排序算法与数据结构复习总结
查找
Arrays工具类中二分查找
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
时间复杂度
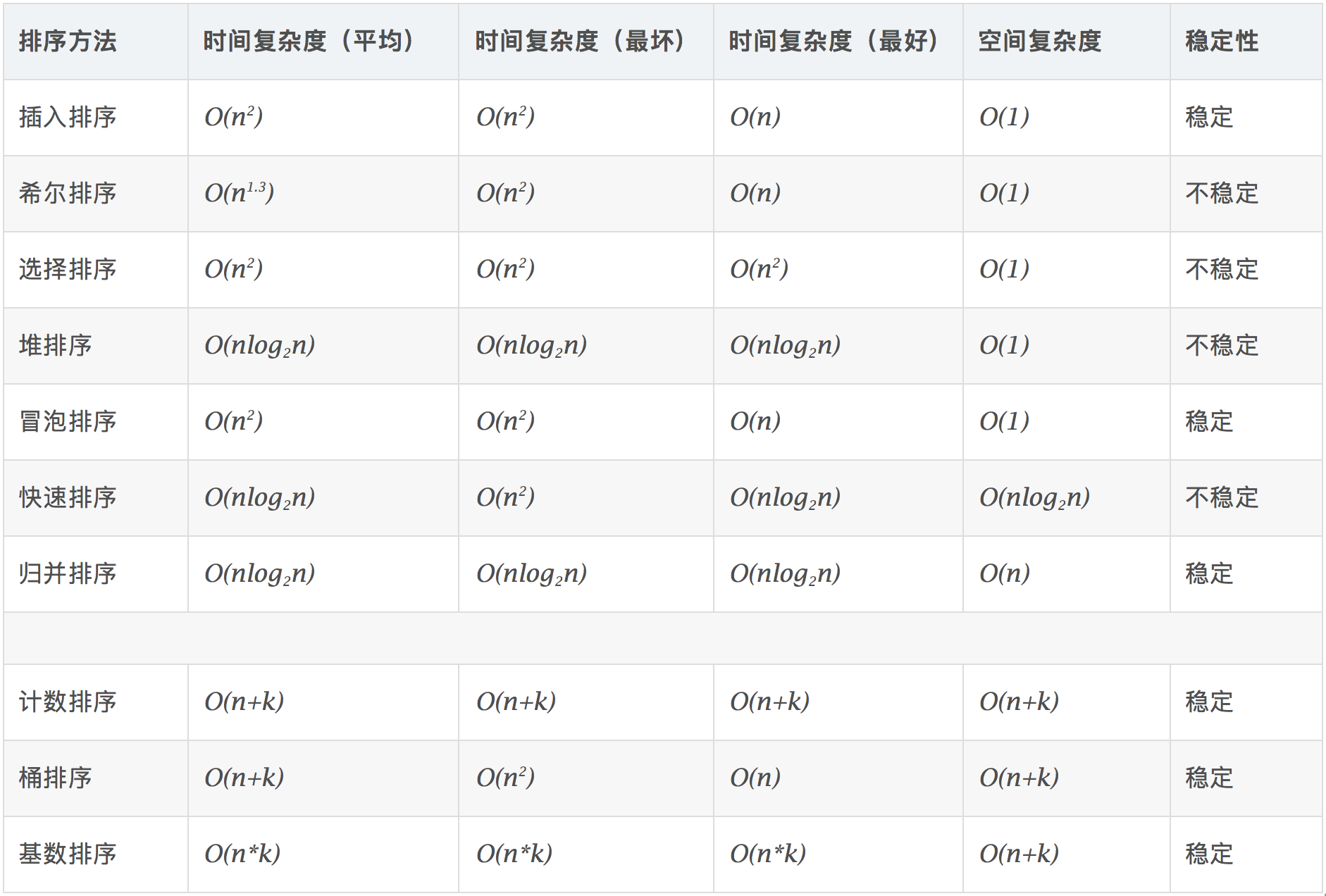
排序
冒泡排序
public static void bubbleSort(int arr[]) {
for(int i =0 ; i<arr.length-1 ; i++) {
for(int j=0 ; j<arr.length-1-i ; j++) {
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
选择排序
public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){
//需要比较的次数,数组长度减一
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++){
//先假设每次循环时,最小数的索引为i
int minIndex = i;
//每一个元素都和剩下的未排序的元素比较
for(int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++){
if(arr[j] < arr[minIndex]){//寻找最小数
minIndex = j;//将最小数的索引保存
}
}
//经过一轮循环,就可以找出第一个最小值的索引,然后把最小值放到i的位置
swap(arr, i, minIndex);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
插入排序
public class Insertion {
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
//将a[]按升序排列
int N=a.length;
for (int i=1;i<N;i++) {
//将a[i]插入到a[i-1],a[i-2],a[i-3]……之中
for(int j=i; j>0 && (a[j].compareTo(a[j-1])<0);j--) {
Comparable temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j-1];
a[j-1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
希尔排序
public void shellSort() {
int gap = array.length;
while (true) {
gap /= 2; //增量每次减半
for (int i = 0; i < gap; i++) {
for (int j = i + gap; j < array.length; j += gap) {
//这个循环里其实就是一个插入排序 int k = j - gap;
while (k >= 0 && array[k] > array[k+gap]) {
int temp = array[k];
array[k] = array[k+gap];
array[k + gap] = temp;
k -= gap;
}
}
}
if (gap == 1)
break;
}
}
归并排序
public static int[] mergeSort(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
if (l == h)
return new int[] { nums[l] };
int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;
int[] leftArr = mergeSort(nums, l, mid); //左有序数组
int[] rightArr = mergeSort(nums, mid + 1, h); //右有序数组
int[] newNum = new int[leftArr.length + rightArr.length]; //新有序数组
int m = 0, i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < leftArr.length && j < rightArr.length) {
newNum[m++] = leftArr[i] < rightArr[j] ? leftArr[i++] : rightArr[j++];
}
while (i < leftArr.length)
newNum[m++] = leftArr[i++];
while (j < rightArr.length)
newNum[m++] = rightArr[j++];
return newNum;
}
快速排序
public static int[] qsort(int arr[],int start,int end) {
int pivot = arr[start];
int i = start;
int j = end;
while (i<j) {
while ((i<j)&&(arr[j]>pivot)) {
j--;
}
while ((i<j)&&(arr[i]<pivot)) {
i++;
}
if ((arr[i]==arr[j])&&(i<j)) {
i++;
} else {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
if (i-1>start) arr=qsort(arr,start,i-1);
if (j+1<end) arr=qsort(arr,j+1,end);
return (arr);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = new int[]{3,3,3,7,9,122344,4656,34,34,4656,5,6,7,8,9,343,57765,23,12321};
int len = arr.length-1;
arr=qsort(arr,0,len);
for (int i:arr) {
System.out.print(i+"\t");
}
}
方式2
public <TextendsComparable<?superT>>
T[] quickSort(T[] targetArr,int start,int end)
{
int i=start+1 , j=end;
T key = targetArr[start];
SortUtil<T> sUtil=new SortUtil<T>();
if(start==end) return (targetArr);
/**
* 从i++和j--两个方向搜索不满足条件的值并交换
* 条件为:i++方向小于key,j--方向大于key
*/
while(true) {
while(targetArr[j].compareTo(key) > 0) j--;
