vue源码之数据驱动 - 2.html模拟vue实现数据渲染
上一次我们简单实现了HTML模拟Vue实现数据渲染,发现还是有很多问题的,这次继续进行优化:
- 代码没有整合
- 只考虑了但属性,而Vue中大量使用了层级( {{ child.name }} )
- Vue使用的是 虚拟DOM
下面将通过这三个内容简单说明Vue的实现
页面节点:
<body> <div id="root"> <div> <p>{{ name }} - {{ message }}</p> </div> <div>{{ name }}</div> <div>{{ message }}</div> </div> </body>
一、封装代码
首先,我们先将之前代码进行封装
let rkuuohao = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/g;
function JGVue(options) {
// 内部数据使用下划线,只读数据使用$开头
this._data = options.data
this._el = options.el
// 准备工作( 准备模版 )
this._templateDOM = document.querySelector(this._el)
this._parent = this._templateDOM.parentNode
// 渲染工作
this.reder()
}
function compiler(tmpNode, data) {
let childNodes = tmpNode.childNodes
for (let i = 0; i < childNodes.length; i++) {
let type = childNodes[i].nodeType // 1 元素,3文本节点
if (type === 3) {
// 文本节点可以判断里面是否含有 {{}} 插值
let txt = childNodes[i].nodeValue // 该属性只有文本节点才有效
txt = txt.replace(rkuuohao, (_, g) => {
let key = g.trim()
let value = data[key]
return value
})
childNodes[i].nodeValue = txt
} else if (type === 1) {
// 元素,考虑有没有子元素
compiler(childNodes[i], data)
}
}
}
// 将模版和数据 => 得到html,加载到页面中
JGVue.prototype.reder = function () {
this.compiler()
}
// 编译,将模版与数据结合
JGVue.prototype.compiler = function () {
let realHTMLDOM = this._templateDOM.cloneNode(true) // 用 模版 拷贝得到一个 准DOM
compiler(realHTMLDOM, this._data)
this.update(realHTMLDOM)
}
// 将DOM对元素,放入页面中
JGVue.prototype.update = function (real) {
this._parent.replaceChild(real, document.querySelector("#root"))
}
let app = new JGVue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: 'zhou',
message: 'info'
}
})
二、实现层级访问
所谓层级,就是通过访问对象的形式( 数据为{info:{infoData:{name},txt:'测试'}},调用通过 {{ info.infoData.name }} {{ info.txt }} )来进行调用。
// 使用 ‘xxx.yyy.zzz’ 可以访问某一个对象 function getValueByPath(obj, path) { let paths = path.split('.') // ['xxx','yyy','zzz'] // 先得到 obj.xxx,再得到结果中的 yyy,再得到结果中的zzz // let res = null; // res = obj[paths[0]] // res = obj[paths[1]] // res = obj[paths[2]] let res = obj; let prop; while (prop = paths.shift()) { res = res[prop] } return res }
