一个项目相同的类Person,两个类相同而不受影响,因为命名空间的作用,下面教你如何在Test项目中访问第一个命名空间的Person类
点击Test下的依赖,添加引用
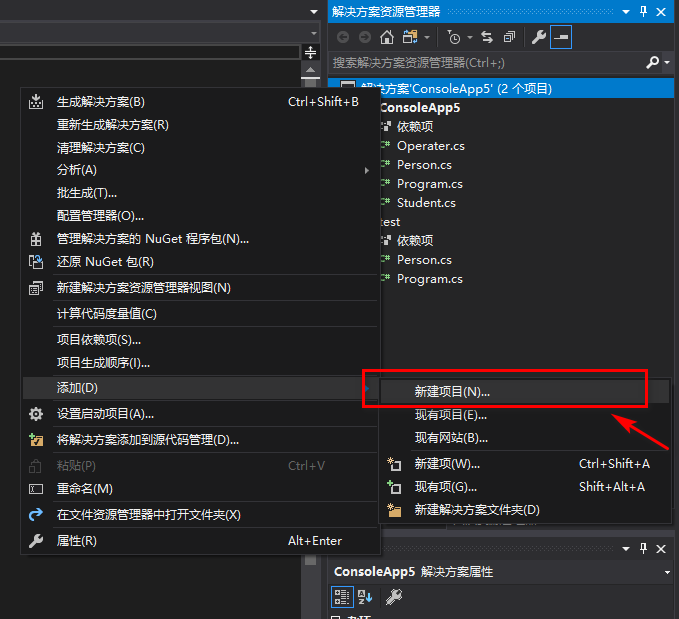
3.引用第一个项目文件
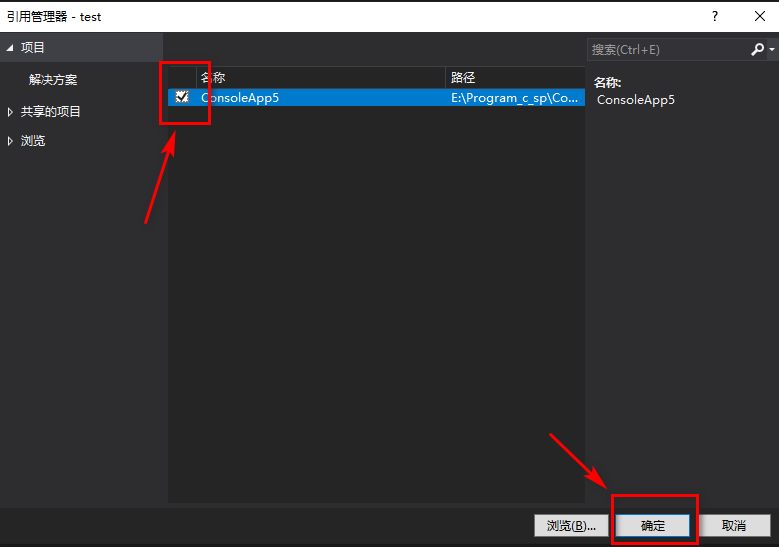
4.在Program.cs中添加上个项目的命名空间
using ConsoleApp5; // 添加引用的命名空间
5.然后在新的项目文件下就可以访问Person类了
访问权限需要注意一下!!!
public 可以被访问权限
private 不能被访问权限
internal 同一个命名空间下可以访问
using System;
using ConsoleApp5; // 添加引用的命名空间
namespace test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// public 可以被访问权限
// private 不能被访问权限
// internal 同一个命名空间下可以访问
ConsoleApp5.Person p = new ConsoleApp5.Person();
}
}
}