while(targetArr[i].compareTo(key) < 0 && i<j) i++;
if(i>=j) break;
sUtil.swap(targetArr,i,j);
if(targetArr[i]==key) {
j--;
} else {
i++;
}
}
/*关键数据放到‘中间’*/
sUtil.swap(targetArr,start,j);
if(start<i-1) {
this.quickSort(targetArr,start,i-1);
}
if(j+1<end) {
this.quickSort(targetArr,j+1,end);
}
returntargetArr;
}
方式3
private<TextendsComparable<?superT>>
voidquickSort(T[]targetArr,intstart,intend) {
inti=start,j=end;
T key=targetArr[start];
while(i<j) {
/*按j--方向遍历目标数组,直到比key小的值为止*/
while(j>i&&targetArr[j].compareTo(key)>=0){
j--;
}
if(i<j) {
/*targetArr[i]已经保存在key中,可将后面的数填入*/
targetArr[i]=targetArr[j];
i++;
}
/*按i++方向遍历目标数组,直到比key大的值为止*/
while(i<j&&targetArr[i].compareTo(key)<=0)
/*此处一定要小于等于零,假设数组之内有一亿个1,0交替出现的话,而key的值又恰巧是1的话,那么这个小于等于的作用就会使下面的if语句少执行一亿次。*/
{
i++;
}
if(i<j) {
/*targetArr[j]已保存在targetArr[i]中,可将前面的值填入*/
targetArr[j]=targetArr[i];
j--;
}
}
/*此时i==j*/
targetArr[i]=key;//应加判断
/*递归调用,把key前面的完成排序*/
this.quickSort(targetArr,start,i-1);
/*递归调用,把key后面的完成排序*/
this.quickSort(targetArr,j+1,end);
//两个递归应加判断
}
堆排序
/**
* 选择排序-堆排序
* @param array 待排序数组
* @return 已排序数组
*/
public static int[] heapSort(int[] array) {
//这里元素的索引是从0开始的,所以最后一个非叶子结点array.length/2 - 1
for (int i = array.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(array, i, array.length); //调整堆
}
// 上述逻辑,建堆结束
// 下面,开始排序逻辑
for (int j = array.length - 1; j > 0; j--) {
// 元素交换,作用是去掉大顶堆
// 把大顶堆的根元素,放到数组的最后;换句话说,就是每一次的堆调整之后,都会有一个元素到达自己的最终位置
swap(array, 0, j);
// 元素交换之后,毫无疑问,最后一个元素无需再考虑排序问题了。
// 接下来我们需要排序的,就是已经去掉了部分元素的堆了,这也是为什么此方法放在循环里的原因
// 而这里,实质上是自上而下,自左向右进行调整的
adjustHeap(array, 0, j);
}
return array;
}
/**
* 整个堆排序最关键的地方
* @param array 待组堆
* @param i 起始结点
* @param length 堆的长度
*/
public static void adjustHeap(int[] array, int i, int length) {
// 先把当前元素取出来,因为当前元素可能要一直移动
int temp = array[i];
for (int k = 2 * i + 1; k < length; k = 2 * k + 1) { //2*i+1为左子树i的左子树(因为i是从0开始的),2*k+1为k的左子树
// 让k先指向子节点中最大的节点
if (k + 1 < length && array[k] < array[k + 1]) { //如果有右子树,并且右子树大于左子树
k++;
}
//如果发现结点(左右子结点)大于根结点,则进行值的交换
if (array[k] > temp) {
swap(array, i, k);
// 如果子节点更换了,那么,以子节点为根的子树会受到影响,所以,循环对子节点所在的树继续进行判断
i = k;
} else { //不用交换,直接终止循环
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 交换元素
* @param arr
* @param a 元素的下标
* @param b 元素的下标
*/
public static void swap(int[] arr, int a, int b) {
int temp = arr[a];
arr[a] = arr[b];
arr[b] = temp;
}
计数排序
//针对c数组的大小,优化过的计数排序
publicclassCountSort{
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
//排序的数组
int a[]={100,93,97,92,96,99,92,89,93,97,90,94,92,95};
int b[]=countSort(a);
for(inti:b){
System.out.print(i+"");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static int[] countSort(int[]a){
int b[] = new int[a.length];
int max = a[0],min = a[0];
for(int i:a){
if(i>max){
max=i;
}
if(i<min){
min=i;
}
}//这里k的大小是要排序的数组中,元素大小的极值差+1
int k=max-min+1;
int c[]=new int[k];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;++i){
c[a[i]-min]+=1;//优化过的地方,减小了数组c的大小
}
for(int i=1;i<c.length;++i){
c[i]=c[i]+c[i-1];
}
for(int i=a.length-1;i>=0;--i){
b[--c[a[i]-min]]=a[i];//按存取的方式取出c的元素
}
return b;
}
}
桶排序
public static void basket(int data[]) {
