Java集合之HashMap源码解析
前言
在前面的博客中,我写到ArrayList和LinkedList时,他们分别采用数组和双向链表的方式实现,下面我们再一次总结一下,
1.数组,元素顺序插入,寻址快,删除慢,插入慢。
2.双向链表, 元素顺序插入,寻址慢,删除快,插入快。
HashMap就是综合以上两种数据结构的优点,即数组+单向链表的方式实现,它是一种K-V键值对的存储结构。
HashMap的基本结构
首先我们先来看一下HashMap中的基本结构,Node是一个静态内部类,它是HashMap数据结构中元素存储的最小单元,源代码如下所示,
1 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 2 final int hash; 3 final K key; 4 V value; 5 Node<K,V> next; 6 7 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 8 this.hash = hash; 9 this.key = key; 10 this.value = value; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 }
Node类成员属性如下图所示,
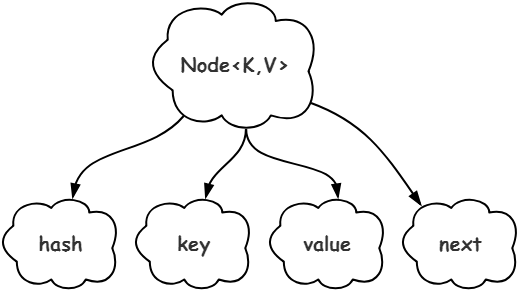
Node这个静态内部类,有四个成员属性,我逐一来介绍一下,
1.hash,哈希,即由Key的通过哈希函数得到的哈希码。
2.key,键,数据结构中的键。
3.value,值,数据结构中的值。
4.next,后继结点的引用。
ps,这里只有后继结点,并无前驱结点,这也说明此处是单向链表,并非双向链表。
HashMap自身的成员属性如下:
1 transient Node<K,V>[] table; 2 transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; 3 transient int size; 4 transient int modCount; 5 int threshold; 6 final float loadFactor;
HashMap的整体结构示意图如下图所示,
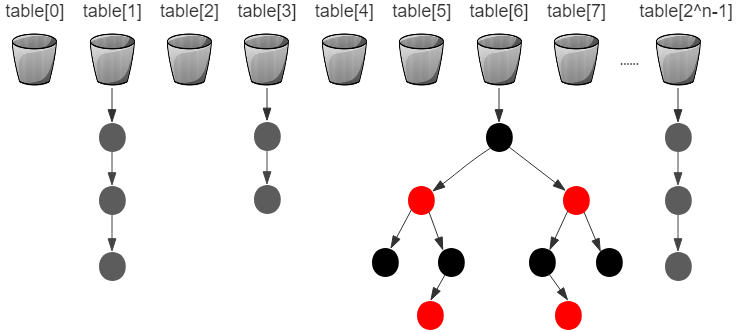
 ☞哈希桶,也叫bucket,一个bucket对应一个table数组中的一个元素。
☞哈希桶,也叫bucket,一个bucket对应一个table数组中的一个元素。 ☞哈希桶中的普通结点,即:Node<K,V>,一个哈希桶中可以有多个Node,构成单向链表结构。
☞哈希桶中的普通结点,即:Node<K,V>,一个哈希桶中可以有多个Node,构成单向链表结构。 ☞红黑树结构中的黑色结点,当一个哈希桶中的结点个数超过一定的阈值,数据结构由单向的链表结构转成红黑树结构。
☞红黑树结构中的黑色结点,当一个哈希桶中的结点个数超过一定的阈值,数据结构由单向的链表结构转成红黑树结构。 ☞红黑树结构中的红色结点,当一个哈希桶中的结点个数超过一定的阈值,数据结构由单向的链表结构转成红黑树结构。
☞红黑树结构中的红色结点,当一个哈希桶中的结点个数超过一定的阈值,数据结构由单向的链表结构转成红黑树结构。
HashMap的put方法解读
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap(); 3 map.put("test", "我是第一个元素"); 4 }
第2行,这个一个不带参数的构造函数,初始化增长因子loadFactor=0.75f,
第3行,我们跟一下代码,
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 3 }
第2行,跟一下putVal方法,
putVal中的前三个参数分别是,
1.hash(key) →根据key得到hashCode,
2.key→ 键,
3.value→值。
1 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 2 boolean evict) { 3 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 4 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 5 n = (tab = resize()).length; 6 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 7 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 8 else { 9 Node<K,V> e; K k; 10 if (p.hash == hash && 11 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 12 e = p; 13 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 14 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 15 else { 16 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 17 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 18 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 19 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 20 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 21 break; 22 } 23 if (e.hash == hash && 24 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 25 break; 26 p = e; 27 } 28 } 29 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 30 V oldValue = e.value; 31 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 32 e.value = value; 33 afterNodeAccess(e); 34 return oldValue; 35 } 36 } 37 ++modCount; 38 if (++size > threshold) 39 resize(); 40 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 41 return null; 42 }
第3行,声明变量Node<K,V>数组类型的 tab,Node<K,V>的类型的 p,整型n,i
第4-5行,将Map的成员属性table赋值给tab,如果数组table为空或者元素个数为0,那么需要重新扩大table的长度,并且把table的长度记作n,
第6行,新的元素将存储在p链表中,如果p链表为空链表时,进入第7行,反之进入进入第9行,
第8行,根据hash,key,value构建一个新Node<K,V>,并且把i这个位置上的数组的引用指向 新Node。
第9-35行,新元素将存储的p链表,且p链表不为空时的处理事件。
写到这里,我想先引申出两个问题,
1.hash值如何计算?
2.如果确认table数组的索引位置?
1.hash值如何计算?
