C++的构造函数和析构函数
背景介绍
在B站上看完侯捷老师讲解的两个类:String类 and complex类,这两个类的实现体现了不带指针和带指针的区别,也可以作为设计类的参考学习。
这两个类的实现过程中有很多小细节的东西需要注意,否则很可能造成编译报错。
编写带指针的类String
在c++的ansi库中有有一个string类,用于处理字符串。那么便仿写一个String类,实现其基本功能。
mystring.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __MYSTRING__
#define __MYSTRING__
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class String
{
public:
String(const char *cstr = 0);
String(const String& str);
String& operator = (const String& str);
~String();
char* get_c_str() const { return m_data; };
private:
char* m_data;
};
/* global function */
ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const String& str);
#endif // !__MYSTRING__
mystring.cpp
#include "mystring.h"
/* 普通构造函数 */
String::String(const char *cstr)
{
if (cstr)
{
m_data = new char[strlen(cstr) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, cstr);
}
else
{
m_data = new char[1];
*m_data = '\0';
}
}
/* 析构函数 */
String::~String()
{
delete[] m_data;
}
/* 拷贝构造函数 */
String::String(const String& str)
{
m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
}
/* 拷贝赋值函数 */
String& String::operator = (const String& str)
{
if (this == &str) // 检测自我赋值 self assignment
{
return *this;
}
delete[] m_data;
m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
return *this;
}
ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const String& str)
{
os << str.get_c_str();
return os;
}
main.cpp
#include "mystring.h"
int main(void)
{
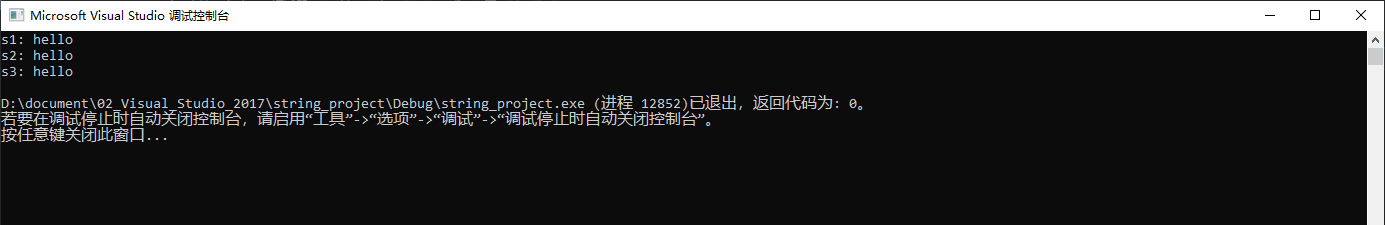
String s1 = "hello";
String s2(s1);
String s3 = s2;
cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2: " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s3: " << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
📌 在侯捷老师的PPT中的mystring.cpp里给很多函数都添加了内联关键字inline(包括构造函数和析构函数),这会直接导致编译报错:undefined reference to xxx,去掉inline编程通过。

📌 若在类的声明文件mystring.h中方法的参数带有默认值,那么请不要在类的实现文件mystring.cpp中其方法的参数默认不要一样抄过来。
例如:mystring.h中 : String(const char *cstr = 0); ,在mystring.cpp中 : String::String(const char *cstr = 0)。 这样会导致编译报错
编写不带指针的类complex
在c++中有一个complex类,用于处理字符串。那么便仿写一个complex类,实现其基本功能。
complex.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __COMPLEX_H__
#define __COMPLEX_H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class complex
{
/* 声明类的友元函数 */
friend complex operator + (const complex& x, const complex& y);
friend complex operator + (const complex& x, double y);
friend complex operator + (double x, const complex& y);
friend complex& __doapl(complex *, const complex&);
public:
/* 声明并定义构造函数,且对成员进行列表初始化 */