int n=data.length;
int bask[][]=new int[10][n];
int index[]=new int[10];
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
max=max>(Integer.toString(data[i]).length())?max:(Integer.toString(data[i]).length());
}
String str;
for(int i=max-1;i>=0;i--) {
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
str="";
if(Integer.toString(data[j]).length()<max) {
for(int k=0;k<max-Integer.toString(data[j]).length();k++){
str+="0";
}
str+=Integer.toString(data[j]);
bask[str.charAt(i)-'0'][index[str.charAt(i)-'0']++]=data[j];
}
int pos=0;
for(int j=0;j<10;j++) {
for(int k=0;k<index[j];k++) {
data[pos++]=bask[j][k];
}
}
for(intx=0;x<10;x++) index[x]=0;
}
}
基数排序
public class RadixSort
{
public static void sort(int[] number, int d) //d表示最大的数有多少位
{
intk = 0;
intn = 1;
intm = 1; //控制键值排序依据在哪一位
int[][]temp = newint[10][number.length]; //数组的第一维表示可能的余数0-9
int[]order = newint[10]; //数组order[i]用来表示该位是i的数的个数
while(m <= d)
{
for(inti = 0; i < number.length; i++)
{
intlsd = ((number[i] / n) % 10);
temp[lsd][order[lsd]] = number[i];
order[lsd]++;
}
for(inti = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if(order[i] != 0)
for(intj = 0; j < order[i]; j++)
{
number[k] = temp[i][j];
k++;
}
order[i] = 0;
}
n *= 10;
k = 0;
m++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[]data =
{73, 22, 93, 43, 55, 14, 28, 65, 39, 81, 33, 100};
RadixSort.sort(data, 3);
for(inti = 0; i < data.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(data[i] + "");
}
}
}
JDK DualPivotQuicksort双基准快速排序
时间复杂度
https://www.cnblogs.com/onepixel/articles/7674659.html
数据结构
栈的实现
链式实现
public class LinkedStack<E> {
private Node<E> topNode;
public LinkedStack() {
topNode = null;
}
public void push(E e) {
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(e, topNode);
topNode = newNode;
}
public E peek() {
// isEmpty()
return topNode.item;
}
public E pop() {
E top = peek();
//topNode != null
topNode = topNode.next;
return top;
}
private class Node<E> {
private E item;
private Node<E> next;
Node(E item, Node<E> topNode) {
this.item = item;
next = topNode;
}
}
}
数组实现
public class ArrayStack<E> {
private E[] stack;
private int topIndex;
private boolean initialized = false;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 50;
private static final int MAX_CAPACITY = 1000;
public ArrayStack() {
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
public ArrayStack(int initCapacity) {
//checkCapacity(initCapacity);
E [] tempStack = (E[])new Object[initCapacity];
stack = tempStack;
topIndex = -1;
initialized = true;
}
public void push(E item) {
// checkInitialization()
ensureCapacity();
stack[topIndex + 1] = item;
topIndex++;
}
private void ensureCapacity() {
if(topIndex == stack.length - 1) {
int newLength = 2 * stack.length;
//checkCapacity(newLength)
stack = Arrays.copyOf(stack, newLength);
}
}
public E peek() {
// checkInitialization()
// isEmpty
return stack[topIndex];
}
public E pop() {
// checkInitialization()
// isEmpty
E top = stack[topIndex];
stack[topIndex] = null;
topIndex--;
return pop();
}
}
JDK继承vector实现的Stack源码
public
class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