1 static final int hash(Object key) { 2 int h; 3 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 4 }
如果key为null,那么hash为0 → HashMap的key允许为空,反之 (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16),
1 int h; 2 String key = "test"; 3 h = (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 4 5 int a = key.hashCode(); 6 int b = h >>> 16; 7 int c = a ^ b; 8 9 System.out.print(String.format("[h]: %s, [c]:%s", h, c));
输出结果为 [h]: 3556516, [c]:3556516,
第①步,调用key的hashCode方法,哈希值记作a,
第②步,h>>>16运算,结果记作b,>>>移位运算符代表无符号右移16位,空位以0补齐,
第③步,a与b的异或运算得到c,异或运算代表按位比较,相同则为0,反之为1,比如1^1 = 0,0^0 = 0,1^0 = 1,0^1 = 1。
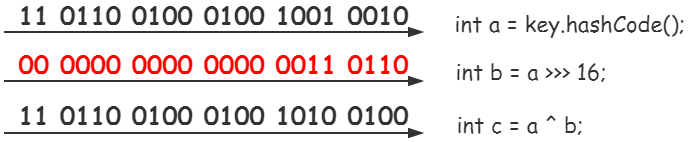
总结一下,hash算法的本质就是1.取到key的哈希码 2.高位的移位运算,3.异或运算。
因此,只要给定两个类型的对象,只要他们的哈希码相同,再经过高位运算,最后经过异或运算得到的hash码值可以断言必然相同,我们把最后得到的hash码记作 int hash,自然想到 hash对 数组的长度 作取模运算,如此,元素最后的分布在数组中会比较的均匀,HashMap却并没有这么做,因为取模运算消耗较大,这也是HashMap源码设计的精妙之处。于是我们再探上述的第二个问题。
2.如果确认table数组的索引位置?
上述putVal方法中的 第6行 i = (n - 1) & hash 就是数组的索引位置,根据上下文环境,n为table的长度,初始值为16, hash为上述分三部得出的哈希码。最后(n-1)和hash “&”。&是二进制中的与运算,举个例子,
0&0=0,0&1=0,1&0=0,1&1=1,即按位运算的规则为同时为1,值才为1,反之为0。
数组的扩容保证长度length为2的n次方,因此当length为2的n次方时,(length-1)与hash作 与运算 等价于 hash%lengh,即hash对数组长度取模,要证明这一点,不难。
举个栗子,length长度是2的4次方,即length=16,二进制为10000,length-1 为 1111,hash我们就取上述算出的hash :1101100100010010100100,与运算如下图所示,

得到的结果为100 十进制为4,我们再看取模运算,3556516 % 16 = 4
那为什么要使用与运算来替代取模运算呢?因为,&比%具有更高的效率。
讨论完引申出来的两个问题,再回到putVal方法,第9-35行,新元素将存储的p链表,且p链表不为空时的处理事件。该事件有三类情况,
第①类:待新增的元素,和哈希桶中链表的第一个元素比较,两者的key相等,则新值替换旧值,代码第10-12行,第29-34行。
第②类:待新增的元素,所在的哈希桶的数据结构如果是红黑树结构,即TreeNode,和之前TreeMap源码中元素新增是非类似,不作详细介绍。
第③类,待新增的元素,和哈希桶中的第一个值比较,两者key不同于是逐个比较,如果找到相同的key,则新值替换旧值,反之,新元素追加到链表尾部。
最后modCount自增,size自增。HashMap的put方法算是讲完辣。接下来我们再看看HashMap的无参构造函数,
1 /** 2 * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity 3 * (16) and the default load factor (0.75). 4 */ 5 public HashMap() { 6 this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted 7 }
第2-3行,注释翻译过来就是无参的构造函数,默认的容量capacity 16,和 默认的装载因子loadFactor 0.75d,
第6行,装载因子默认值为0.75d,
第6行,all other fileds defaulted? 既然叫[defaulted],您的意思是其他成员属性在此初始化了的?我表示看不见。
这是否说明一个问题?不恰当的注释容易给阅读者带来误导,楼主我在软件开发中,往往偏向于:做可读性更高的优雅代码,不太偏向于做复杂的注释。
好啦,回到问题本身,HashMap默认是容量初始化,在put方法的resize方法中,代码如下
1 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; 2 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
HashMap的容量初始为16,需要扩容的阈值: 容量 * 装载因子,即16*0.75,即当下一次新增元素超过了 原容量的0.75倍,进行一次扩容,每一次扩容,原容量的两倍增长。
HashMap的remove方法解读
1 public V remove(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? 4 null : e.value; 5 }
和put方法一致,同样调用hash()函数,根据key,三步计算得到哈希码。跟一下removeNode方法,
1 final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, 2 boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { 3 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; 4 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 5 (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 6 Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; 7 if (p.hash == hash && 8 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 9 node = p; 10 else if ((e = p.next) != null) { 11 if (p instanceof TreeNode) 12 node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); 13 else { 14 do { 15 if (e.hash == hash && 16 ((k = e.key) == key || 17 (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { 18 node = e; 19 break; 20 } 21 p = e; 22 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 23 } 24 } 25 if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || 26 (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { 27 if (node instanceof TreeNode) 28 ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); 29 else if (node == p) 30 tab[index] = node.next; 31 else 32 p.next = node.next; 33 ++modCount; 34 --size; 35 afterNodeRemoval(node); 36 return node; 37 } 38 } 39 return null; 40 }
第5行,index = (n - 1) & hash],哈希桶的寻址和put方法一致。
第4-24行,找出待删除的结点。
第27-32行,删除结点Node,并返回该结点。
这里没什么太多可以讲解的,也就不逐行分析了。


