zlog
一、安装#
二、配置文件#
编程时,在zlog_init()函数需要指定配置文件,而配置文件可以根据用户的需求进行个性化定制。
2.1 基本配置#
test_hello.conf
[global]
strict init = true
buffer min = 1024
buffer max = 2048
rotate lock file = /tmp/zlog.lock
default format = "%d.%us %-6V (%c:%F:%L) - %m%n"
[formats]
simple = "%d %V %m%n"
simple2 = "%d.%ms %V %m%n"
simple3 = "%d.%us %V %m%n"
full = "%d.%ms %-6V [%c:%p:%f:%U:%L] - %m%n"
[rules]
*.=debug >stdout;simple
*.=info >stdout;simple2
*.=warn >stdout;simple3
*.=notice >stdout;
*.=fatal >stdout;
*.=error >stdout;full
my_cat.info "test.log", 1MB; full
📌 注意事项:
[rules]中 *.=debug 的 * 代表的是category_name,只不过这里用通配符 * 表示所有的category_name。
源文件:test_hello.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "zlog.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int rc;
zlog_category_t *zc;
rc = zlog_init("../config/test_hello.conf");
if (rc)
{
printf("init failed\n");
return -1;
}
zc = zlog_get_category("my_cat");
if (!zc)
{
printf("get cat fail\n");
zlog_fini();
return -2;
}
zlog_info(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_debug(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_warn(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_error(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_notice(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_fatal(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_fini();
return 0;
}
项目目录树:
注意:build用来保存cmake命令后的中间过程文件
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8.0)
project(zlog_demo)
set(CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX /home/user/project/zlog-1.2.16/example)
set(SRCS
src/test_hello.c
)
include_directories(include)
link_directories(lib)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} ${SRCS})
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} zlog)
install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME} DESTINATION bin)
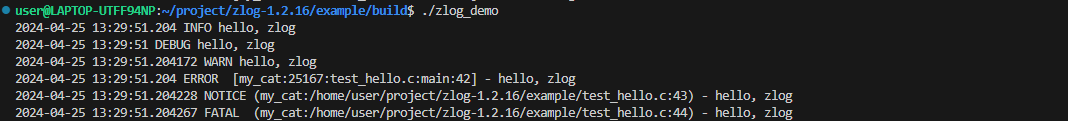
执行结果:
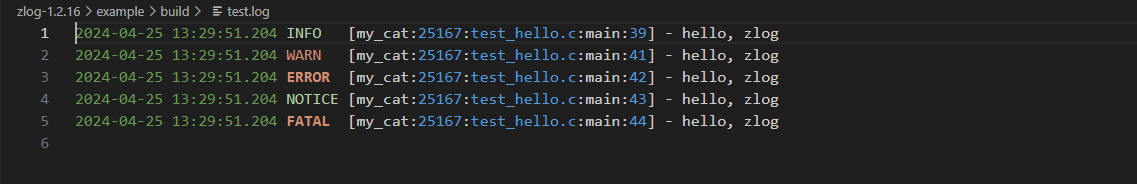
test.log:
注意:my_cat是程序中zlog_get_category("my_cat")函数创建的类别,当然也可以使用通配符处理。test.log中是没有debug级别的日志的,因为日志级别是:"DEBUG" < "INFO" < "NOTICE" < "WARN" < "ERROR" < "FATAL"
2.2 日志文件按大小自动创建新文件#
test_hello_2.conf
[global]
strict init = true
buffer min = 1024
buffer max = 2048
rotate lock file = /tmp/zlog.lock
default format = "%d.%us %-6V (%c:%F:%L) - %m%n"
