EL表达式知识点总结
1 只可以获取内置对象的属性值,不可以获取JSP页面中局部java变量的值
<% String name = "James"; request.setAttribute("name",name); int age = 30; %> <h2>${name}</h2> <h2>${age}</h2>
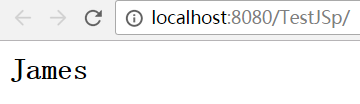
2 只有“${”两个字符连续出现时,才表示EL的开始,任何单独字符出现时都可正常显示
<% String name = "James"; request.setAttribute("name",name); %> <h2>${name}</h2> <h2>$${name}</h2> <h2>{${name}</h2>

3 如果只出现了“${”,而没有“}”作为结束,则服务器报错,出现空的“${}”时,服务器报错
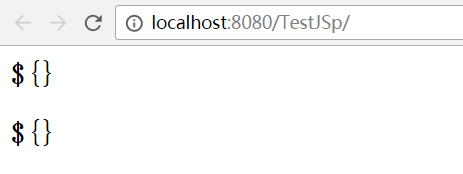
4 需要输出“${”时,需要写为“\${”(页面最终显示时会去掉“\”),或者写成“${'${'}”
<h2>\${}</h2> <h2>${"${}"}</h2>
5 EL运算符中的“+”的操作数只可以是数字运算或者可以转换为数字的字符串,对不可以转换为数字的字符串运用“+”运算讲产生错误
<h2>${123+"124"}</h2>

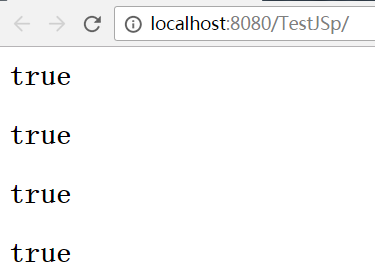
6 对于EL的empty运算符,null对象与空字符串“”、空数组、空list等是等价的
<% request.setAttribute("emptyString",""); request.setAttribute("nullObject",null); request.setAttribute("emptyList",new ArrayList<String>()); request.setAttribute("emptyMap",new HashMap<String,String>()); %> <h2>${empty emptyString}</h2> <h2>${empty nullObject}</h2> <h2>${empty emptyList}</h2> <h2>${empty emptyMap}</h2> </body>
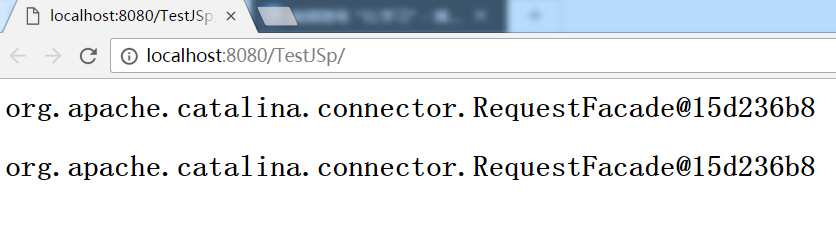
7 EL获取某个对象的值时,本质是调用该对象的toString()方法
<% request.setAttribute("requestString",request.toString()); %> <html> <body> <h2>${requestString}</h2> <h2>${pageContext.request}</h2> </body> </html>
8 EL的内置对象与JSP的内置对象并不相同(除了pageContext对象),两者关系是:EL的内置对象可以访问对应的JSP内置对象通过setAttribute方法存储的值
- EL内置对象共有11个:pageContext、pageScope、requestScope、sessionScope、applicationScope、param、paramValues、header、headerValues、initParam、cookie(注意不存在responseScope,因为EL的本质是为了获取某个值,而不是设置)
- JSP的内置对象共有9个:pageContext、page、resquest、response、session、application、out、config、exception
- 在页面中直接使用${request}等会报错
- 通过pageContext可以实现EL对JSP内置对象的获取,${pageContext.request}
- 通过pageContext可以获取的对象有page、resquest、response、session、out、exception、servletContext
- 不可以通过pageContext可以获取的对象有application、config、pageContext
9 获取JSP作用于范围对象attribute的两种方法
<% request.setAttribute("name","Shao"); %> <h2>${requestScope["name"]}</h2> <h2>${requestScope.name}</h2>
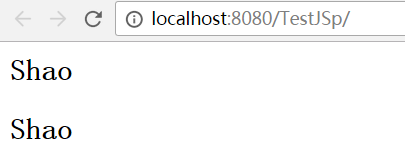
注意,下面的写法是错误的,因为request对象并不存在getName方法
<h2>${pageContext.request.name}</h2>
10 获取JSP作用于范围对象属性的方法
<h2>${pageContext.request.serverPort}</h2>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号