深度学习:循环神经网络(下)
一些经典的RNN模型...
1、门控循环神经网络
⭐
- 门控循环神经网络可以更好地捕获时间步距离很长的序列上的依赖关系。
- 重置门有助于捕获序列中的短期依赖关系。
- 更新门有助于捕获序列中的长期依赖关系。
- 重置门打开时,门控循环单元包含基本循环神经网络;更新门打开时,门控循环单元可以跳过子序列。
📣 计算图:
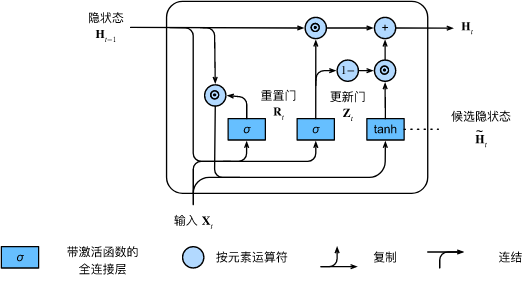
\[\begin{aligned}
\mathbf{R}_t = \sigma(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xr} + \mathbf{H}_{t-1} \mathbf{W}_{hr} + \mathbf{b}_r),\\
\mathbf{Z}_t = \sigma(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xz} + \mathbf{H}_{t-1} \mathbf{W}_{hz} + \mathbf{b}_z),
\end{aligned}
\]
\[\tilde{\mathbf{H}}_t = \tanh(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xh} + \left(\mathbf{R}_t \odot \mathbf{H}_{t-1}\right) \mathbf{W}_{hh} + \mathbf{b}_h),
\]
\[\mathbf{H}_t = \mathbf{Z}_t \odot \mathbf{H}_{t-1} + (1 - \mathbf{Z}_t) \odot \tilde{\mathbf{H}}_t.
\]
2、长短期记忆网络(LSTM)
LSTM它有许多与门控循环单元( :numref:sec_gru)一样的属性。但长短期记忆网络的设计比门控循环单元稍微复杂一些。
⭐
- 长短期记忆网络有三种类型的门:输入门、遗忘门和输出门。
- 长短期记忆网络的隐藏层输出包括“隐状态”和“记忆元”。只有隐状态会传递到输出层,而记忆元完全属于内部信息。
- 长短期记忆网络可以缓解梯度消失和梯度爆炸。
📣计算图
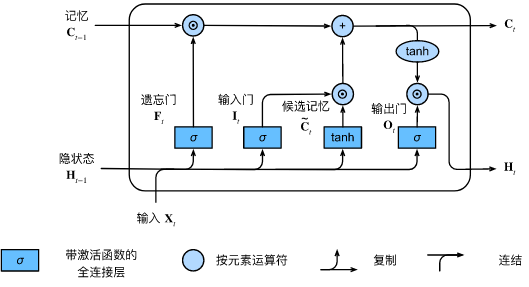
\[\begin{aligned}
\mathbf{I}_t &= \sigma(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xi} + \mathbf{H}_{t-1} \mathbf{W}_{hi} + \mathbf{b}_i),\\
\mathbf{F}_t &= \sigma(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xf} + \mathbf{H}_{t-1} \mathbf{W}_{hf} + \mathbf{b}_f),\\
\mathbf{O}_t &= \sigma(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xo} + \mathbf{H}_{t-1} \mathbf{W}_{ho} + \mathbf{b}_o),
\end{aligned}
\]
\[\tilde{\mathbf{C}}_t = \text{tanh}(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xc} + \mathbf{H}_{t-1} \mathbf{W}_{hc} + \mathbf{b}_c),
\]
\[\mathbf{C}_t = \mathbf{F}_t \odot \mathbf{C}_{t-1} + \mathbf{I}_t \odot \tilde{\mathbf{C}}_t.
\]
\[\mathbf{H}_t = \mathbf{O}_t \odot \tanh(\mathbf{C}_t).
\]
3、深度循环神经网络
⭐
- 在深度循环神经网络中,隐状态的信息被传递到当前层的下一时间步和下一层的当前时间步。
- 有许多不同风格的深度循环神经网络,
如长短期记忆网络、门控循环单元、或经典循环神经网络。
这些模型在深度学习框架的高级API中都有涵盖。 - 总体而言,深度循环神经网络需要大量的调参(如学习率和修剪)
来确保合适的收敛,模型的初始化也需要谨慎。
📣
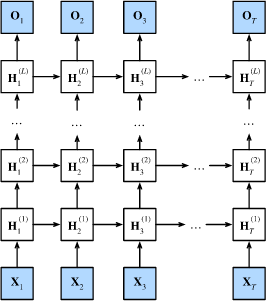
\[\mathbf{H}_t^{(l)} = \phi_l(\mathbf{H}_t^{(l-1)} \mathbf{W}_{xh}^{(l)} + \mathbf{H}_{t-1}^{(l)} \mathbf{W}_{hh}^{(l)} + \mathbf{b}_h^{(l)}),
\]
\[\mathbf{O}_t = \mathbf{H}_t^{(L)} \mathbf{W}_{hq} + \mathbf{b}_q,
\]
4、双向循环神经网络
⭐
- 在双向循环神经网络中,每个时间步的隐状态由当前时间步的前后数据同时决定。
- 双向循环神经网络与概率图模型中的“前向-后向”算法具有相似性。
- 双向循环神经网络主要用于序列编码和给定双向上下文的观测估计。
- 由于梯度链更长,因此双向循环神经网络的训练代价非常高。
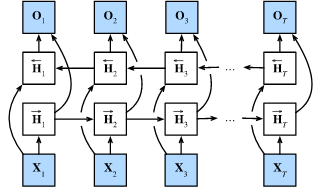
\[\begin{aligned}
\overrightarrow{\mathbf{H}}_t &= \phi(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xh}^{(f)} + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{H}}_{t-1} \mathbf{W}_{hh}^{(f)} + \mathbf{b}_h^{(f)}),\\
\overleftarrow{\mathbf{H}}_t &= \phi(\mathbf{X}_t \mathbf{W}_{xh}^{(b)} + \overleftarrow{\mathbf{H}}_{t+1} \mathbf{W}_{hh}^{(b)} + \mathbf{b}_h^{(b)}),
\end{aligned}
\]
\[\mathbf{O}_t = \mathbf{H}_t \mathbf{W}_{hq} + \mathbf{b}_q.
\]
参考文献
《动手学深度学习》


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号