[formats]
simple = "%d %V %m%n"
simple2 = "%d.%ms %V %m%n"
simple3 = "%d.%us %V %m%n"
full = "%d.%ms %-6V [%c:%p:%f:%U:%L] - %m%n"
[rules ]
*.=debug >stdout;simple
*.=info >stdout;simple2
*.=warn >stdout;simple3
*.=notice >stdout;
*.=fatal >stdout;
*.=error >stdout;full
my_cat.info "test.log", 50KB * 2 ~ "test.#r.log"; full
在 2.1 的基础上修改源代码和zlog配置文件(即test_hell_2.conf),源文件如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "zlog.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int rc;
zlog_category_t *zc;
rc = zlog_init("../config/test_hello.conf");
if (rc)
{
printf("init failed\n");
return -1;
}
zc = zlog_get_category("my_cat");
if (!zc)
{
printf("get cat fail\n");
zlog_fini();
return -2;
}
int count = 200;
while (count--)
{
zlog_info(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_debug(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_warn(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_error(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_notice(zc, "hello, zlog");
zlog_fatal(zc, "hello, zlog");
usleep(100000);
}
zlog_fini();
return 0;
}
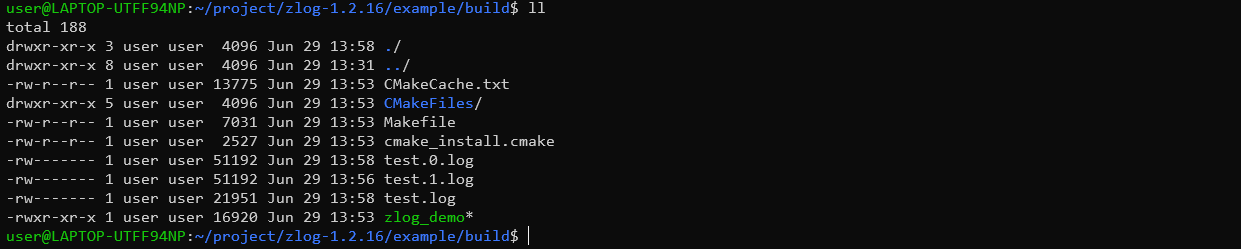
执行结果生产的log文件:
当test.log文件超过50KB,就会创建新的日志文件test.0.log,当接下来的日志再一次超过50KB,又会创建新的日志文件test.1.log。后续再有超过50KB,不会再创建新文件,只会进行轮询覆盖的方式进行。因为在配置文件中的 50KB * 2 就限定了文件数量。
2.3 日志文件按日期自动创建新文件#
test_hello_3.conf
[global]
strict init = true
buffer min = 1024
buffer max = 2048
rotate lock file = /tmp/zlog.lock
default format = "%d.%us %-6V (%c:%F:%L) - %m%n"
[formats]
simple = "%d %V %m%n"
simple2 = "%d.%ms %V %m%n"
simple3 = "%d.%us %V %m%n"
full = "%d.%ms %-6V [%c:%p:%f:%U:%L] - %m%n"
[rules ]
*.=debug >stdout;simple
*.=info >stdout;simple2
*.=warn >stdout;simple3
*.=notice >stdout;
*.=fatal >stdout;
*.=error >stdout;full
my_cat.info "test.%d(%F).log", 1MB; full
2.1 中的源代码都不用修改,仅修改zlog的配置文件(即 test_hello_3.conf)就行了。
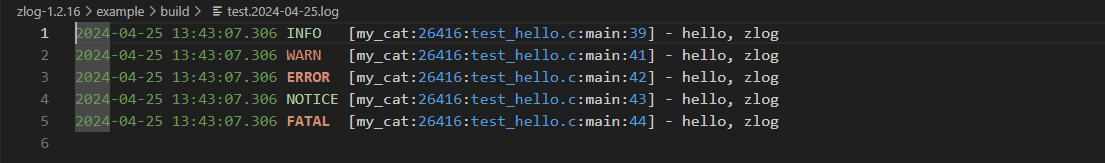
日志文件每天生成一个,且文件最大大小是1MB。文件格式:test.2024-04-25.log
作者:caojun97
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/caojun97/p/18156234
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。






【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 互联网不景气了那就玩玩嵌入式吧,用纯.NET开发并制作一个智能桌面机器人(四):结合BotSharp
· Vite CVE-2025-30208 安全漏洞
· 《HelloGitHub》第 108 期
· MQ 如何保证数据一致性?
· 一个基于 .NET 开源免费的异地组网和内网穿透工具