JavaScript—window对象使用
window 对象是 JavaScript 浏览器对象模型中的顶层对象,包含多个常用方法和属性:
1、 打开新窗口
window.open(pageURL,name,parameters)
其中:pageURL 为子窗口路径、name 为子窗口句柄、parameters 为窗口参数(各参数用逗号分隔)
window.open("http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouhb/","open",'height=100,width=400,top=0,left=0,toolbar=no,menubar=no,scrollbars=no,resizable=no,location=no,status=no');
2 、打开模式窗口
window.showModalDialog("http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouhb/","open","toolbars=0;width=200;height=200");
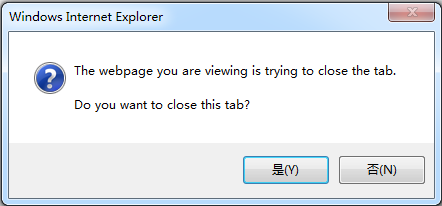
3 、关闭窗口(兼容IE)
如果网页不是通过脚本程序打开的(window.open();),调用 window.close(); 脚本关闭窗口前,必须先将 window.opener 对象置为null,否则浏览器 (IE7、IE8) 会弹出一个确定关闭的对话框。
老式:
<input type='button' value='关闭窗口' onClick="closeWindow()"> <script language="javaScript"> function closeWindow() { window.opener = null; window.open('', '_self', ''); window.close(); } </script>
或
open(location, '_self').close();
4、 location对象使用
window.location.reload();//刷新当前页 window.location.href="http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouhb/"; //载入其他页面
5 、history对象使用
window.history.go(1); //前进 window.history.go(-1); //后退上一页
6、 子窗体向父窗体传值(17年4月18日,发现代码不好使了。)
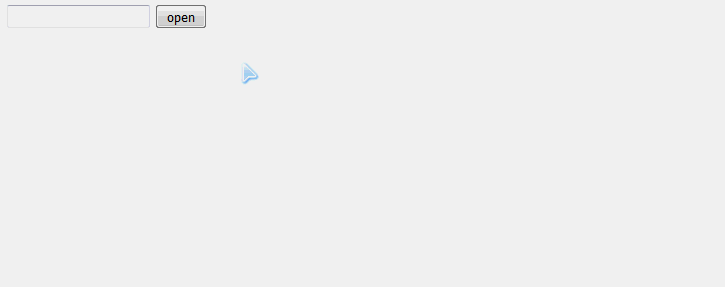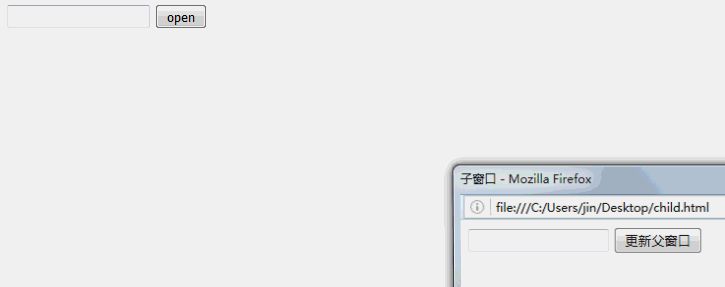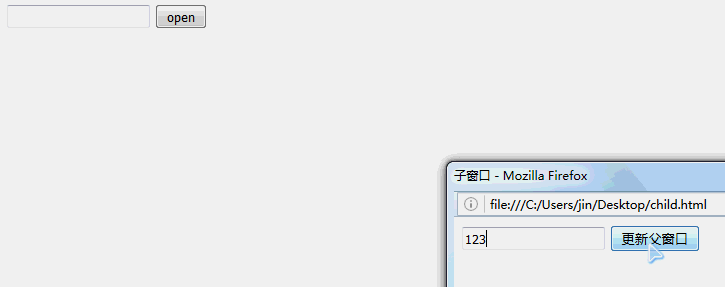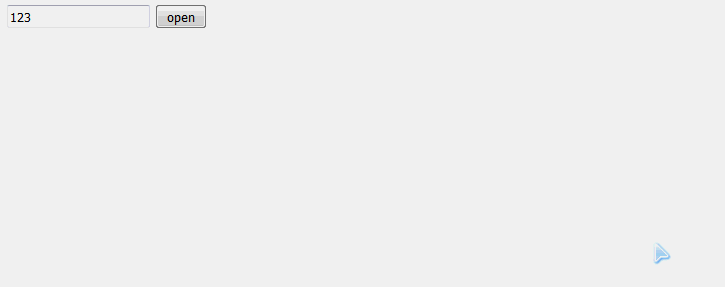
父窗口代码:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> <title>父窗口</title> <script type="text/javascript"> var child; //通过判断子窗体的引用是否为空,可以控制它只能打开一个子窗体 function opendialog() { //例一 这里用window对象作为参数传递(对应子窗口例一) //window.showModalDialog("child.html", window, "win", "toolbar=no,scrollbars=no,location=no,statusbar=no,menubar=no,resizable=0,width=300,height=80"); //例二(对应子窗口例二) //window.open("child.html", "Popup", "toolbar=no,scrollbars=no,location=no,statusbar=no,menubar=no,resizable=0,width=300,height=80"); //例三 打开子窗体的同时,对子窗体的元素进行赋值,因为window.open函数同样会返回一个子窗体的引用(对应子窗口例三,此例子不好使) if (!child) { child = window.open('child.html'); //需要等待子窗口加载完成,赋值才能成功 child.onload = function() { child.document.getElementById('name').value = document.getElementById('name').value; } } //例四(对应子窗口例四) //var resultStr = showModalDialog("child.html", this, "dialogWidth:1000px;dialogHeight:800px"); //document.getElementById('name').value = resultStr; } </script> </head> <body> <form> <input type="text" id="name" value="123" /> <input type="button" id="open" value="open" onclick="opendialog()" /> </form> </body> </html>
子窗口代码:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <title>子窗口</title> <script type="text/javascript"> function updateParent() { //例一(对应父窗口例一) //var pathelem = window.dialogArguments; //子窗口获取传递的参数 //if (pathelem != undefined) { // pathelem.document.getElementById("name").value = document.getElementById("name").value; //} //例二(对应父窗口例一和例二) //var pathelem = this.opener.document.getElementById('name'); //pathelem.value = document.getElementById('name').value; //例三(对应父窗口例三,此例子不好使) window.opener.document.getElementById('name').value = document.getElementById('name').value; window.opener.child = null; //例四(对应父窗口例四) //window.parent.returnValue = document.getElementById('name').value; this.close(); } </script> </head> <body> <form> <input type="text" id="name" /> <input type="button" id="update" value="更新父窗口" onclick="updateParent()" /> </form> </body> </html>
分类:
JavaScript




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?