public Stack() {
}
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L;
}
队列实现
链式队列实现
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
public LinkedList() {}
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
数组队列实现
public class ArrayDeque<E> extends AbstractCollection<E>
implements Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
transient int head;
transient int tail;
public ArrayDeque() {
elements = new Object[16];
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public void addLast(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[tail] = e;
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[h];
// Element is null if deque empty
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
public E peekFirst() {
// elements[head] is null if deque empty
return (E) elements[head];
}
}
线性表实现
ArrayList
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient Object[] elementData;
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
迭代器实现
HashMap类中迭代器
abstract class HashIterator {
Node<K,V> next; // next entry to return
Node<K,V> current; // current entry
int expectedModCount; // for fast-fail
int index; // current slot
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
Node<K,V>[] t = table;
current = next = null;
index = 0;
if (t != null && size > 0) { // advance to first entry
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final Node<K,V> nextNode() {
Node<K,V>[] t;
Node<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
}
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().key; }
}
final class ValueIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
}
final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
散列
树
二叉查找树
public class BinaryNode<T> {
private T data;
private BinaryNode<T> leftChild;
private BinaryNode<T> rightChild;
public BinaryNode() {
this(null);
}
public BinaryNode(T data) {
this(data, null, null);
}
public BinaryNode(T data, BinaryNode<T> leftChild, BinaryNode<T> rightChild) {
this.data = data;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
public boolean hasLeftChild() {
return leftChild != null;
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return (leftChild == null) && (rightChild == null);
}
public int getNumberOfNodes() {
int leftNumber = 0;
int rightNumber = 0;
if (leftChild != null) {
leftNumber = leftChild.getNumberOfNodes();
}
if(rightChild != null) {
rightNumber = rightChild.getNumberOfNodes();
}
return 1 + leftNumber + rightNumber;
}
public int getHeight(BinaryNode<T> node) {
int height = 0;
if (node != null) {
height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.getLeftChild()), getHeight(node.getRightChild()));
}
return height;
}
public BinaryNode<T> copy() {
BinaryNode<T> newRoot = new BinaryNode<>(data);
if(leftChild != null) {
newRoot.setLeftChild(leftChild.copy());
}
if(rightChild != null) {
newRoot.setRightChild(rightChild.copy());
}
return newRoot;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public BinaryNode<T> getLeftChild() {
return leftChild;
}
public void setLeftChild(BinaryNode<T> leftChild) {
this.leftChild = leftChild;
