D-Bus
一、D-Bus简介#
什么是D-Bus? 详细介绍参考D-Bus
D-Bus是一个在不同程序之间传递消息的系统总线,进程间通信方式的一种,但与传统进程间通信方法(管道、FIFO、消息队列、信号量、共享内存)有区别。
1.1 D-Bus的一些关键概念#
D-Bus的关键概念参考链接
-
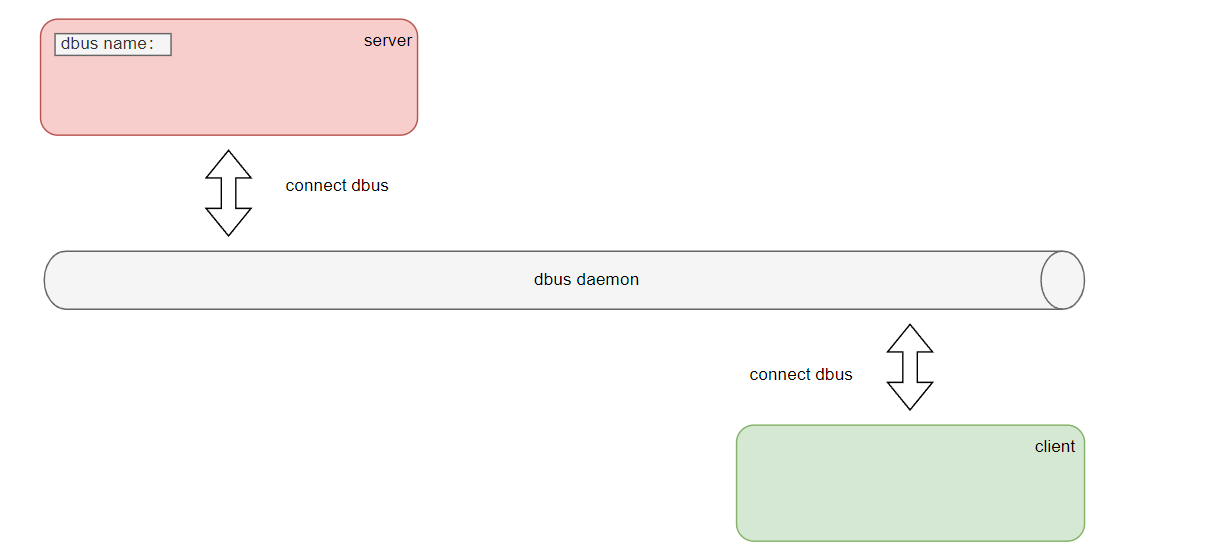
dbus name:
服务端程序在D-Bus上注册的服务名称(即 dbus name),在D-Bus上的注册的服务后会产生一个地址(例如:/run/user/1000/bus)和唯一名称(例如:1.466),地址和唯一名称都是随机生成的,客户端通过dbus name来知道服务名称。dbus name的格式,例如:cn.whowin.dbus,这是D-Bus的规定,没有为什么。 -
对象(Object):
对象以路径的形式表示,对象路径代表一个对象实例。对象路径的前缀以dbus name为参考,接上其他的。例如,上述dbus name:cn.whowin.dbus,那么对象路径前缀是:/cn/whowin/dbus,接上其他的,形成完成的对象路径,例如:/cn/whowin/dbus/yes、/cn/whowin/dbus/no、/cn/whowin/dbus/quit等。 -
接口(Interface):
接口,顾名思义。接口名称的格式规定与dbus name一样,例如:cn.whowin.dbus_demo、com.example.MusicPlayer1,com.example.MusicPlayer1.Track、com.example.MusicPlayer1.Seekable -
成员名称(Member name):
成员包括:方法(Method)和信号(Signal),在大多数方面,他们几乎是一样的,除了两点:1. Signal是在总线中进行广播的,而Method是指定发给某个进程的。2. Signal 不会有返回,而 Method 一定会有返回(同步的或是异步的)。从 C API 的层面来看,Member name 最大的作用就是在两个进程间共享“发出的消息的类型信息”,DBus 只能以 Signal or Method 来进行消息通信。
1.2 消息类型和数据类型#
在 dbus-protocol.h 定义了消息的类型:
/* Types of message */
/** This value is never a valid message type, see dbus_message_get_type() */
#define DBUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_INVALID 0
/** Message type of a method call message, see dbus_message_get_type() */
#define DBUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_METHOD_CALL 1
/** Message type of a method return message, see dbus_message_get_type() */
#define DBUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_METHOD_RETURN 2
/** Message type of an error reply message, see dbus_message_get_type() */
#define DBUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_ERROR 3
/** Message type of a signal message, see dbus_message_get_type() */
#define DBUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_SIGNAL 4
#define DBUS_NUM_MESSAGE_TYPES 5
消息传递的数据类型,分为两种:基本类型和组合类型。
-
基本类型:BYTE、BOOLEAN、INT16、UINT16、INT32、UINT32、INT64、UINT64、DOUBLE、STRING、OBJECT_PATH、SIGNATURE
-
组合类型:ARRAY、STRUCT、VARIANT、DICT_ENTRY
数据类型系统:
在Dbus中将数据类型用格式符号代替,多个数据类型组合形成一种variant的变量。variant变量有点像JSON类型格式,格式符号代表一种基本的数据类型,如下:
| 常规名字 | ASCII符号 | 编码存储 |
|---|---|---|
| BYTE | y | unsigned 8-bit integer |
| BOOlEAN | b | boolean value: 1 is false, 1 is true |
| INT16 | b | signed 16-bit integer |
| UINT16 | q | unsigned 16-bit integer |
| INT32 | i | signed 32-bit integer |
| UINT32 | u | unsigned 32-bit integer |
| INT64 | x | signed 64-bit integer |
| UINT64 | t | unsigned 64-bit integer |
| DOUBLE | d | double-precision floating point |
| UNIX_FD | h | unsigned 32-bit representing an index into an out-of-band array of file descriptors |
| STRING | s | string, like "" |
| OBJECT_PATH | o | object, like {} |
| SIGNATURE | g | |
| ARRAY | a | array, like [] |
| VARIANT | v |
D-Bus通信示意图:
二、dbus开发环境#
下载dbus开发环境:sudo apt install libdbus-1-dev
头文件按照目录:
# sudo dpkg -L libdbus-1-dev
/usr
/usr/include
/usr/include/dbus-1.0
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-address.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-bus.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-connection.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-errors.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-macros.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-memory.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-message.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-misc.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-pending-call.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-protocol.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-server.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-shared.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-signature.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-syntax.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-threads.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus-types.h