在封装中调用
function compiler(tmpNode, data) { let childNodes = tmpNode.childNodes for (let i = 0; i < childNodes.length; i++) { let type = childNodes[i].nodeType // 1 元素,3文本节点 if (type === 3) { // 文本节点可以判断里面是否含有 {{}} 插值 let txt = childNodes[i].nodeValue // 该属性只有文本节点才有效 txt = txt.replace(rkuuohao, (_, g) => { let path = g.trim() let value = getValueByPath(data, path) // 深度获取对象值 return value }) childNodes[i].nodeValue = txt } else if (type === 1) { // 元素,考虑有没有子元素 compiler(childNodes[i], data) } } }
在 compiler() 中调用 getValueByPath() ,传入数据data和路径path,实现深度取值。
三、使用虚拟DOM
使用虚拟DOM,那么虚拟DOM的结构又是什么样的呢?先简单说几种
<div / > => { tag: 'div' }
文本节点 => { tag: undefined, value: '文本节点' }
<div title="1" class="c" /> => { title: '1', class: 'c' }
<div><div/ ></div> => { tag: 'div', children:[ { tag: 'div' } ] }
下面针对几种情况实现虚拟DOM
首先创建节点类
class VNode { constructor(tag, data, value, type) { this.tag = tag && tag.toLowerCase() this.data = data this.value = value this.type = type this.children = [] } appendChild(vnode) { this.children.push(vnode) } }
使用递归遍历DOM元素,生成虚拟DOM
// Vue源码使用栈结构,使用栈存储父元素来实现递归生成 function getVNode(node) { let nodeType = node.nodeType let _vnode = null if (nodeType === 1) { // 元素 let nodeName = node.nodeName let attrs = node.attributes let _attrObj = {} for (let i = 0; i < attrs.length; i++) { _attrObj[attrs[i].nodeName] = attrs[i].nodeValue } _vnode = new VNode(nodeName, _attrObj, undefined, nodeType) // 考虑 node 的子元素 let childNodes = node.childNodes for (let i = 0; i < childNodes.length; i++) { _vnode.appendChild(getVNode(childNodes[i])) // 递归 } } else if (nodeType === 3) { // 文本 _vnode = new VNode(undefined, undefined, node.nodeValue) } return _vnode }
虚拟 DOM 转换为真正的 DOM