}
public BinaryNode<T> getRightChild() {
return rightChild;
}
public void setRightChild(BinaryNode<T> rightChild) {
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
}
public class BinaryTree<T> {
private BinaryNode<T> root;
public BinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
public BinaryTree(T rootData) {
root = new BinaryNode<>(rootData);
}
public BinaryTree(T rootData, BinaryTree<T> leftTree, BinaryTree<T> rightTree) {
privateSetTree(rootData, leftTree, rightTree);
}
public void setTree(T rootData) {
root = new BinaryNode<>(rootData);
}
private void privateSetTree(T rootData, BinaryTree<T> leftTree, BinaryTree<T> rightTree) {
root = new BinaryNode<>(rootData);
if((leftTree != null) && !leftTree.isEmpty()) {
root.setLeftChild(leftTree.root.copy());
}
if((rightTree != null) && !leftTree.isEmpty()) {
root.setRightChild(rightTree.root.copy());
}
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
public int getHeight() {
return root.getHeight(root);
}
public int getNumberOfNodes() {
return root.getNumberOfNodes();
}
public void inOrderTraverse() {
inOrderTraverse(root);
}
private void inOrderTraverse(BinaryNode<T> node) {
if(node != null) {
System.out.println(node.getData());
inOrderTraverse(node.getLeftChild());
inOrderTraverse(node.getRightChild());
}
}
// 中序遍历
private void iterativeInorderTraverse() {
Deque<BinaryNode> nodeStack = new LinkedList<>();
BinaryNode<T> currentNode = root;
while(!nodeStack.isEmpty() || currentNode != null) {
while (currentNode != null) {
nodeStack.push(currentNode);
currentNode = currentNode.getLeftChild();
}
if (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) {
BinaryNode<T> nextNode = nodeStack.pop();
assert nextNode != null;
System.out.println(nextNode.getData());
currentNode = nextNode.getRightChild();
}
}
}
}
二叉树遍历
前序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
res.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, res);
preorder(root.right, res);
}
}
中序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, res);
}
}
后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, res);
postorder(root.right, res);
res.add(root.val);
}
}
层序遍历
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null) {
return ret;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int currentLevelSize = queue.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= currentLevelSize; ++i) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
ret.add(level);
}
return ret;
}
}
红黑树
TreeMap
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> r = p.right;
p.right = r.left;
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
r.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
else
p.parent.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
}
/** From CLR */
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> l = p.left;
p.left = l.right;
if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
l.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
else p.parent.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
}
}
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出。