complex(double r = 0, double i = 0) : re(r), im(i) {}
/* 返回实部 */
inline double real() const;
/* 返回虚部 */
inline double imag() const;
/* 重载操作符+= */
complex& operator += (const complex&);
private:
double re;
double im;
};
/* =============================global function============================= */
/* 重载运算符<< */
ostream&
operator << (ostream& os, const complex& x);
#endif // !__COMPLEX_H__
complex.cpp
#include "complex.h"
double
complex::real() const
{
return re;
}
double
complex::imag() const
{
return im;
}
complex&
__doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
ths->re += r.re;
ths->im += r.im;
return *ths;
}
// 重载+=
complex&
complex::operator += (const complex& r)
{
return __doapl(this, r);
}
// 重载+
complex
operator + (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex(x.re + y.re, x.im + y.im);
}
complex
operator + (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex(x.re + y, x.im);
}
complex
operator + (double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex(x + y.re, y.im);
}
/* 重载<< */
ostream&
operator << (ostream& os, const complex& x)
{
return os << '(' << x.real() << ',' << x.imag() << ')';
}
main.cpp
#include "complex.h"
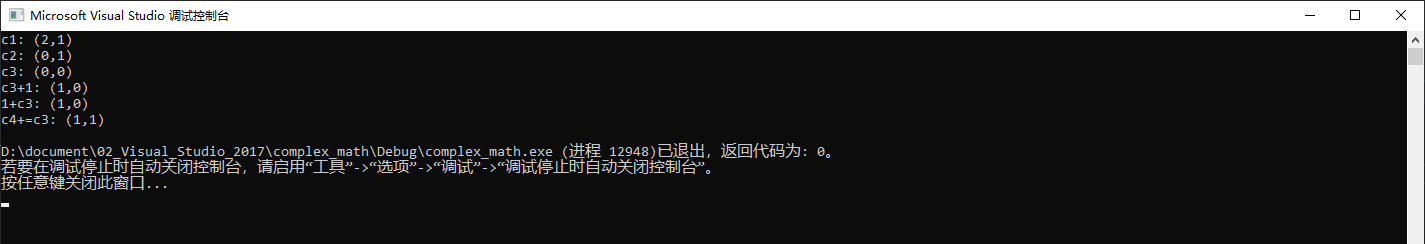
int main(void)
{
complex c1(2,1);
complex c2(0,1);
complex c3;
complex c4(1,1);
cout << "c1: " << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2: " << c2 << endl;
cout << "c3: " << c3 << endl;
cout << "c3+1: " << c3 + 1 << endl;
cout << "1+c3: " << 1 + c3 << endl;
c4 += c3;
cout << "c4+=c3: " << c4 << endl;
return 0;
}
反思总结
解读String类中的拷贝赋值函数
/* 拷贝赋值函数 */
String& String::operator = (const String& str)
{
if (this == &str) // 检测自我赋值 self assignment
{
return *this;
}
delete[] m_data;
m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
return *this;
}
第一步:检查右值是否等于左值,若相等,则判定为自我赋值。若不相等,进行第二步
第二步:在拷贝右值时,左值其实m_data已经存在内存空间(由构造函数申请的空间),必须先释放掉这部分内存空间
第三步:申请和右值一样大的空间,并将右值拷贝到左值空间中。
解读complex类的友元函数和运算符重载
class complex
{
/* 声明类的友元函数 */
friend complex operator + (const complex& x, const complex& y);
friend complex operator + (const complex& x, double y);
friend complex operator + (double x, const complex& y);
friend complex& __doapl(complex *, const complex&);
public:
//...
private:
//...
};
对于类中的成员变量,基本上都是封装起来成为private。通常,共有类方法提供唯一的访问途径,但是有时候这中限制太严格,以至于不适合特定的编程问题。在这种情况下,C++提供了另外一种形式的访问权限:友元
友元包括:
- 友元函数
- 友元类
- 友元成员函数
解读构造函数初始值列表,在声明文件中直接对类成员直接初始化。注意:只能对构造函数这样处理
complex(double r = 0, double i = 0) : re(r), im(i) {}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号