function parseVNode(vnode) { // 创建真实DOM let type = vnode.type if (type === 3) { return document.createTextNode(vnode.value) // 创建文本节点 } else if (type === 1) { let _node = document.createElement(vnode.tag) // 属性 let data = vnode.data Object.keys(data).forEach(key => { let attrName = key let attrValue = data[key] _node.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue) }) // 子元素 let children = vnode.children children.forEach(subvnode => { _node.appendChild(parseVNode(subvnode)); // 递归转换子元素 ( 虚拟DOM ) }) return _node } }
到这里,虚拟DOM已经实现,下面来测试
let root = document.querySelector("#root")
let vroot = getVNode(root)
console.log(vroot, 'vroot');
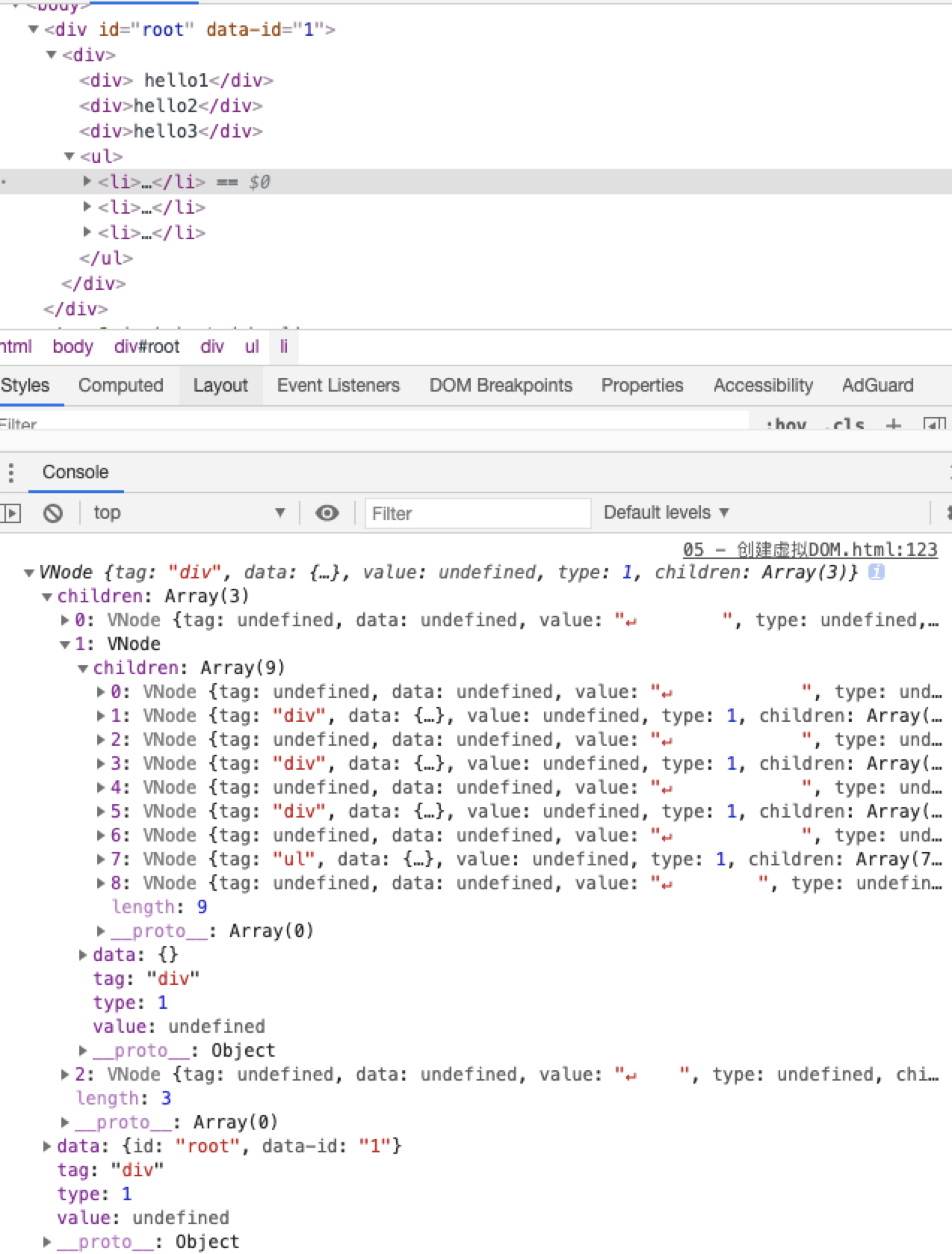
let dom = parseVNode(vroot)
console.log(dom);
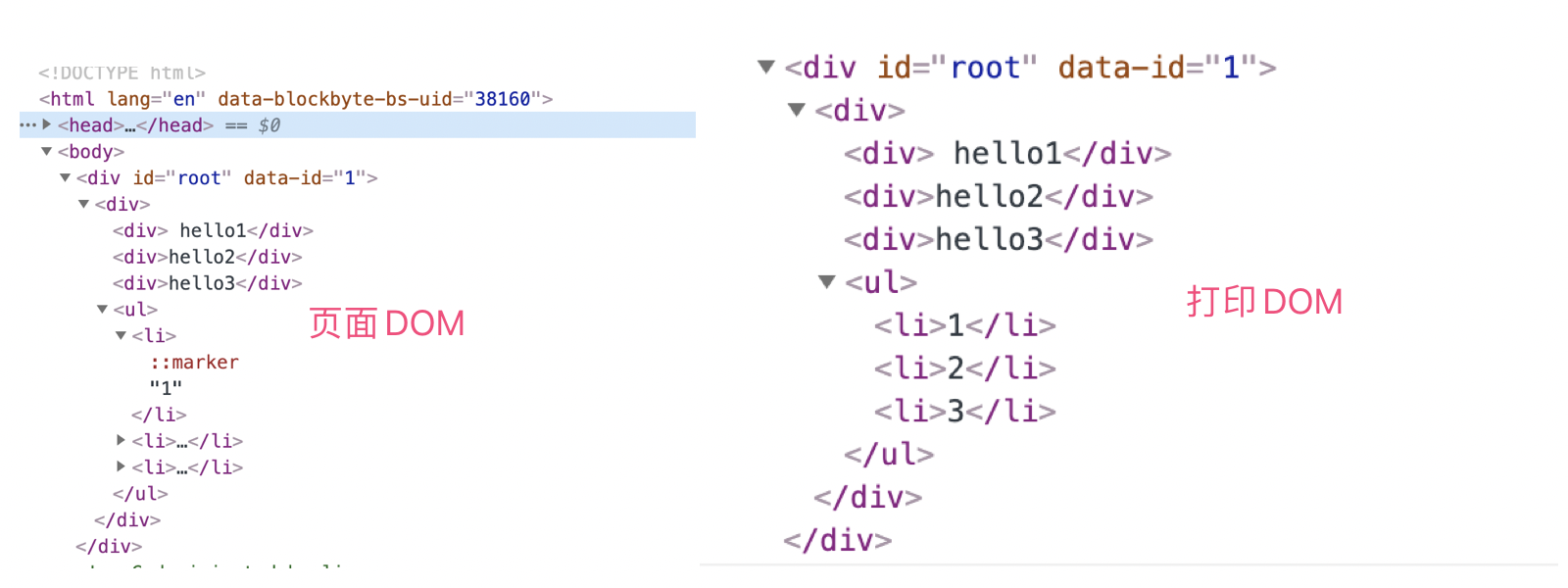
现在,我们说的三个问题已经完成了,下面将代码整合,附上完整代码
/******** 虚拟DOM - start *********/ class VNode { constructor(tag, data, value, type) { this.tag = tag && tag.toLowerCase() this.data = data this.value = value this.type = type this.children = [] } appendChild(vnode) { this.children.push(vnode) } } // 使用递归便利DOM元素,生成虚拟DOM // Vue源码使用栈结构,使用栈存储父元素来实现递归生成 function getVNode(node) { let nodeType = node.nodeType let _vnode = null if (nodeType === 1) { // 元素 let nodeName = node.nodeName let attrs = node.attributes let _attrObj = {} for (let i = 0; i < attrs.length; i++) { _attrObj[attrs[i].nodeName] = attrs[i].nodeValue } _vnode = new VNode(nodeName, _attrObj, undefined, nodeType) // 考虑 node 的子元素 let childNodes = node.childNodes for (let i = 0; i < childNodes.length; i++) { _vnode.appendChild(getVNode(childNodes[i])) // 递归 } } else if (nodeType === 3) { // 文本 _vnode = new VNode(undefined, undefined, node.nodeValue, nodeType) } return _vnode } // 将 vnode 转换为真正的 DOM function parseVNode(vnode) { // 创建真实DOM let type = vnode.type if (type === 3) { return document.createTextNode(vnode.value) // 创建文本节点 } else if (type === 1) { let _node = document.createElement(vnode.tag) // 属性 let data = vnode.data Object.keys(data).forEach(key => { let attrName = key let attrValue = data[key] _node.