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/dbus.h
/usr/lib
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cmake
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cmake/DBus1
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cmake/DBus1/DBus1Config.cmake
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cmake/DBus1/DBus1ConfigVersion.cmake
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dbus-1.0
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dbus-1.0/include
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dbus-1.0/include/dbus
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dbus-1.0/include/dbus/dbus-arch-deps.h
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdbus-1.a
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/pkgconfig
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/pkgconfig/dbus-1.pc
/usr/share
/usr/share/doc
/usr/share/doc/libdbus-1-dev
/usr/share/doc/libdbus-1-dev/copyright
/usr/share/lintian
/usr/share/lintian/overrides
/usr/share/lintian/overrides/libdbus-1-dev
/usr/share/xml
/usr/share/xml/dbus-1
/usr/share/xml/dbus-1/busconfig.dtd
/usr/share/xml/dbus-1/introspect.dtd
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdbus-1.so
/usr/share/doc/libdbus-1-dev/AUTHORS.gz
/usr/share/doc/libdbus-1-dev/NEWS.gz
/usr/share/doc/libdbus-1-dev/README.gz
/usr/share/doc/libdbus-1-dev/changelog.Debian.gz
在 /usr/include 下新建目录 dbus,然后将下面两个目录下的头文件拷贝进去。
/usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dbus-1.0/include/dbus
拷贝命令: sudo cp /usr/include/dbus-1.0/dbus/*.h /usr/include/dbus 和 sudo cp /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dbus-1.0/include/dbus/*.h /usr/include/dbus
三、C API#
dbus.h的结构体、宏、以及函数定义可以查看D-Bus low-level public API
3.1 服务端#
📌 服务端-客户端源文件下载地址
该服务端和客户端代码均可以编译运行,若出现错误,可能原因是wsl的问题。虚拟机Ubuntu和宿主机Ubuntu均正常运行
-
Step 1: get dbus connection
-
Step 2: ask bus to assign the given name
-
Step 3: Loop when something can be read or writen
-
Step 4: Read the message
-
Step 5: Reply the message and flush the message
3.2 客户端#
Step 1: get dbus connection
Step 2: Constructs a new message to invoke a method on a remote object
Step 3: sends the message and gets the reply
四、标准接口#
Standard Interfaces:
-
org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer
-
org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable
-
org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties:用于提供一种统一的机制来获取和设置对象的属性
method:
- Get: 用于获取特定属性的当前值。它接收两个参数:一个是对象支持的接口名称,另一个是要获取的属性名称。返回值是该属性的当前值。
- Set: 用于设置特定属性的值。它接收三个参数:接口名称、属性名称和新的属性值
- GetAll: 于获取对象上所有属性的值。它接收一个参数,即对象支持的接口名称。返回值是一个字典,其中键是属性名称,值是对应的属性值
signal:
- PropertiesChanged: 当对象的属性发生变化时,会发出这个信号
-
org.freedesktop.DBus.ObjectManager:这个接口允许客户端请求服务提供所有当前注册的对象路径和其关联的接口列表
method:
- GetManagedObjects: 返回一个字典,形式:{object_path: {interface: {property: value}}}
signal:
- InterfacesAdded:当服务在其命名树中添加了新对象或新对象的新接口时,此信号会被发送
- InterfacesRemoved:当服务移除了对象上的接口时,此信号会被发送
五、参考引用#
作者:caojun97
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/caojun97/p/18247318
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
2023-06-16 宏(Macro)的使用