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue) }) // 子元素 let children = vnode.children children.forEach(subvnode => { _node.appendChild(parseVNode(subvnode)); // 递归转换子元素 ( 虚拟DOM ) }) return _node } } /******** 虚拟DOM - end *********/ let rkuohao = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/g; function JGVue(options) { // 内部数据使用下划线,只读数据使用$开头 this._data = options.data this._el = options.el // 准备工作( 准备模版 ) this._templateDOM = document.querySelector(this._el) this._parent = this._templateDOM.parentNode // 渲染工作 this.reder() } // 根据路径访问对象成员 function getValueByPath(obj, path) { let paths = path.split('.') let res = obj; let prop; while (prop = paths.shift()) { res = res[prop] } return res } function combine(vnode, data) { let _type = vnode.type let _data = vnode.data let _value = vnode.value let _tag = vnode.tag let _children = vnode.children let _vnode = null if (_type === 3) { // 文本 // 对文本处理 _value = _value.replace(rkuohao, (_, g) => { return getValueByPath(data, g.trim()) }) _vnode = new VNode(_tag, _data, _value, _type) } else if (_type === 1) { // 元素 _vnode = new VNode(_tag, _data, _value, _type) _children.forEach(_subvnode => _vnode.appendChild(combine(_subvnode, data))); } return _vnode } // 将模版和数据 => 得到html,加载到页面中 JGVue.prototype.reder = function () { this.compiler() } // 编译,将模版与数据结合 JGVue.prototype.compiler = function () { let ast = getVNode(this._templateDOM) let _tmp = combine(ast, this._data) this.update(_tmp) } // 将DOM对元素,放入页面中 JGVue.prototype.update = function (real) { let realDOM = parseVNode(real) this._parent.replaceChild(realDOM, document.querySelector("#root")) } let app = new JGVue({ el: '#root', data: { name: 'zhou', message: 'info' } })
注意:这里对“将虚拟DOM与数据结合”方法进行重新封装,并有 compiler 更名为 combine 。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号